Mechanism of Evolution
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
CHAPTER 16 NOTES
... the recessive allele for brown fur may appear 60% In genetic terms, evolution is any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population ...
... the recessive allele for brown fur may appear 60% In genetic terms, evolution is any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population ...
VOCAB- Evolution
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION (DIVERGENT EVOLUTION) – process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in e ...
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION (DIVERGENT EVOLUTION) – process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in e ...
Microevolution - MrCarlsonsBiologyClass
... Microevolution Natural Selection, Mechanisms of Evolution, and Evidence ...
... Microevolution Natural Selection, Mechanisms of Evolution, and Evidence ...
9.1 - How Do Populations Evolve SG
... Mutation: a change that occurs in the DNA of an individual. Gene flow: the net movement of alleles from one population to another due to the migration of individuals. Non-random mating: mating among individuals on the basis of mate selection for a particular phenotype or due to breeding. Genetic dri ...
... Mutation: a change that occurs in the DNA of an individual. Gene flow: the net movement of alleles from one population to another due to the migration of individuals. Non-random mating: mating among individuals on the basis of mate selection for a particular phenotype or due to breeding. Genetic dri ...
Population Genetics
... •Genome = total genes for individual (or species) •Gene pool = total genes of population •Population Genetics = Mendel + Darwin (Genetics) + (natural selection) •Microevolution = change in allele frequency (same as population genetics) •Hardy-Weinberg Law mathematical concepts to represent alleles i ...
... •Genome = total genes for individual (or species) •Gene pool = total genes of population •Population Genetics = Mendel + Darwin (Genetics) + (natural selection) •Microevolution = change in allele frequency (same as population genetics) •Hardy-Weinberg Law mathematical concepts to represent alleles i ...
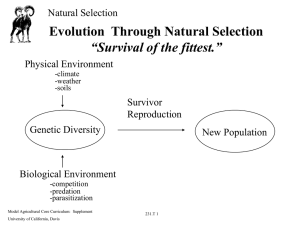
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
Process of Evolution - Woodstown
... Used to calculate the genotype and gene frequencies of a population States: equilibrium of allele frequencies in a gene pool will remain in effect in each generation of ...
... Used to calculate the genotype and gene frequencies of a population States: equilibrium of allele frequencies in a gene pool will remain in effect in each generation of ...
12 Evolution 2016
... Genetic Drift– random changes in allele frequency. Stabilizing Selection– favors maintaining allele frequencies. Selects against extreme phenotypes. Disruptive Selection– selects for extreme phenotypes and against the “average.” Can lead to speciation. Directional Selection– favors one phenotype ove ...
... Genetic Drift– random changes in allele frequency. Stabilizing Selection– favors maintaining allele frequencies. Selects against extreme phenotypes. Disruptive Selection– selects for extreme phenotypes and against the “average.” Can lead to speciation. Directional Selection– favors one phenotype ove ...
13 Evolution 2015
... Genetic drift– random changes in allele frequency. Stabilizing Selection– Favors maintaining allele frequencies. Selects against extreme phenotypes. Disruptive Selection– Selects for extreme phenotypes and against the “average.” Can lead to speciation. Directional Selection– Favors one phenotype ove ...
... Genetic drift– random changes in allele frequency. Stabilizing Selection– Favors maintaining allele frequencies. Selects against extreme phenotypes. Disruptive Selection– Selects for extreme phenotypes and against the “average.” Can lead to speciation. Directional Selection– Favors one phenotype ove ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genetic selection and variation Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene ...
... Genetic selection and variation Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene ...
Evolution Study Guide – Part I If natural selection is to take place
... 9. Any structure that is reduced in function in a living organism but may have been used in an ancestor is known as a vestigial structure. 10. The concept that evolution occurs over long periods of stability that are interrupted by geologically brief periods of change is known as punctuated equilibr ...
... 9. Any structure that is reduced in function in a living organism but may have been used in an ancestor is known as a vestigial structure. 10. The concept that evolution occurs over long periods of stability that are interrupted by geologically brief periods of change is known as punctuated equilibr ...
BIOL212TestTopicsAPR2012
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence Genetic variation makes evolution possible The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to test whether a population is evolving Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter ...
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence Genetic variation makes evolution possible The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to test whether a population is evolving Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter ...
Concept Sheet
... Objectives: Students will 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the fiv ...
... Objectives: Students will 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the fiv ...
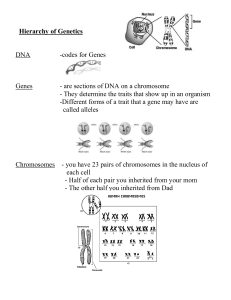
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
Intro To Evolutionary Process
... Now that we have established what evolution is, how do we get genes to change? There are 5 mechanisms that result in a change in genes and new alleles to form…. 1. Mutations- missense mutations are point level changes in the DNA. A single mutation can have a large effect, but in many cases, evoluti ...
... Now that we have established what evolution is, how do we get genes to change? There are 5 mechanisms that result in a change in genes and new alleles to form…. 1. Mutations- missense mutations are point level changes in the DNA. A single mutation can have a large effect, but in many cases, evoluti ...
Evolution: three coordinated legs
... • Environments can be “stable” or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different variations can be selected in each generation. • What evidence do you have from the Grant’s finch study to support this claim? ...
... • Environments can be “stable” or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different variations can be selected in each generation. • What evidence do you have from the Grant’s finch study to support this claim? ...
Bio Chp 15.2 Page 1
... 12. Genetic equilibrium is the alteration of allelic frequencies by chance processes. ___________________ 13. Genetic drift is more likely to occur in large populations. __________________ 14. The factor that can significantly change the genetic equilibrium of a population’s gene pool is ...
... 12. Genetic equilibrium is the alteration of allelic frequencies by chance processes. ___________________ 13. Genetic drift is more likely to occur in large populations. __________________ 14. The factor that can significantly change the genetic equilibrium of a population’s gene pool is ...
acquired
... This term refers to a population forming a new species because of geographical isolation from the parent population. ...
... This term refers to a population forming a new species because of geographical isolation from the parent population. ...
Evidence of Macroevolution
... spurts followed by periods of neutral change in species Evidence, like we have seen, supports that both may happen at once. Subtle changes and sudden “catastrophic events” to a species environment have shaped and continue to shape species on the planet ...
... spurts followed by periods of neutral change in species Evidence, like we have seen, supports that both may happen at once. Subtle changes and sudden “catastrophic events” to a species environment have shaped and continue to shape species on the planet ...
Study guide for exam 1
... inferences. 3. List and describe the evidence for evolution as discussed in this class. 4. Describe the difference between macroevolution and microevolution. 5. What is the smallest unit of evolutionary change (i.e., does evolution occur at the gene, individual, or population level)? 6. Define: gene ...
... inferences. 3. List and describe the evidence for evolution as discussed in this class. 4. Describe the difference between macroevolution and microevolution. 5. What is the smallest unit of evolutionary change (i.e., does evolution occur at the gene, individual, or population level)? 6. Define: gene ...