Atomic Theory Worksheet
... a. number of protons = b. number of electrons = c. number of neutrons = d. mass number = e. the charge on an ion = 9. What does it mean for an atom to be a. neutral – b. an ion – c. an isotope 10. How do you represent an isotope (how is it to be written)? 11. What does amu stand for? 12. What is a n ...
... a. number of protons = b. number of electrons = c. number of neutrons = d. mass number = e. the charge on an ion = 9. What does it mean for an atom to be a. neutral – b. an ion – c. an isotope 10. How do you represent an isotope (how is it to be written)? 11. What does amu stand for? 12. What is a n ...
Vocabulary and Section Summary
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is that atom’s atomic number. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. Different isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. Isotopes of an element share most chemical and physical properties. The mass number ...
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is that atom’s atomic number. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. Different isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. Isotopes of an element share most chemical and physical properties. The mass number ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... Cr anomalies observed in primitive meteorites and planetary bodies [9,10] are now accepted as widespread nebula wide phenomena. There are some unresolved issues in Cr isotope cosmochemistry, however. For example 54Cr anomalies were observed by one laboratory [9] but not by the other [7] in the same ...
... Cr anomalies observed in primitive meteorites and planetary bodies [9,10] are now accepted as widespread nebula wide phenomena. There are some unresolved issues in Cr isotope cosmochemistry, however. For example 54Cr anomalies were observed by one laboratory [9] but not by the other [7] in the same ...
1412-PracticeExam4
... Which of these species are structural isomers of C6H14? A. I and II B. I and III C. II and III D. II and IV E. III and IV Which of these species is an aromatic compound? A. C2H2 B. C6H12 C. C6H4Br2 D. C5H10 E. C2H4Br2 The name for the compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2OH is A. ...
... Which of these species are structural isomers of C6H14? A. I and II B. I and III C. II and III D. II and IV E. III and IV Which of these species is an aromatic compound? A. C2H2 B. C6H12 C. C6H4Br2 D. C5H10 E. C2H4Br2 The name for the compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2OH is A. ...
Problem set 1
... 3. Iron (Fe) can be produced from iron oxide (Fe2 O3 ) by reaction with carbon-monoxide gas (CO) according to: Fe2 O3 (s) + 3CO(g) −→ 2Fe(s) + 3CO2 (g) When 7.56 kg of CO gas are combined with 15.02 kg iron oxide in a furnace, it is observed that 9.54 kg of iron are produced. What is the percentage ...
... 3. Iron (Fe) can be produced from iron oxide (Fe2 O3 ) by reaction with carbon-monoxide gas (CO) according to: Fe2 O3 (s) + 3CO(g) −→ 2Fe(s) + 3CO2 (g) When 7.56 kg of CO gas are combined with 15.02 kg iron oxide in a furnace, it is observed that 9.54 kg of iron are produced. What is the percentage ...
Isotopes
... All elements beyond polononium (Po) with zPo = 84 are radioactive and eventually decay into some lighter atoms. This radioactive decay might be very fast or very slow. It is always characterized by the half-life, the time during which 50 % of some bunch of radioactive atoms has split asunder. The at ...
... All elements beyond polononium (Po) with zPo = 84 are radioactive and eventually decay into some lighter atoms. This radioactive decay might be very fast or very slow. It is always characterized by the half-life, the time during which 50 % of some bunch of radioactive atoms has split asunder. The at ...
The Band of Stability
... tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear forces require ideal distances between the protons. The neutrons help create these ideal distances. If there are too few neutrons, or too many neutrons, the nucleus becomes unstable. If an ato ...
... tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear forces require ideal distances between the protons. The neutrons help create these ideal distances. If there are too few neutrons, or too many neutrons, the nucleus becomes unstable. If an ato ...
Quiz: The Atom (Open Notes)
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
7.1 Note Outline
... Radiation is a term used to describe the high energy rays and particles given off by radioactive substances. An isotope is an atom of an element that has a slight difference in the number of neutrons as compared to other isotopes of the same element. Radioisotopes decay into normal isotopes, releasi ...
... Radiation is a term used to describe the high energy rays and particles given off by radioactive substances. An isotope is an atom of an element that has a slight difference in the number of neutrons as compared to other isotopes of the same element. Radioisotopes decay into normal isotopes, releasi ...
Setting up Programmable PRS Keypad as Fixed ID Keypads
... Parser06 example6
The identity of an element is determined by the number of…
Q
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
A molecule may consist of one atom.
Q
True
False
Molybdenum has atomic number 42. Its molar mass is 95.94 grams/mole. How many neutrons does
the most common isotope have?
Q
...
... Parser06 example
Measuring the Atom
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
Ionic And Covalent Bonds
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...
Lecture 38 - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... waters is the same as the local precipitation and groundwater, but the δ18O is shifted to higher values. The shift in δ18O results from hightemperature reaction (≲300°C) of the local meteoric water with hot rock. Acidic, sulfur-rich waters from hydrothermal systems can have δD that is different from ...
... waters is the same as the local precipitation and groundwater, but the δ18O is shifted to higher values. The shift in δ18O results from hightemperature reaction (≲300°C) of the local meteoric water with hot rock. Acidic, sulfur-rich waters from hydrothermal systems can have δD that is different from ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Conservation of mass and Law of
... Atoms of the same element have the same mass. Atoms of different elements have different masses. Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in simple whole numbers. Atoms are chemically indestructible. ...
... Atoms of the same element have the same mass. Atoms of different elements have different masses. Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in simple whole numbers. Atoms are chemically indestructible. ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
PP - myndrs.com
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
Nurse Shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum)
... • the sum of that atom’s protons and neutrons • can only be found on the periodic table for stable atoms, cannot be found on the periodic table for an isotope ...
... • the sum of that atom’s protons and neutrons • can only be found on the periodic table for stable atoms, cannot be found on the periodic table for an isotope ...
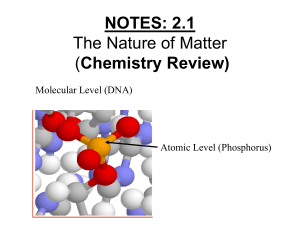
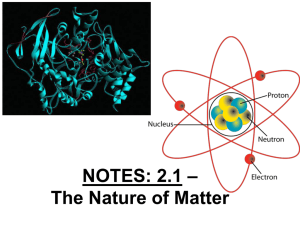
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... symbol ● # of neutrons can vary in an element, but proton # is constant ...
... symbol ● # of neutrons can vary in an element, but proton # is constant ...
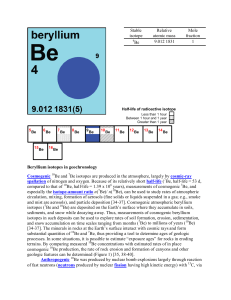
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... circulation, mixing, formation of aerosols (fine solids or liquids suspended in a gas; e.g., smoke and mist are aerosols), and particle deposition [34-37]. Cosmogenic atmospheric beryllium isotopes (7Be and 10Be) are deposited on the Earth’s surface where they accumulate in soils, sediments, and sno ...
... circulation, mixing, formation of aerosols (fine solids or liquids suspended in a gas; e.g., smoke and mist are aerosols), and particle deposition [34-37]. Cosmogenic atmospheric beryllium isotopes (7Be and 10Be) are deposited on the Earth’s surface where they accumulate in soils, sediments, and sno ...
Beyond Element 83 are very unstable (radioactive)
... Stable isotopes have… 1:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements <20) 1.5:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements >20) ...
... Stable isotopes have… 1:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements <20) 1.5:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements >20) ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
MrsB-Chemistry
... A. Alpha particles were shot at a sheet of gold foil. He found that some went straight through while others bounced back B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elemen ...
... A. Alpha particles were shot at a sheet of gold foil. He found that some went straight through while others bounced back B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elemen ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.