* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Genetics
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
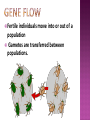
The science of genetic change in populations. Population- interbreeding single-species group individuals of the same species, living in the same place at the same time Populations evolve. are the smallest unit that can As a change in the prevalence of certain traits in a population over several generations Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time Spontaneous mutations may produce new traits Segregation & independent assortment produce variations in gametes & offspring Genes are passed through gametes from parents to offspring Theory developed in the 1940’s Includes genetics and evolution GENE POOL = where all members of the next generation get their genes! When allele frequencies in a population change over generations, evolution is occurring at its smallest scale. Species distributed over a geographic range –> have different gene pool THAN Species localized due to water, islands, mountains etc.!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. genetic drift bottleneck effect founder effect gene flow mutation A change in the gene pool of a small population due to chance! Ex: flipping coin 10X Type of genetic drift colonization of a new location by a small number of individuals small size, less representative of the gene pool. Fertile individuals move into or out of a population Gametes are transferred between populations. Allele frequency with ONLY sexual reproduction involved! NO OUTSIDE AGENTS p = dominant q = recessive 2pq = heterozygous p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 1. very large population 2. population is isolated 3. mutations (changes in genes) do not alter the gene pool 4. mating is random 5. all indiv. Are equal in reproductive success NO NATURAL SELECTION OCCURS! Conditions rarely met by a natural population Gives us a basis to compare nonevolving population vs. actual ones with gene pools that are changing!