Why Study Chemistry
... o Great freedom to move (high energy) o Variable volume and shape (expands to fill any container) ...
... o Great freedom to move (high energy) o Variable volume and shape (expands to fill any container) ...
CHM 101
... You know that a particular reaction is exothermic. On the axes below, sketch a graph of the energy versus the reaction progress for this exothermic reaction. Indicate how you would calculate the activation energy and ∆H for the reaction. ...
... You know that a particular reaction is exothermic. On the axes below, sketch a graph of the energy versus the reaction progress for this exothermic reaction. Indicate how you would calculate the activation energy and ∆H for the reaction. ...
Chemical Equations
... Chemical formula A representation of a substance in which the elements are represented by their symbols and subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element ...
... Chemical formula A representation of a substance in which the elements are represented by their symbols and subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element ...
Lecture 8
... the initial and final states and not on the reaction pathway) or kinetic ones (very dependent on the reaction pathway). Both factors depend on the conditions, and on the possibility of different routes to decomposition or reaction. ...
... the initial and final states and not on the reaction pathway) or kinetic ones (very dependent on the reaction pathway). Both factors depend on the conditions, and on the possibility of different routes to decomposition or reaction. ...
Science 9 Unit 2
... Substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants and the products During a chemical reaction the reactants are used up During a chemical reaction the products are created or produced Law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical change the total mass of the new substance is the ...
... Substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants and the products During a chemical reaction the reactants are used up During a chemical reaction the products are created or produced Law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical change the total mass of the new substance is the ...
Presentation - Chem Rxns - stpats-sch3u-sem1-2013
... Chemical Equation = a representation of a chemical reaction that indicates the: Chemical formulas Relative number of entities States of matter of the reactants and products ...
... Chemical Equation = a representation of a chemical reaction that indicates the: Chemical formulas Relative number of entities States of matter of the reactants and products ...
Notes
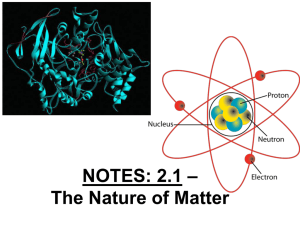
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
Themodynamic notes section 6.1
... thermodynamic system is equal to the amount of heat energy (q) added to or lost by the system plus work done (w) on or by the system. DE = q + w • For work that only involves gas expansion or compression, w = -pDV; ...
... thermodynamic system is equal to the amount of heat energy (q) added to or lost by the system plus work done (w) on or by the system. DE = q + w • For work that only involves gas expansion or compression, w = -pDV; ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Thermodynamics
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
Matter and Its Changes
... Two liquids that don’t mix and stay mixed. They may make a suspension, but they don’t make a solution ...
... Two liquids that don’t mix and stay mixed. They may make a suspension, but they don’t make a solution ...
Document
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
Free energy and Equilibrium
... the energy of the system plus surrounding remains constant(principle of energy conservation). Second law of thermodynamics; In all processes the entropy(disorder or randomness) of the system plus the surroundings always increases. The 2nd Law explains why chemical reactions tend to favor a particu ...
... the energy of the system plus surrounding remains constant(principle of energy conservation). Second law of thermodynamics; In all processes the entropy(disorder or randomness) of the system plus the surroundings always increases. The 2nd Law explains why chemical reactions tend to favor a particu ...
V α - Springer
... the extensive parameters of any composite system, defined for all equilibrium states and having the following property: The values assumed by the extensive parameters in the absence of an internal constraint are those that maximize the entropy over the manifold of constrained equilibrium states. 3. ...
... the extensive parameters of any composite system, defined for all equilibrium states and having the following property: The values assumed by the extensive parameters in the absence of an internal constraint are those that maximize the entropy over the manifold of constrained equilibrium states. 3. ...
Thermochemistry
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
Chapter One Outline
... Identifying Matter: Physical Properties Physical properties can be observed and measured without changing the composition of a substance. Examples include temperature, mass, density, etc. Density is the ratio of an objects mass to its volume; D = m/v Chemical Properties A substances chemical propert ...
... Identifying Matter: Physical Properties Physical properties can be observed and measured without changing the composition of a substance. Examples include temperature, mass, density, etc. Density is the ratio of an objects mass to its volume; D = m/v Chemical Properties A substances chemical propert ...
Elements, Compounds and Chemical Reactions
... name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes from the Latin ...
... name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes from the Latin ...
Chapter 1
... *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound you should __add____ the subscripts. *Notes-If there is no subscript, only __1_____ atom of that element is prese ...
... *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound you should __add____ the subscripts. *Notes-If there is no subscript, only __1_____ atom of that element is prese ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atoms of one element replace atoms of another in a compound: A + BC AC + B Most often, AC and BC are ionic compounds, which means A and B are metals, and C is a nonmetal or negative polyatomic ion. As an analogy, imagine that BC are ...
... AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atoms of one element replace atoms of another in a compound: A + BC AC + B Most often, AC and BC are ionic compounds, which means A and B are metals, and C is a nonmetal or negative polyatomic ion. As an analogy, imagine that BC are ...
thermodynamics - CHM152-SP10
... In thermodynamics, entropy is a measure of the degree of disorder. Entropy tends to increase. ...
... In thermodynamics, entropy is a measure of the degree of disorder. Entropy tends to increase. ...
Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.