• Bond: come together • Charge: there is either a positive or negative
... Electron level: A quantum-mechanical concept for energy levels of electrons about the nucleus; electron energies are functions of each particular atomic species. ...
... Electron level: A quantum-mechanical concept for energy levels of electrons about the nucleus; electron energies are functions of each particular atomic species. ...
1H Atomic Theory Quiz Review
... What is the atomic mass of Copper with isotopes Cu-63 (mass of 63.0 amu and 69.2% abundance) and Cu-65 (mass 65.0 amu and 30.8% abundance)? Do the equation including units with sig figs. ...
... What is the atomic mass of Copper with isotopes Cu-63 (mass of 63.0 amu and 69.2% abundance) and Cu-65 (mass 65.0 amu and 30.8% abundance)? Do the equation including units with sig figs. ...
Chemistry 1 CP Concept 4 Nuclear Chemistry Study Guide
... 9. Which waves of energy travel fastest? ______________________________________ 10. All radioactive nuclides undergo _________________________ 11. What device uses controlled nuclear fission to produce new radioactive substances and energy? _______________________________________ 12. Among atoms wit ...
... 9. Which waves of energy travel fastest? ______________________________________ 10. All radioactive nuclides undergo _________________________ 11. What device uses controlled nuclear fission to produce new radioactive substances and energy? _______________________________________ 12. Among atoms wit ...
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Science
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relati ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relati ...
“earth, air, fire and water" matter was composed of small particles
... rearranged, but matter cannot be created or destroyed. This is the Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter). 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in whole number ratios to form compounds a. Law of Definite Proportion-use water to identify the ratios: i. Ratio of atoms ii. Ratio of moles iii. Ratio ...
... rearranged, but matter cannot be created or destroyed. This is the Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter). 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in whole number ratios to form compounds a. Law of Definite Proportion-use water to identify the ratios: i. Ratio of atoms ii. Ratio of moles iii. Ratio ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
TERM 2 Unit 3 YR 9 SCI It is elementary
... reaction, and are able to list and describe the possible changes that can be observed during a chemical reaction. Students will be able to use the particle theory of matter to explain what is happening during a chemical reaction, and relate this to the Law of conservation of matter. They identify th ...
... reaction, and are able to list and describe the possible changes that can be observed during a chemical reaction. Students will be able to use the particle theory of matter to explain what is happening during a chemical reaction, and relate this to the Law of conservation of matter. They identify th ...
Lecture4
... All elements have isotope(s). Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable. An unstable atom has too many neutrons in its nucleus. To get rid of the excess, the nucleus decays into different nucleus by throwing out (emitting) particles and energy. Whenever there is a disintegration of atomic nucle ...
... All elements have isotope(s). Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable. An unstable atom has too many neutrons in its nucleus. To get rid of the excess, the nucleus decays into different nucleus by throwing out (emitting) particles and energy. Whenever there is a disintegration of atomic nucle ...
isotopes
... be destroyed by exposing them to the same radiation. In fact, cancerous cells are more susceptible to destruction by radiation than are healthy ones, allowing radiation to be used effectively in the treatment of cancer. As early as 1904, physicians attempted to use the radiation emitted by radioacti ...
... be destroyed by exposing them to the same radiation. In fact, cancerous cells are more susceptible to destruction by radiation than are healthy ones, allowing radiation to be used effectively in the treatment of cancer. As early as 1904, physicians attempted to use the radiation emitted by radioacti ...
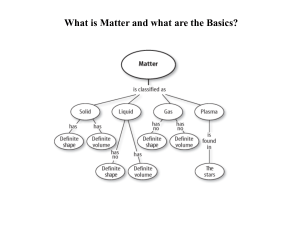
Matter Study Guide
... metals/nonmetals, solids, gasses, liquids, man-made, symbols, atomic number, atomic mass -Know what chemical symbols and formulas are and how to read the formulas -Recognize symbols for basic elements and compounds including Ca (calcium), C (carbon), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), CO (carbon monoxide), C ...
... metals/nonmetals, solids, gasses, liquids, man-made, symbols, atomic number, atomic mass -Know what chemical symbols and formulas are and how to read the formulas -Recognize symbols for basic elements and compounds including Ca (calcium), C (carbon), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), CO (carbon monoxide), C ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... 13. What does each number on the shorthand notation indicate? 24 E ...
... 13. What does each number on the shorthand notation indicate? 24 E ...
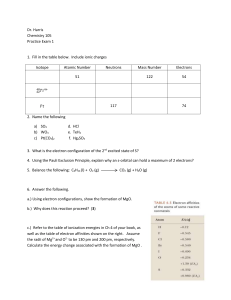
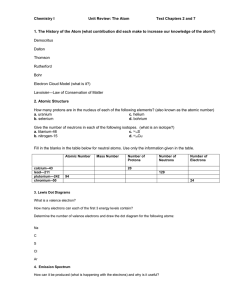
Chemistry I Unit Review: The Atom Text Chapters 2 and 7 1. The
... How many protons are in the nucleus of each of the following elements? (also known as the atomic number) a. uranium c. helium b. selenium d. bohrium Give the number of neutrons in each of the following isotopes. (what is an isotope?) a. titanium-46 c. 3416S b. nitrogen-15 d. 6529Cu Fill in the blank ...
... How many protons are in the nucleus of each of the following elements? (also known as the atomic number) a. uranium c. helium b. selenium d. bohrium Give the number of neutrons in each of the following isotopes. (what is an isotope?) a. titanium-46 c. 3416S b. nitrogen-15 d. 6529Cu Fill in the blank ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom 4.1 The
... •Democritus (460-370 B.C.) was the first to use the term atom. He, and the atomists, described atoms as the indivisible particle. •Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) critisized Democritus by asking what held atoms together, developed the idea of earth, fire, water and wind as the 4 elements of all natural sub ...
... •Democritus (460-370 B.C.) was the first to use the term atom. He, and the atomists, described atoms as the indivisible particle. •Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) critisized Democritus by asking what held atoms together, developed the idea of earth, fire, water and wind as the 4 elements of all natural sub ...
CHM 50 Exam 1 Review Name Due Tuesday 9/29/09 Exam 1 will
... b. Potassium chlorate when heated yields potassium chlorate plus oxygen gas. c. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide solution yields water and solid calcium phosphate. 5. A cartain alloy of copper has a density of 3.75g/ml and is 65.0% by mass copper. How many atoms ...
... b. Potassium chlorate when heated yields potassium chlorate plus oxygen gas. c. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide solution yields water and solid calcium phosphate. 5. A cartain alloy of copper has a density of 3.75g/ml and is 65.0% by mass copper. How many atoms ...
SS18A - Atoms, Isotopes and Ions
... In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers ...
... In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers ...
Expected paths Observed paths Nuclear atom • Rutherford
... o Different compounds with the same molecular formula may be distinguished by their names. o We avoid having to learn millions of trivial (non-systematic) names such as water and ammonia. Names and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds • Binary compounds of metals and nonmetals: o Usually are ionic. o Rul ...
... o Different compounds with the same molecular formula may be distinguished by their names. o We avoid having to learn millions of trivial (non-systematic) names such as water and ammonia. Names and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds • Binary compounds of metals and nonmetals: o Usually are ionic. o Rul ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
3-2 Radioactivity and the nucleus
... He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
... He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
10.2
... • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
... • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
22-Introduction to Radioactivity
... In this activity, you will first review some of the important ideas about atoms. Then you will begin to learn about two important ways in which radioactivity can occur. This prepares you for conducting an experiment that models what happens during radioactive decay. Reviewing Some Ideas about Atoms ...
... In this activity, you will first review some of the important ideas about atoms. Then you will begin to learn about two important ways in which radioactivity can occur. This prepares you for conducting an experiment that models what happens during radioactive decay. Reviewing Some Ideas about Atoms ...
periodic table elements
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
- Elliott Hudson College
... Atoms consist of a central ____________ containing protons and ___________. The nucleus is _______ compared to the size of the whole atom. The nucleus is surrounded by ___________ in energy levels (also called _________). Atoms have no electric charge because they contain the same number of protons ...
... Atoms consist of a central ____________ containing protons and ___________. The nucleus is _______ compared to the size of the whole atom. The nucleus is surrounded by ___________ in energy levels (also called _________). Atoms have no electric charge because they contain the same number of protons ...
Slide 1
... P. 124 – Q – 76 Rutherford’s atomic theory proposed a dense nucleus surrounded by very small electrons. This implies that atoms are composed mainly of empty space. If all matter is mainly empty space, why is it impossible to walk through walls or pass your hand through your desk? P. 122 – Q – 46 Wh ...
... P. 124 – Q – 76 Rutherford’s atomic theory proposed a dense nucleus surrounded by very small electrons. This implies that atoms are composed mainly of empty space. If all matter is mainly empty space, why is it impossible to walk through walls or pass your hand through your desk? P. 122 – Q – 46 Wh ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.