Chapter 16
... -does not work for extinct species -does not work for asexual reproduction -The modern definition of a species includes both the morphological and biological species concept. -A species is a single type of organism. Members of a species are morphologically similar and can interbreed to produce ...
... -does not work for extinct species -does not work for asexual reproduction -The modern definition of a species includes both the morphological and biological species concept. -A species is a single type of organism. Members of a species are morphologically similar and can interbreed to produce ...
definition - Humble ISD
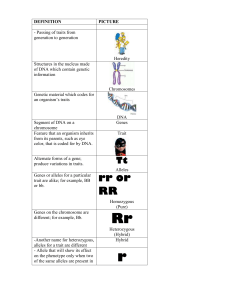
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
Diapositiva 1
... The best example of Lamarck’s theory is about giraffes. Lamarck believed that giraffes stretched their necks to reach food. Their offspring and later generations inherited the resulting long necks. ...
... The best example of Lamarck’s theory is about giraffes. Lamarck believed that giraffes stretched their necks to reach food. Their offspring and later generations inherited the resulting long necks. ...
Evolution Bingo Review
... c. No ___________________ that cause changes in genes. d. No movement of genetic information from one population to another - _______________/emigration. e. No natural selection (no one is more fit to the environment than another). 5. ___________________ structures, similar structure but different f ...
... c. No ___________________ that cause changes in genes. d. No movement of genetic information from one population to another - _______________/emigration. e. No natural selection (no one is more fit to the environment than another). 5. ___________________ structures, similar structure but different f ...
Review for Final: Chap 16: Evolulution of Populations
... No, genetic drift: a series of random occurences in a small population may change the relative frequency of an allele by chance ...
... No, genetic drift: a series of random occurences in a small population may change the relative frequency of an allele by chance ...
Notes Chapter 16 - Spring Branch ISD
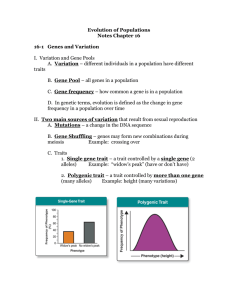
... C. Gene frequency – how common a gene is in a population D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes ma ...
... C. Gene frequency – how common a gene is in a population D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes ma ...
Evolution of Populations
... • The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance and evolution • Scientists know that… –genes control traits and that many genes have at least two forms, or alleles -members of all species are heterozygous for many genes ...
... • The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance and evolution • Scientists know that… –genes control traits and that many genes have at least two forms, or alleles -members of all species are heterozygous for many genes ...
Lecture #10 Date ______
... – Type of genetic drift resulting from a reduction in population (natural disaster) where the surviving population does have the same genetic make up of the original population ...
... – Type of genetic drift resulting from a reduction in population (natural disaster) where the surviving population does have the same genetic make up of the original population ...
Enriched Biology DeCamp BB3
... 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, allele frequencies change because of… 10. Genetic drift tends to occur in populations that… 11. One similarity between natural selection and genetic drift is that both events… 12. The situation in which allele frequencies of a po ...
... 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, allele frequencies change because of… 10. Genetic drift tends to occur in populations that… 11. One similarity between natural selection and genetic drift is that both events… 12. The situation in which allele frequencies of a po ...
Chapter 23 - Cloudfront.net
... pattern of change in the allele frequency of a gene in a population. – _______ (in sex cells) are the source of new genes and new alleles. – Point mutations change little, chromosomal mutations cause greater changes. – Sexual _________ (crossing over, IA, and random fertilization) account for most v ...
... pattern of change in the allele frequency of a gene in a population. – _______ (in sex cells) are the source of new genes and new alleles. – Point mutations change little, chromosomal mutations cause greater changes. – Sexual _________ (crossing over, IA, and random fertilization) account for most v ...
Selection and Adaptation - WFSC 406 | Wildlife Habitat Management
... while a recessive allele is masked by a dominant allele. In most multi-cellular organisms, each individual cell contains 2 copies of each type of chromosome or alleles of a gene; 1 from the male and 1 from the female. 5. The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usu ...
... while a recessive allele is masked by a dominant allele. In most multi-cellular organisms, each individual cell contains 2 copies of each type of chromosome or alleles of a gene; 1 from the male and 1 from the female. 5. The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usu ...
Ch 17 RNO
... What is genetic drift? Be detailed in your explanation. Describe the characteristics of the bottleneck effect. Give an example of how this can happen. Describe the characteristics of the founder effect. Provide an example. What is genetic equilibrium? What conditions are required to maintain it? Wha ...
... What is genetic drift? Be detailed in your explanation. Describe the characteristics of the bottleneck effect. Give an example of how this can happen. Describe the characteristics of the founder effect. Provide an example. What is genetic equilibrium? What conditions are required to maintain it? Wha ...
No Slide Title
... and assortative mating) – Population is large (if appropriately chosen!) – No mutation (but there is) – No migration (but migration occurs) – No selection (but there can be selection) ...
... and assortative mating) – Population is large (if appropriately chosen!) – No mutation (but there is) – No migration (but migration occurs) – No selection (but there can be selection) ...
Evolution
... The specific chemical form of a gene at an individual locus cause variation in the appearance of an organism Different gene forms that exist at a given locus are called alleles Heterozygosity: ...
... The specific chemical form of a gene at an individual locus cause variation in the appearance of an organism Different gene forms that exist at a given locus are called alleles Heterozygosity: ...
Ways Genetic Eqilibrium can Change
... • Change in an organisms DNA that creates a new allele which leads to new phenotypes. • The source of genetic variability. • Need to be recombined • Rare; take long time to develop, can reduce fitness • (e.g.) Sickle cell anemia ...
... • Change in an organisms DNA that creates a new allele which leads to new phenotypes. • The source of genetic variability. • Need to be recombined • Rare; take long time to develop, can reduce fitness • (e.g.) Sickle cell anemia ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Insertions and deletions • They shift the reading frame of the genetic message… remember bases are read in groups of three • Entire protein can be ruined ...
... • Insertions and deletions • They shift the reading frame of the genetic message… remember bases are read in groups of three • Entire protein can be ruined ...
Microevolution
... population’s frequency of alleles Even if the allele frequencies of only one gene (ie. flower color) are changing, the change in the gene pool is known as microevolution ...
... population’s frequency of alleles Even if the allele frequencies of only one gene (ie. flower color) are changing, the change in the gene pool is known as microevolution ...
Evolution - SchoolNotes
... Darwin (con’t) Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. The characteristics that make them survive are passed on to their offspring. Species change over time. Species alive today have descended with modifications from species that used to live in t ...
... Darwin (con’t) Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. The characteristics that make them survive are passed on to their offspring. Species change over time. Species alive today have descended with modifications from species that used to live in t ...
Lecture #10 Date ______
... type of genetic drift resulting from a reduction in population (natural disaster) such that the surviving population is no ...
... type of genetic drift resulting from a reduction in population (natural disaster) such that the surviving population is no ...
practice
... following statements are inferences of natural selection. Which one is NOT an inference made by Charles Darwin in developing his Theory of Natural Selection? A) Subsequent generations of a population should have greater proportions of individuals that possess favorable traits. B) An individual organ ...
... following statements are inferences of natural selection. Which one is NOT an inference made by Charles Darwin in developing his Theory of Natural Selection? A) Subsequent generations of a population should have greater proportions of individuals that possess favorable traits. B) An individual organ ...
Name: Block: ______ Lab Biology Chapter 16 The Evolution of
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...