* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
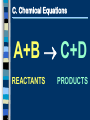
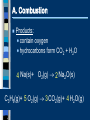
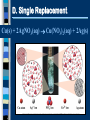
Unit 7 – Chemical Reactions I. Intro to Reactions I II III IV V A.Signs of a Chemical Reaction Evolution of heat and light Formation of a gas Formation of a precipitate Color change B.Law of Conservation of Mass mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction total mass stays the same atoms can only rearrange 4H 36 g 2O 4H 2O 4g 32 g C. Chemical Equations A+B C+D REACTANTS PRODUCTS C. Chemical Equations p. 246 D. Writing Equations 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) Identify the substances involved. Use symbols to show: How many? - coefficient Of what? - chemical formula In what state? - physical state Remember the diatomic elements. D. Writing Equations Two atoms of aluminum react with three units of aqueous copper(II) chloride to produce three atoms of copper and two units of aqueous aluminum chloride. • How many? • Of what? • In what state? 2Al(s) + 3CuCl2(aq) 3Cu(s) + 2AlCl3(aq) E. Describing Equations Describing Coefficients: individual atom = “atom” covalent substance = “molecule” ionic substance = “unit” 3CO2 3 molecules of carbon dioxide 2Mg 2 atoms of magnesium 4MgO 4 units of magnesium oxide E. Describing Equations Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? One atom of solid zinc reacts with two molecules of aqueous hydrochloric acid to produce one unit of aqueous zinc chloride and one molecule of hydrogen gas. Unit 7 – Chemical Reactions II. Types of Chemical Reactions I II III IV V A. Combustion the burning of any substance in O2 to produce heat A + O2 B CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) A. Combustion Products: contain oxygen hydrocarbons form CO2 + H2O 4 Na(s)+ O2(g) 2 Na2O(s) C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g) B. Synthesis the combination of 2 or more substances to form a compound only one product A + B AB B. Synthesis H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) B. Synthesis Products: ionic - cancel charges covalent - hard to tell 2 Al(s)+ 3 Cl2(g) 2 AlCl3(s) C. Decomposition a compound breaks down into 2 or more simpler substances only one reactant AB A + B C. Decomposition 2 H2O(l) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) C. Decomposition Products: binary - break into elements others - hard to tell 2 KBr(l) 2 K(s) + Br2(l) D. Single Replacement one element replaces another in a compound metal replaces metal (+) nonmetal replaces nonmetal (-) A + BC B + AC D. Single Replacement Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s) D. Single Replacement Products: metal metal (+) nonmetal nonmetal (-) free element must be more active (check activity series) Fe(s)+ CuSO4(aq) Cu(s)+ FeSO4(aq) Br2(l)+ NaCl(aq) N.R. E. Double Replacement ions in two compounds “change partners” cation of one compound combines with anion of the other AB + CD AD + CB E. Double Replacement Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) PbCrO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq) E. Double Replacement Products: switch negative ions one product must be insoluble (check solubility table) Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ 2KI(aq) PbI2(s)+2KNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq)+ KI(aq) N.R. Unit 7 – Chemical Reactions III. Balancing Equations I II III IV V A. Balancing Steps 1. Write the unbalanced equation. 2. Count atoms on each side. 3. Add coefficients to make #s equal. Coefficient subscript = # of atoms 4. Reduce coefficients to lowest possible ratio, if necessary. 5. Double check atom balance!!! B. Helpful Tips Balance one element at a time. Update ALL atom counts after adding a coefficient. If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last. Balance polyatomic ions as single units. “1 SO4” instead of “1 S” and “4 O” C. Balancing Example Aluminum and copper(II) chloride react to form copper and aluminum chloride. 2 Al + 3 CuCl2 3 Cu + 2 AlCl3 2 1 Al 1 2 3 1 Cu 1 3 6 2 Cl 3 6