Unit 2: Chemical Reactions
... • A chemical formula is an abbreviation for a chemical compound using chemical symbols and numbers. • The subscript number tells how many atoms of the element are present in the compound • Example: CO2 = Carbon Dioxide – Di = 2 – 1 Carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms ...
... • A chemical formula is an abbreviation for a chemical compound using chemical symbols and numbers. • The subscript number tells how many atoms of the element are present in the compound • Example: CO2 = Carbon Dioxide – Di = 2 – 1 Carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Chemical Reactions Mr. Campbell
... ► Temperature, Color, Texture, Flexibility ► Physical Change- any change that alters the form or appearance of a substance but doesn’t change it into another substance. ...
... ► Temperature, Color, Texture, Flexibility ► Physical Change- any change that alters the form or appearance of a substance but doesn’t change it into another substance. ...
Thermodynamics: Spontaneity, Entropy and Free energy
... • 3rd Law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (S =0) ...
... • 3rd Law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (S =0) ...
Headline Text 28 Point Color Text 2
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
... for this reaction is: Reactants Products propane + oxygen => carbon dioxide + water are consumed are produced The chemical equation is: C3H8 + 5 O2 -----> 3 CO2 + 4 H2O The balanced equation is: ...
... for this reaction is: Reactants Products propane + oxygen => carbon dioxide + water are consumed are produced The chemical equation is: C3H8 + 5 O2 -----> 3 CO2 + 4 H2O The balanced equation is: ...
Lecture I
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
Notes on Chapter 12 Chemical Equilibrium
... 1. For a reaction to occur 3 conditions must be met: a. collision-reactants must collide so the molecules can make contact to react together. b. orientation-reactants must align properly in order to existing break and form new bonds. c. energy-the collision must provide sufficient energy to supply t ...
... 1. For a reaction to occur 3 conditions must be met: a. collision-reactants must collide so the molecules can make contact to react together. b. orientation-reactants must align properly in order to existing break and form new bonds. c. energy-the collision must provide sufficient energy to supply t ...
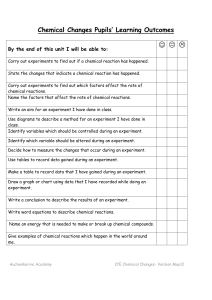
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... By the end of this unit I will be able to: Carry out experiments to find out if a chemical reaction has happened. State the changes that indicate a chemical reaction has happened. Carry out experiments to find out which factors effect the rate of chemical reactions. Name the factors that affect the ...
... By the end of this unit I will be able to: Carry out experiments to find out if a chemical reaction has happened. State the changes that indicate a chemical reaction has happened. Carry out experiments to find out which factors effect the rate of chemical reactions. Name the factors that affect the ...
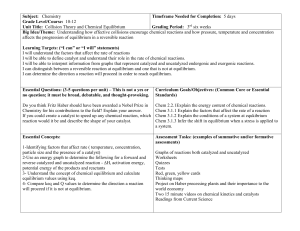
Subject:
... I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach equilibrium. Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and t ...
... I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach equilibrium. Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and t ...
EXAM REVIEW !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! The examination is scheduled
... Calculations: (you should be familiar with the following in terms of calculations) Use of Expressions for Work, Heat, Enthalpy etc of adiabatic, reversible, isothermal etc. process Use of Heat Capacity to Determine the Enthalpy Change Expression for dH and dE for ideal gas Expressing E in Terms of H ...
... Calculations: (you should be familiar with the following in terms of calculations) Use of Expressions for Work, Heat, Enthalpy etc of adiabatic, reversible, isothermal etc. process Use of Heat Capacity to Determine the Enthalpy Change Expression for dH and dE for ideal gas Expressing E in Terms of H ...
Chemical Reactions
... Father of Modern Chemistry • Lavoisier is known as the Father of Modern Chemistry for this work along with the work he did on types of reactions • Wrote a book called “Elements of Chemistry” in 1790 • He developed the nomenclature we use today to describe chemical compounds and reactions. ...
... Father of Modern Chemistry • Lavoisier is known as the Father of Modern Chemistry for this work along with the work he did on types of reactions • Wrote a book called “Elements of Chemistry” in 1790 • He developed the nomenclature we use today to describe chemical compounds and reactions. ...
TERM 2 Unit 3 YR 9 SCI It is elementary
... 9 SCIENCE – Term 2 Unit 3: IT’S ELEMENTARY (5 WEEKS) ...
... 9 SCIENCE – Term 2 Unit 3: IT’S ELEMENTARY (5 WEEKS) ...
Chemical Potential.
... We give a brief introduction to this concept as we will need to refer to it later in the course. As the name suggests, it is very important for studying chemical reactions and your will encounter this concept in a first course in physical chemistry. Just as the temperature governs the flow of energy ...
... We give a brief introduction to this concept as we will need to refer to it later in the course. As the name suggests, it is very important for studying chemical reactions and your will encounter this concept in a first course in physical chemistry. Just as the temperature governs the flow of energy ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Effervescence (bubbles and/or gives off gas) Precipitate (solid crystals form) Odor (change of smell is detected) Color change Heat (reaction either heats up or cools down) Does sighting evidence of a chemical reaction mean that a chemical reaction has undoubtedly taken place? ...
... Effervescence (bubbles and/or gives off gas) Precipitate (solid crystals form) Odor (change of smell is detected) Color change Heat (reaction either heats up or cools down) Does sighting evidence of a chemical reaction mean that a chemical reaction has undoubtedly taken place? ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.