5 Agents of Evolutionary Change
... = random circumstance causes a certain genetic trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
... = random circumstance causes a certain genetic trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
Chapter 17
... ****The species that exist at any time are the net result of both speciation and extinction. -if you think of speciation as like a branch off of a family tree, then extinction is like the loss of one of those branches. ...
... ****The species that exist at any time are the net result of both speciation and extinction. -if you think of speciation as like a branch off of a family tree, then extinction is like the loss of one of those branches. ...
Population Genetics Vocabulary - Liberty Union High School District
... population moves to a new location,& brings only a small fraction of genes/variation seen in the parent population, such as The Galapagos Finches ...
... population moves to a new location,& brings only a small fraction of genes/variation seen in the parent population, such as The Galapagos Finches ...
natural selection
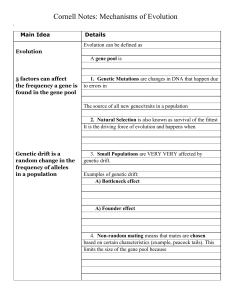
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
Divergent evolution: Same basic structure, different appearance
... Divergent evolution: Same basic structure, different appearance, different function, common ancestor Convergent evolution (analogous structure): Evolved independently for similar purposes Parallel evolution: Evolved similar features due to similar environments Taxonomy: Kingdom, phylum, class, order ...
... Divergent evolution: Same basic structure, different appearance, different function, common ancestor Convergent evolution (analogous structure): Evolved independently for similar purposes Parallel evolution: Evolved similar features due to similar environments Taxonomy: Kingdom, phylum, class, order ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The total number of fossils, and their locations in rock formations and sedimentary layers which provides information about those organisms ...
... The total number of fossils, and their locations in rock formations and sedimentary layers which provides information about those organisms ...
Adaptation and Speciation
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
Population Genetics
... traits in a population over several generations Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
... traits in a population over several generations Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
Evolutionary forces: in small populations
... 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single chromosomes + complete se ...
... 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single chromosomes + complete se ...
Quiz 3, February 6, 2003
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
Population Genetics and evolution with notes
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
Enriched Biology Dremann Metzendorf Bag 3
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
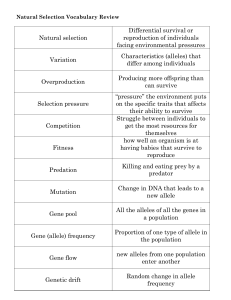
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
Causes of Evolution
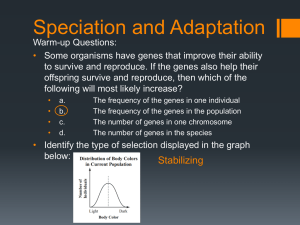
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
16-1 Genes and Variation
... species in a given area. (Share a common gene pool) Gene pool—combined genetic info of all members of a population. Relative frequency—is the number of times an allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
... species in a given area. (Share a common gene pool) Gene pool—combined genetic info of all members of a population. Relative frequency—is the number of times an allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
Genetic engineering
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
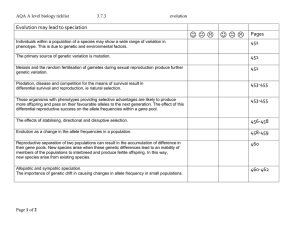
doc 3.7.3 evolution checklist
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...