Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... Substances that release hydrogen ions ( H ) when dissolved in water are called __________. Substances that release hydroxide ions ( OH ) when dissolved in water are called __________. pH and Buffers: The measure of concentration of H in a solution is called __________. ...
... Substances that release hydrogen ions ( H ) when dissolved in water are called __________. Substances that release hydroxide ions ( OH ) when dissolved in water are called __________. pH and Buffers: The measure of concentration of H in a solution is called __________. ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... - It provides a framework for relating the microscopic properties of individual atoms and molecules to the macroscopic or bulk properties of materials that can be observed in everyday life, therefore explaining thermodynamics as a natural result of statistics and mechanics (classical and quantum) at ...
... - It provides a framework for relating the microscopic properties of individual atoms and molecules to the macroscopic or bulk properties of materials that can be observed in everyday life, therefore explaining thermodynamics as a natural result of statistics and mechanics (classical and quantum) at ...
Introductory Chemistry Test Review
... 28. Hydrogen peroxide can decompose to water and oxygen by the following reaction: 2 H2O2(l) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g) ΔH = –196 kJ/mol Calculate the value of q when 5.00 g of H2O2(l) decomposes at constant pressure. ...
... 28. Hydrogen peroxide can decompose to water and oxygen by the following reaction: 2 H2O2(l) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g) ΔH = –196 kJ/mol Calculate the value of q when 5.00 g of H2O2(l) decomposes at constant pressure. ...
Thermochemistry (Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... ways; two possible ways are shown above, that of melting and heating ice, or cooling boiling water. You can't drink either the frozen or boiling water, because they have energy content that is either too low or too high to be comfortable by virtue of their temperature. But the room temperature glass ...
... ways; two possible ways are shown above, that of melting and heating ice, or cooling boiling water. You can't drink either the frozen or boiling water, because they have energy content that is either too low or too high to be comfortable by virtue of their temperature. But the room temperature glass ...
Burning Pupil Task File
... Levels 3 and 4 Draw a candle like the one above. Label where there is a change of state happening and where there is a chemical reaction happening. Write down the differences between a physical and chemical change. Draw particle diagrams to show the changes of state. Levels 5-7 Divide your candle in ...
... Levels 3 and 4 Draw a candle like the one above. Label where there is a change of state happening and where there is a chemical reaction happening. Write down the differences between a physical and chemical change. Draw particle diagrams to show the changes of state. Levels 5-7 Divide your candle in ...
durfee high school science department
... 0002 Hand lab on physical and chemical properties and changes discuss pre-lab questions ticket to entry. Introduce Atomic Structure, teaching students about atomic number and atomic mass ...
... 0002 Hand lab on physical and chemical properties and changes discuss pre-lab questions ticket to entry. Introduce Atomic Structure, teaching students about atomic number and atomic mass ...
Chemistry Entropy Notes 1. What is entropy? How many ways can
... Yes. Your table of thermodynamic values also contains ∆G° values. ∆G° is named the Gibbs Free Energy of a system. It incorporates the system’s entropy change and the system’s heat change (heat from the system increases the entropy of the surroundings). So, ∆G° is a useful predictor of whether or not ...
... Yes. Your table of thermodynamic values also contains ∆G° values. ∆G° is named the Gibbs Free Energy of a system. It incorporates the system’s entropy change and the system’s heat change (heat from the system increases the entropy of the surroundings). So, ∆G° is a useful predictor of whether or not ...
Section 15
... product(s). Molecular formulas are usually used to represent the reactants and products and the phase of each substance is sometimes represented by an s, g, or l for solid, gas or liquid; materials that are dissolved in water are designated as aq for aqueous. Coefficients are also placed in front of ...
... product(s). Molecular formulas are usually used to represent the reactants and products and the phase of each substance is sometimes represented by an s, g, or l for solid, gas or liquid; materials that are dissolved in water are designated as aq for aqueous. Coefficients are also placed in front of ...
Slide 1
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... The standard Gibbs energy of formation of NH3(g) is –16.5 kJ mol–1 at 298 K. What is the reaction Gibbs energy when the partial pressure of the N2, H2, and NH3 (treated as perfect gases) are 3.0 bar, 1.0 bar, and 4.0 bar, respectively? What is the spontaneous direction of the reaction in this case? ...
... The standard Gibbs energy of formation of NH3(g) is –16.5 kJ mol–1 at 298 K. What is the reaction Gibbs energy when the partial pressure of the N2, H2, and NH3 (treated as perfect gases) are 3.0 bar, 1.0 bar, and 4.0 bar, respectively? What is the spontaneous direction of the reaction in this case? ...
MECH TECH MEET S08
... INITIATING THE CARTwo minutes would be provided for setup of your model. Once the car crosses the starting line, team members cannot touch their bot i.e. no chemicals can be added. Any type of contact with the car thereafter will lead to disqualification. Pushing the vehicle or a mechanical starti ...
... INITIATING THE CARTwo minutes would be provided for setup of your model. Once the car crosses the starting line, team members cannot touch their bot i.e. no chemicals can be added. Any type of contact with the car thereafter will lead to disqualification. Pushing the vehicle or a mechanical starti ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... State in which the forward & reverse paths of a change take place at the same rate Physical equilibrium – when physical change does not go to completion, a physical equilibrium is established Ex. Water evaporating in a sealed bottle H2O(l) ↔ H2O(g) ...
... State in which the forward & reverse paths of a change take place at the same rate Physical equilibrium – when physical change does not go to completion, a physical equilibrium is established Ex. Water evaporating in a sealed bottle H2O(l) ↔ H2O(g) ...
Lecture 5 - Thermodynamics II
... • The entropy (order) of a system can decrease, but in order for this to happen, the entropy (disorder) of the surroundings must increase to a greater extent, so that the total entropy of the universe always increases. ...
... • The entropy (order) of a system can decrease, but in order for this to happen, the entropy (disorder) of the surroundings must increase to a greater extent, so that the total entropy of the universe always increases. ...
Tutorial 1 / SS 2013
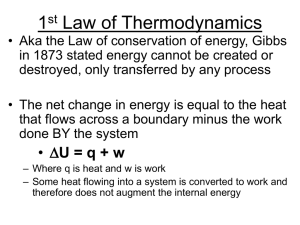
... The energy of the universe is constant. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy is conserved. The internal energy U denotes the total energy of a system (kinetic/thermal energy, potential energy, electric energy…); dU is the infinitesimal change of the internal energy. By doing work on/by ...
... The energy of the universe is constant. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy is conserved. The internal energy U denotes the total energy of a system (kinetic/thermal energy, potential energy, electric energy…); dU is the infinitesimal change of the internal energy. By doing work on/by ...
Document
... • Temperature tells us whether or not two systems will change when brought into thermal contact with one another. • A thermometer is just a very small system with only one state variable. ...
... • Temperature tells us whether or not two systems will change when brought into thermal contact with one another. • A thermometer is just a very small system with only one state variable. ...
Chapter-2-Human-Chemistry
... and negative ions • Drinks such as Gatorade replenish body with ions to balance body’s homeostasis and diminish anaerobic respiration and ...
... and negative ions • Drinks such as Gatorade replenish body with ions to balance body’s homeostasis and diminish anaerobic respiration and ...
Energy and Matter
... Energy Measurements – Calories (cal)= 4.184 J – BTU – Joules (J)- the work done when one kg is accelerated 1 m per second (1J= 1kg X m / s. – KWh ...
... Energy Measurements – Calories (cal)= 4.184 J – BTU – Joules (J)- the work done when one kg is accelerated 1 m per second (1J= 1kg X m / s. – KWh ...
03. The Theoretic bases of bioenergetics
... The large the surface area of the reactants, the faster is rate of reaction. It has been observed that if one the reactants is a solid, then the rate of the reaction depends upon the state of sub-division of the solid. 6. Exposure to radiation. In some cases, the rate is considerably increased by th ...
... The large the surface area of the reactants, the faster is rate of reaction. It has been observed that if one the reactants is a solid, then the rate of the reaction depends upon the state of sub-division of the solid. 6. Exposure to radiation. In some cases, the rate is considerably increased by th ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.