Name_______________________________
... more phosphate groups and are used to store genetic information. B. Carbohydrates are organic macromolecules that are insoluble in water and have the ability to store energy for extended periods of time. C. Carbohydrates are organic macromolecules that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ato ...
... more phosphate groups and are used to store genetic information. B. Carbohydrates are organic macromolecules that are insoluble in water and have the ability to store energy for extended periods of time. C. Carbohydrates are organic macromolecules that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ato ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... Excited elements emit only certain wavelengths of radiation, which are unique for each element This distinct pattern can be used to identify individual atoms. This practice is termed SPECTROSCOPY ...
... Excited elements emit only certain wavelengths of radiation, which are unique for each element This distinct pattern can be used to identify individual atoms. This practice is termed SPECTROSCOPY ...
History - E. R. Greenman
... of differing characteristics.) 2.All atoms of an element are identical. All atoms of one element are different from atoms of other elements. 3.Compounds are made of atoms of more than one element. The ratio of the elements is a simple fraction. 4.A chemical reaction involves separation, combination ...
... of differing characteristics.) 2.All atoms of an element are identical. All atoms of one element are different from atoms of other elements. 3.Compounds are made of atoms of more than one element. The ratio of the elements is a simple fraction. 4.A chemical reaction involves separation, combination ...
The Atom
... • Oil drop experiment determined the charge (e=1.602 x 10 -19 coulomb) and the mass (m = 9.11 x 10 -28 gram) of an electron. ...
... • Oil drop experiment determined the charge (e=1.602 x 10 -19 coulomb) and the mass (m = 9.11 x 10 -28 gram) of an electron. ...
Atomic Structure
... having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are ____________ from other elements Atoms cannot be ____________ , ____________ , or ...
... having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are ____________ from other elements Atoms cannot be ____________ , ____________ , or ...
Levels of Organization - Bremen High School District 228
... one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) at the other. ...
... one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) at the other. ...
In a nuclear reaction
... 1- The mass numbers and atomic numbers in a nuclear reaction are balance, the total mass of products are less. 2- In a nuclear reaction- the mass lost is converted to ...
... 1- The mass numbers and atomic numbers in a nuclear reaction are balance, the total mass of products are less. 2- In a nuclear reaction- the mass lost is converted to ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
Slide 1 - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Unfinished business from April 4!
... Steady state alone can be misleading pool size constant but coordinated increase in flux (activities altered) ...
... Steady state alone can be misleading pool size constant but coordinated increase in flux (activities altered) ...
called “organic molecules”
... •Polymer – straight chain of monomers, about a total of 50 in number ...
... •Polymer – straight chain of monomers, about a total of 50 in number ...
The Atom Power point - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists use the following notation: Mass Number ...
... Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists use the following notation: Mass Number ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
Jeopardy Review Guide
... That atoms are very small That atoms are very large That in a copper penny, there is one atom for every person on Earth ...
... That atoms are very small That atoms are very large That in a copper penny, there is one atom for every person on Earth ...
Cobalt isotopes in industry 60Co is used to irradiate food sources as
... that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), bet ...
... that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), bet ...
THE ATOM - A COMPUTER GUIDED LESSON
... Part I. Use the computer PowerPoint to answer the following questions. Answer the questions on a separate sheet of white paper. 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evi ...
... Part I. Use the computer PowerPoint to answer the following questions. Answer the questions on a separate sheet of white paper. 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evi ...
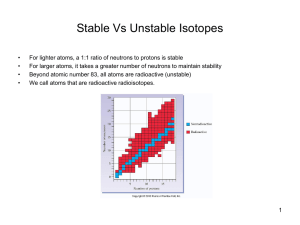
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... Nuclear reactions are accompanied by tremendous energy changes as an unstable isotope spontaneously undergoes changes. ...
... Nuclear reactions are accompanied by tremendous energy changes as an unstable isotope spontaneously undergoes changes. ...
Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’‛s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or ...
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’‛s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or ...
1st Semester Final Exam Review Guide
... Given 238U. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Also determine its mass number. ...
... Given 238U. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Also determine its mass number. ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.