PowerPoint
... the system initially consists of only CO and H2 in a 1:3 (CO:H2) ratio. Ideal gas behavior may be assumed. ...
... the system initially consists of only CO and H2 in a 1:3 (CO:H2) ratio. Ideal gas behavior may be assumed. ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
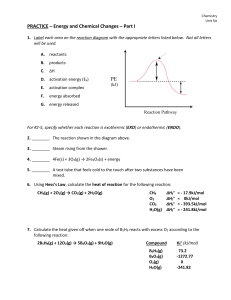
... lowers the energy barriers for a reaction to occur c. it has strong attraction for anions and cations d. it reacts independently of temperature and pressure 2CO + O2 = 2CO2 , which will cause a decrease in the rate of the reaction a. raise the temperature b. increase the volume inside the reaction c ...
... lowers the energy barriers for a reaction to occur c. it has strong attraction for anions and cations d. it reacts independently of temperature and pressure 2CO + O2 = 2CO2 , which will cause a decrease in the rate of the reaction a. raise the temperature b. increase the volume inside the reaction c ...
Matter
... permeability permittivity plasticity radiance resistivity reflectivity refractive index spin solubility specific heat strength temperature tension viscosity ...
... permeability permittivity plasticity radiance resistivity reflectivity refractive index spin solubility specific heat strength temperature tension viscosity ...
PY2104 - Introduction to thermodynamics and Statistical physics
... internal energy, V is the volume and σ is constant. Calculae the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume, cp and cv for this gas. 2) (i) Show that for a perfect gas undergoing adiabatic expansion, pV γ is constant, where γ = cp /cv . (ii) What is the physical reason for the differenc ...
... internal energy, V is the volume and σ is constant. Calculae the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume, cp and cv for this gas. 2) (i) Show that for a perfect gas undergoing adiabatic expansion, pV γ is constant, where γ = cp /cv . (ii) What is the physical reason for the differenc ...
After separation into groups students got working sheets and
... The second law of thermodynamics, in terms of probability, reduces to the statement that those processes occur which are most probable. That way students learned and understood concept of probability in interpretation of entropy. ...
... The second law of thermodynamics, in terms of probability, reduces to the statement that those processes occur which are most probable. That way students learned and understood concept of probability in interpretation of entropy. ...
August 30, 2016 Lecture 1: Thermodynamics vs. Statistical Mechanics
... 4. The degrees of freedom described in the Gibbs phase rule are the number of intensive variables to define a system. The extensive variables are r+2 where r is the number of species in the system. The extensive variable number is independent of the number of phases. For example, for a water in a bo ...
... 4. The degrees of freedom described in the Gibbs phase rule are the number of intensive variables to define a system. The extensive variables are r+2 where r is the number of species in the system. The extensive variable number is independent of the number of phases. For example, for a water in a bo ...
3_2: More Chemical Changes
... When I test this solution with litmus paper, it turns yellow. This shows me that the chemicals produced are ACIDS (pH 1-6) ...
... When I test this solution with litmus paper, it turns yellow. This shows me that the chemicals produced are ACIDS (pH 1-6) ...
Chemical Thermodynamics: Principles and Applications Brochure
... focuses on "real" systems in the discussion and figures, in contrast to the generic examples that are often used in other textbooks. The book provides a basic review of thermodynamic principles, equations, and applications of broad interest. It covers the development of thermodynamics as one of the ...
... focuses on "real" systems in the discussion and figures, in contrast to the generic examples that are often used in other textbooks. The book provides a basic review of thermodynamic principles, equations, and applications of broad interest. It covers the development of thermodynamics as one of the ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... Of what? – chemical formulas In what state? – physical state Letters in parentheses indicate the physical state of each substance involved in the reaction (g) gas ; (l) liquid ; (s) solid ; (aq) aqueous solution ...
... Of what? – chemical formulas In what state? – physical state Letters in parentheses indicate the physical state of each substance involved in the reaction (g) gas ; (l) liquid ; (s) solid ; (aq) aqueous solution ...
D - MrsMackScience
... pile of ashes. The mass of the ashes was less than the mass of the paper before it was burned. What can you conclude based on the law of conservation of mass? ...
... pile of ashes. The mass of the ashes was less than the mass of the paper before it was burned. What can you conclude based on the law of conservation of mass? ...
Chem 152 Chapter 4
... Melting, freezing, etc. Some Chemical Properties – Propane gas reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water (burns). – Iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide (rust). – Protein can be digested by enzymes in the stomach. – These processes are called chemical changes. Chemical Reactions – ...
... Melting, freezing, etc. Some Chemical Properties – Propane gas reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water (burns). – Iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide (rust). – Protein can be digested by enzymes in the stomach. – These processes are called chemical changes. Chemical Reactions – ...
Chemistry 434 - St. Francis Xavier University
... Gibbs Energy and Spontaneity sysG < 0 - spontaneous process sysG > 0 - non-spontaneous process (note that this process would be spontaneous in the reverse direction) sysG = 0 - system is in equilibrium ...
... Gibbs Energy and Spontaneity sysG < 0 - spontaneous process sysG > 0 - non-spontaneous process (note that this process would be spontaneous in the reverse direction) sysG = 0 - system is in equilibrium ...
CHEMICAL REACTION
... Characteristics of a Chemical Equation • Represents the known facts • Contains the correct formulas of reactants and products • The Law of Conservation of Mass is followed both in number of atoms and masses ...
... Characteristics of a Chemical Equation • Represents the known facts • Contains the correct formulas of reactants and products • The Law of Conservation of Mass is followed both in number of atoms and masses ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.