Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
... ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for ______________ of the __________________ lost during _________________________ decays. Since g ...
... ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for ______________ of the __________________ lost during _________________________ decays. Since g ...
File
... All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass, properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine to form chemical compounds ...
... All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass, properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine to form chemical compounds ...
Chapter 9 Natural Radioactivity
... • This defines an isotope of boron • In nuclear chemistry often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
... • This defines an isotope of boron • In nuclear chemistry often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
CHAPTER 6sThe Chemistry of Life2015
... a. most atoms have outer orbitals/shells that are not completely full b. 6. atoms contain the same number of electrons & protons no net chargeneutral 7. atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter B. How are elements identified? 1. By letter symbols on the periodic table Na=sodium, H=hydrog ...
... a. most atoms have outer orbitals/shells that are not completely full b. 6. atoms contain the same number of electrons & protons no net chargeneutral 7. atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter B. How are elements identified? 1. By letter symbols on the periodic table Na=sodium, H=hydrog ...
Chapter 21 Powerpoint: Nuclear Chemistry
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
Terms to Know
... Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather than negative. Radioactivity : Radioactivity is the emission of radiation by unstable nuclei. That radiation ma ...
... Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather than negative. Radioactivity : Radioactivity is the emission of radiation by unstable nuclei. That radiation ma ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... Elements ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Periodic Table of Elements Over 100 elements known, but only about 2 dozen commonly found in living systems ...
... Elements ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Periodic Table of Elements Over 100 elements known, but only about 2 dozen commonly found in living systems ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... Demonstrate how carbon atoms form four covalent bonds to make large molecules. Identify the functions of these molecules (e.g., plant and animal tissue, polymers, sources of food and nutrition, fossil fuels). Describe at least three chemical reactions of particular importance to humans (e.g., bu ...
... Demonstrate how carbon atoms form four covalent bonds to make large molecules. Identify the functions of these molecules (e.g., plant and animal tissue, polymers, sources of food and nutrition, fossil fuels). Describe at least three chemical reactions of particular importance to humans (e.g., bu ...
Chapter 2 Notes: The Chemistry of Life
... B. 7 is neutral; between 0-7 is acidic; between 7-14 is basic C. acid – a compound that forms H+ in solution D. base – a compound that forms OH- in water E. buffer – weak acids or bases that help keep the pH in living things near the neutral range ...
... B. 7 is neutral; between 0-7 is acidic; between 7-14 is basic C. acid – a compound that forms H+ in solution D. base – a compound that forms OH- in water E. buffer – weak acids or bases that help keep the pH in living things near the neutral range ...
04 Atoms_ molecules _ ions
... • Review PPs 1 – 4 • Work the attached assignment & turn it in tomorrow. ...
... • Review PPs 1 – 4 • Work the attached assignment & turn it in tomorrow. ...
Atomic Numbers Practice Problems
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
Ch. 3.1 ppt. Democritus to Dalton
... size of the sample or source of the compound. – Example: water – hydrogen to oxygen ratio is always 2 to 1. ...
... size of the sample or source of the compound. – Example: water – hydrogen to oxygen ratio is always 2 to 1. ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
Atomic Structure
... 4 parts of Dalton’s theory: 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically c ...
... 4 parts of Dalton’s theory: 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically c ...
Topic Review: Nuclear Chemistry 1. The stability of an isotope
... 1. The stability of an isotope depends on the ratio of protons to neutrons in the nucleus. Most nuclei are stable, but some are unstable. These nuclei will spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. Stable isotopes of small atoms have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes ...
... 1. The stability of an isotope depends on the ratio of protons to neutrons in the nucleus. Most nuclei are stable, but some are unstable. These nuclei will spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. Stable isotopes of small atoms have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes ...
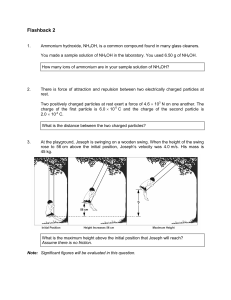
Flashback 2
... rose to 56 cm above the initial position, Joseph’s velocity was 4.0 m/s. His mass is 45 kg. ...
... rose to 56 cm above the initial position, Joseph’s velocity was 4.0 m/s. His mass is 45 kg. ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... All atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determi ...
... All atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determi ...
Unit 2 Chemistry Review
... c) Putting the beaker on a hot plate _______________ 12. Isotopes are atoms with different number of neutrons and thus different atomic masses. Some isotopes undergo radioactive decay. (Alpha, Beta, and gamma) (pg.294- 298) LABEL: ...
... c) Putting the beaker on a hot plate _______________ 12. Isotopes are atoms with different number of neutrons and thus different atomic masses. Some isotopes undergo radioactive decay. (Alpha, Beta, and gamma) (pg.294- 298) LABEL: ...
Exam 1 Review Questions
... Covalent compounds contain both metal and nonmetal atoms. Ionic compounds are made of molecules. Dmitri Mendeleev published the first modern atomic theory in 1805. Fluorine is found as a metal in its pure form. Francium chloride FrCl is a covalent compound. Graphite is a compound containing carbon a ...
... Covalent compounds contain both metal and nonmetal atoms. Ionic compounds are made of molecules. Dmitri Mendeleev published the first modern atomic theory in 1805. Fluorine is found as a metal in its pure form. Francium chloride FrCl is a covalent compound. Graphite is a compound containing carbon a ...
“HOTMOTA”
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chem ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chem ...
File - Norris Science
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... How are all of the isotopes of an element similar? What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happ ...
... How are all of the isotopes of an element similar? What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happ ...
SCH3U Unit 1 review
... Physical and chemical change Classifying matter Atoms Modern atomic theory Structure of an atom Determining protons, neutrons, electrons Isotopes How to calculate average atomic mass and isotopic abundance Periodic table Categorizing groups, periodic/group patterns Lewis Dot structures Atomic size ...
... Physical and chemical change Classifying matter Atoms Modern atomic theory Structure of an atom Determining protons, neutrons, electrons Isotopes How to calculate average atomic mass and isotopic abundance Periodic table Categorizing groups, periodic/group patterns Lewis Dot structures Atomic size ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.