Atomic Theory Notes Page
... His hypothesis: atoms are eternally unchanging and indivisible (he was not able to prove his thoughts due to lack of technology) o John Dalton Father of Atomic Theory; First to show proof of atoms Experiment: He observed elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds; Matter is NOT ...
... His hypothesis: atoms are eternally unchanging and indivisible (he was not able to prove his thoughts due to lack of technology) o John Dalton Father of Atomic Theory; First to show proof of atoms Experiment: He observed elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds; Matter is NOT ...
Biology Class Notes 3-1
... Ex: Na, C, H, O, N K, Cl, Au The 4 most abundant elements found in organisms is C, H, O, N Atomic number of an elements is the number of protons Carbon has an atomic number of 6 Helium has an atomic number of 2 (C) Chemical Compounds In nature, most elements are found as compounds Comp ...
... Ex: Na, C, H, O, N K, Cl, Au The 4 most abundant elements found in organisms is C, H, O, N Atomic number of an elements is the number of protons Carbon has an atomic number of 6 Helium has an atomic number of 2 (C) Chemical Compounds In nature, most elements are found as compounds Comp ...
Topic 13 – 14.1
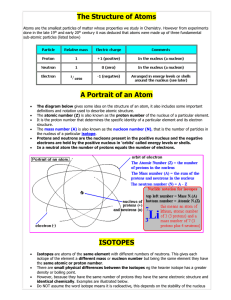
... that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
... that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
Atomic Mass
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
Document
... Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be triggered off by something. There are 3 different kinds of emissions identified: ...
... Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be triggered off by something. There are 3 different kinds of emissions identified: ...
BEAT_Sheet_for_Atoms_2016_ACA
... Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in isotopes written in general format and hyphen notation. ...
... Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in isotopes written in general format and hyphen notation. ...
Isotopes and Mass Number
... Calculating Atomic Mass Atomic Mass is the average of all an element’s masses You need two values ...
... Calculating Atomic Mass Atomic Mass is the average of all an element’s masses You need two values ...
THE ATOM - A COMPUTER GUIDED LESSON
... Part I. Use the computer PowerPoint to answer the following questions. Answer the questions on a separate sheet of white paper. 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evi ...
... Part I. Use the computer PowerPoint to answer the following questions. Answer the questions on a separate sheet of white paper. 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evi ...
Atom Models - Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, Bohr
... • These values are given on the periodic table. • For now, round the mass # to a whole number. • These numbers tell you a lot about atoms. # of protons = # of electrons = atomic number # of neutrons = mass number – atomic number • Calculate # of e–, n0, p+ for Ca, Ar, and Br. ...
... • These values are given on the periodic table. • For now, round the mass # to a whole number. • These numbers tell you a lot about atoms. # of protons = # of electrons = atomic number # of neutrons = mass number – atomic number • Calculate # of e–, n0, p+ for Ca, Ar, and Br. ...
Problem Set 4 - Morrisville.org
... 54) How long will it take 100 grams of radioactive sample to decay so that only 6.25 grams remain and the samples half life is 3 days? 55) How long is the half life of an isotope if 2.0 grams of sample remain from a 64 gram sample after 30 years? After having read through chapter 25, respond to thes ...
... 54) How long will it take 100 grams of radioactive sample to decay so that only 6.25 grams remain and the samples half life is 3 days? 55) How long is the half life of an isotope if 2.0 grams of sample remain from a 64 gram sample after 30 years? After having read through chapter 25, respond to thes ...
Chapter 9: Nuclear Chemistry
... A. Alpha ( ) emission: particles that consist of _____________ and ______________ (like a _________ atom without the electrons.) ________________ charged. Emitted at about _________the speed of light. _____________, but the ____________ penetrating. Symbol: B. Beta ( ) emission” particles that are _ ...
... A. Alpha ( ) emission: particles that consist of _____________ and ______________ (like a _________ atom without the electrons.) ________________ charged. Emitted at about _________the speed of light. _____________, but the ____________ penetrating. Symbol: B. Beta ( ) emission” particles that are _ ...
Chemistry Unit Test Review
... Students added liver to hydrogen peroxide. The mass of the substance after the reaction took place was less than the mass before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
... Students added liver to hydrogen peroxide. The mass of the substance after the reaction took place was less than the mass before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
atom book - District 196
... a. All elements are made of indivisible particles called ____________________ b. All atoms of the same element are ______________ but are different from other elements. c. Reactions ____________________ atoms but do not create or destroy them. d. _______________________ are made from combining atoms ...
... a. All elements are made of indivisible particles called ____________________ b. All atoms of the same element are ______________ but are different from other elements. c. Reactions ____________________ atoms but do not create or destroy them. d. _______________________ are made from combining atoms ...
BillNyeAtoms
... Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘light’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Whic ...
... Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘light’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Whic ...
CF#10854 Bean Bag Isotopes
... thus chemically identical—they form the same compounds, undergo the same reactions, etc. Isotopes are distinguished from one another based on their mass number, defined as the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. Chlorine, for example, occurs naturally in the form of ...
... thus chemically identical—they form the same compounds, undergo the same reactions, etc. Isotopes are distinguished from one another based on their mass number, defined as the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. Chlorine, for example, occurs naturally in the form of ...
Chapter Two - Alfred State College intranet site
... Atomic Mass Units (amu) 1 amu = Protons and neutrons nearly more massive than electrons ...
... Atomic Mass Units (amu) 1 amu = Protons and neutrons nearly more massive than electrons ...
Matter and Energy
... energy in the form of high-energy particles that are ionizing. As they rearrange themselves, they become a different, more stable isotope at a predictable rate. The amount of time it takes for 50% of a substance to naturally degrade to a stable isotope is expressed as its “half-life”. Radioactive su ...
... energy in the form of high-energy particles that are ionizing. As they rearrange themselves, they become a different, more stable isotope at a predictable rate. The amount of time it takes for 50% of a substance to naturally degrade to a stable isotope is expressed as its “half-life”. Radioactive su ...
Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... __________ are positively charged particles. __________ are particles that have no charge. __________ are negatively charged particles that are located outside the __________. Elements: An __________ is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical ...
... __________ are positively charged particles. __________ are particles that have no charge. __________ are negatively charged particles that are located outside the __________. Elements: An __________ is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical ...
... butter. All of its carbon to carbon bonds are single. Too much of this can increase the chance of cardiovascular disease 11. What are unsaturated fats? A fat that contains fewer numbers of hydrogen (less stored energy) and is liquid at room temperature, found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds. Atle ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... 5. Why do you think that Rutherford said an atom is composed mostly of empty space? ...
... 5. Why do you think that Rutherford said an atom is composed mostly of empty space? ...
04-Atoms_ molecules_ ions_etc
... Atomic Mass • The weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope ...
... Atomic Mass • The weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... changes. This is how you identify an element. If the number of protons are changed, you have a whole new element. Atoms are electrically neutral (protons = electrons). • If an atom is heavier/lighter than expected (greater or lower atomic mass than on the PTE), neutrons have been added or lost. This ...
... changes. This is how you identify an element. If the number of protons are changed, you have a whole new element. Atoms are electrically neutral (protons = electrons). • If an atom is heavier/lighter than expected (greater or lower atomic mass than on the PTE), neutrons have been added or lost. This ...
Ch. 2 note packet
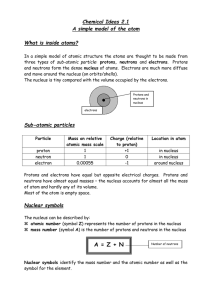
... IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called _________, which retain their identity in ____________________. In a compound, atoms of two or more elements are combined in a fixed ratio of ___________________. Gay-Lussac - (1809) Combining Volumes of Gases • Performed experiments in which he m ...
... IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called _________, which retain their identity in ____________________. In a compound, atoms of two or more elements are combined in a fixed ratio of ___________________. Gay-Lussac - (1809) Combining Volumes of Gases • Performed experiments in which he m ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.