Sample File
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
Evolution Learning Objectives
... mutations between species B and species C, and 15 mutations between species A and C. Which species are most closely related based on this data alone? 16. Describe two ways that genetic variation occurs in gene pools. 17. What is the allele frequency for an allele that is present 25 times out of 100? ...
... mutations between species B and species C, and 15 mutations between species A and C. Which species are most closely related based on this data alone? 16. Describe two ways that genetic variation occurs in gene pools. 17. What is the allele frequency for an allele that is present 25 times out of 100? ...
Chapter 16-1 - greinerudsd
... The two main sources of genetic variation are _____________________________: any change in DNA the ______________________ that results from sexual reproduction, including ________________________________ Single Gene vs. Polygenic Traits The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends o ...
... The two main sources of genetic variation are _____________________________: any change in DNA the ______________________ that results from sexual reproduction, including ________________________________ Single Gene vs. Polygenic Traits The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends o ...
Chapter 23 outline
... Genetic Drift – Change in the population’s allele frequencies due to chance. Bottleneck Effect – Genetic drift due to a drastic reduction in population size. Founder Effect – Genetic drift in a new colony. ...
... Genetic Drift – Change in the population’s allele frequencies due to chance. Bottleneck Effect – Genetic drift due to a drastic reduction in population size. Founder Effect – Genetic drift in a new colony. ...
2.4 measuring evolution of populations2010edit
... genetic mutations? 3. Genetic mutations are always harmful 4. Mutations can occur when DNA molecules are copied 5. Mutations are the ultimate source of all variations in a population 6. Mutations that occur in the skin cells of parents can be passed to offspring 7. Mutations are the raw material tha ...
... genetic mutations? 3. Genetic mutations are always harmful 4. Mutations can occur when DNA molecules are copied 5. Mutations are the ultimate source of all variations in a population 6. Mutations that occur in the skin cells of parents can be passed to offspring 7. Mutations are the raw material tha ...
16-1 Genetic Equilibrium
... evolving (not changing over time) 5 criteria (must be met) No net mutations occur No one enters or leaves the population The population is large Individuals mate randomly Selection does not occur ...
... evolving (not changing over time) 5 criteria (must be met) No net mutations occur No one enters or leaves the population The population is large Individuals mate randomly Selection does not occur ...
Genetics Quiz- Matching, Short answer
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Study Guide
... How might a gel electrophoresis be used? Give TWO applications. ...
... How might a gel electrophoresis be used? Give TWO applications. ...
HERE
... 3. Evolution was not an idea original to Darwin, so what was Darwin’s key contribution to this theory.____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Distinguish between Lamarck’s concept of evolution a ...
... 3. Evolution was not an idea original to Darwin, so what was Darwin’s key contribution to this theory.____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Distinguish between Lamarck’s concept of evolution a ...
Natural Selection PPT WS
... Natural Selection (Darwin’s Mechanism) Natural Selection – the process by which organisms that are better suited to an environment survive and reproduce in greater number than those less suited. ...
... Natural Selection (Darwin’s Mechanism) Natural Selection – the process by which organisms that are better suited to an environment survive and reproduce in greater number than those less suited. ...
Allele frequencies
... A. Allele frequencies in a population remain the same from generation to generation unless acted on by outside influences. B. Assumptions about an ideal “made up” population that is not evolving 1. No net mutations occur; allele frequencies do not change because of mutation. 2. Individuals neither e ...
... A. Allele frequencies in a population remain the same from generation to generation unless acted on by outside influences. B. Assumptions about an ideal “made up” population that is not evolving 1. No net mutations occur; allele frequencies do not change because of mutation. 2. Individuals neither e ...
AP Biology Natural selection acts on individuals “survival of the fittest”
... Evolution of Populations Natural selection acts on individuals “survival of the fittest” ...
... Evolution of Populations Natural selection acts on individuals “survival of the fittest” ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
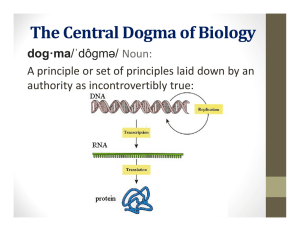
... THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of p ...
... THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of p ...
10 - gwbiology
... 10. Species help to distinguish between different types of plants and animals by their difference appearances. Species can be determined by their physical form or structure called morphology, other factors that can determine a species is differentiation in body functions, biochemistry, behavior and ...
... 10. Species help to distinguish between different types of plants and animals by their difference appearances. Species can be determined by their physical form or structure called morphology, other factors that can determine a species is differentiation in body functions, biochemistry, behavior and ...
Biological Change over Time
... • If successful, genetically modified individual is mass produced ...
... • If successful, genetically modified individual is mass produced ...
G. fortis
... • Nat’l selection shapes existing variation in pop’ns • Individuals are selected, but populations evolve • What is a population? – Group of individuals belonging to the same species – Gene pool = collection of alleles – Evolution happens when allele frequencies change over ...
... • Nat’l selection shapes existing variation in pop’ns • Individuals are selected, but populations evolve • What is a population? – Group of individuals belonging to the same species – Gene pool = collection of alleles – Evolution happens when allele frequencies change over ...
PROCESS OF EVOLUTION I Evolution in a Genetic Context
... It increases both homozygous dominant & recessive Assortative mating: favors similar phenotypes It divides the population into two or more phenotypes Sexual selection: e.g., female chose their mates ...
... It increases both homozygous dominant & recessive Assortative mating: favors similar phenotypes It divides the population into two or more phenotypes Sexual selection: e.g., female chose their mates ...
Keystone Vocabulary 61-70
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
Factors that Cause Evolutionary Change
... suited to survive and reproduce than others in the population. The most significant factor in the formation of new species (speciation). E: Over many generations, frequencies of alleles of many different genes may change, resulting in significant changes in the characteristics of a population. D: Mu ...
... suited to survive and reproduce than others in the population. The most significant factor in the formation of new species (speciation). E: Over many generations, frequencies of alleles of many different genes may change, resulting in significant changes in the characteristics of a population. D: Mu ...