Atomic Structure
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
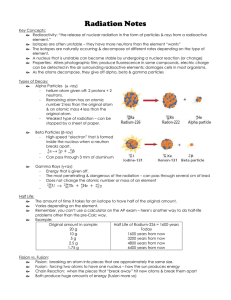
Half-Life
... Initial Mass (1\2)x where x = number of half-lives Transmutation Reactions – Conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element. Transuranium Elements- All elements above atomic number 92 all undergo transmutation and do not occur naturally. Nuclear Fission versus Fusion Fission – Wh ...
... Initial Mass (1\2)x where x = number of half-lives Transmutation Reactions – Conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element. Transuranium Elements- All elements above atomic number 92 all undergo transmutation and do not occur naturally. Nuclear Fission versus Fusion Fission – Wh ...
u3-1-atom-vocabulary-diagrams
... – Neutral (0) charge – Found in the nucleus – Accounts for part of the atom’s mass – If lost or gained, the mass changes ...
... – Neutral (0) charge – Found in the nucleus – Accounts for part of the atom’s mass – If lost or gained, the mass changes ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... States that matter can not be created nor destroyed. During a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants will be the same as the mass of the products. ...
... States that matter can not be created nor destroyed. During a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants will be the same as the mass of the products. ...
Chemistry Review
... 1. a. What is the difference between an atom, element, molecule, and compound? ...
... 1. a. What is the difference between an atom, element, molecule, and compound? ...
Download: Worksheet - New York Science Teacher
... neutron to produce two lighter nuclei, a neutron and a conversion of mass to energy ...
... neutron to produce two lighter nuclei, a neutron and a conversion of mass to energy ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... The element samarium is known to have three isotopes - Sm-148, Sm-149, and Sm-152. The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abund ...
... The element samarium is known to have three isotopes - Sm-148, Sm-149, and Sm-152. The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abund ...
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS LAB
... new element. Mr. Burns, the plant’s owner, says, “We have tentatively named this element Beanium.” Mr. Smithers, assistant to Mr. Burns adds, “We derived this element from the protein nodules we put into our chili.” Further research of the new element will be conducted in more suitable surroundings, ...
... new element. Mr. Burns, the plant’s owner, says, “We have tentatively named this element Beanium.” Mr. Smithers, assistant to Mr. Burns adds, “We derived this element from the protein nodules we put into our chili.” Further research of the new element will be conducted in more suitable surroundings, ...
Ions and isotopes
... • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
... • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
File
... Radioactivity: “the release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles & rays from a radioactive element.” Isotopes are often unstable – they have more neutrons than the element “wants” The isotopes are naturally occurring & decompose at different rates depending on the type of element. A ...
... Radioactivity: “the release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles & rays from a radioactive element.” Isotopes are often unstable – they have more neutrons than the element “wants” The isotopes are naturally occurring & decompose at different rates depending on the type of element. A ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... -329._______ The element samarium is known to have three isotopes - Sm-148, Sm-149, and Sm-152. The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to b ...
... -329._______ The element samarium is known to have three isotopes - Sm-148, Sm-149, and Sm-152. The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to b ...
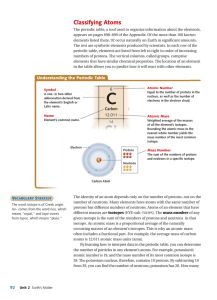
Classifying Atoms
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
Basic Chemistry Notes II
... 3. The atomic number is the number of protons B. Neutrons 1. Found in nucleus 2. No charge 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most impo ...
... 3. The atomic number is the number of protons B. Neutrons 1. Found in nucleus 2. No charge 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most impo ...
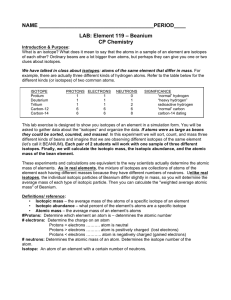
LAB- Beanium_CP Chemistry
... (let’s call it BEANIUM). Each pair of 2 students will work with one sample of three different isotopes. Finally, we will calculate the isotopic mass, the isotopic abundance, and the atomic mass of the bean element. These experiments and calculations are equivalent to the way scientists actually dete ...
... (let’s call it BEANIUM). Each pair of 2 students will work with one sample of three different isotopes. Finally, we will calculate the isotopic mass, the isotopic abundance, and the atomic mass of the bean element. These experiments and calculations are equivalent to the way scientists actually dete ...
hapter 2
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment Atoms have a nucleus Atoms are made up mostly of space Protons exist in the nucleus with a + charge Electrons mass is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, the charge is Protons mass is 1.66 x 10-27 kg, the charge is + Neutrons mass is 1.67 x 10-27 kg, there is no charge AMU means ...
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment Atoms have a nucleus Atoms are made up mostly of space Protons exist in the nucleus with a + charge Electrons mass is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, the charge is Protons mass is 1.66 x 10-27 kg, the charge is + Neutrons mass is 1.67 x 10-27 kg, there is no charge AMU means ...
Ch4StudyGuide
... Although the nucleus is almost 100% of the mass of an atom, what determines the volume? ...
... Although the nucleus is almost 100% of the mass of an atom, what determines the volume? ...
Worksheet 2: 1-19-17 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
Ch. 14.2 Notes
... plant or animal dies, the decaying ____________ no longer can be ________________. 31. When archeologists find an ancient item, they can find out how much carbon-14 it has and compare with _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________ 32. By knowing ...
... plant or animal dies, the decaying ____________ no longer can be ________________. 31. When archeologists find an ancient item, they can find out how much carbon-14 it has and compare with _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________ 32. By knowing ...
Atomic Structure
... Most of the mass and all of the positive charge in an atom forms the nucleus – the rest of the atom is ...
... Most of the mass and all of the positive charge in an atom forms the nucleus – the rest of the atom is ...
Topic 12- Nuclear Chem Reg Rev
... symbols that represent atomic nuclei with mass number and atomic number, subatomic particles with mass and charge and emitted particles ...
... symbols that represent atomic nuclei with mass number and atomic number, subatomic particles with mass and charge and emitted particles ...
Practice questions
... The average atomic mass of Eu is 151.96 amu. There are only two naturally occurring isotopes of europium, 151Eu with a mass of 151.0 amu and 153Eu with a mass of 153.0 amu. The natural abundance of the 131Eu isotope must be approximately a) ...
... The average atomic mass of Eu is 151.96 amu. There are only two naturally occurring isotopes of europium, 151Eu with a mass of 151.0 amu and 153Eu with a mass of 153.0 amu. The natural abundance of the 131Eu isotope must be approximately a) ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.