Population
... A. Causes of Evolution 1. Genetic mutations or variation – differences either already occur in the population (e.g. color variations) or they appear through random mutation. Different environments lead to the increase or decrease of these traits through natural selection. ...
... A. Causes of Evolution 1. Genetic mutations or variation – differences either already occur in the population (e.g. color variations) or they appear through random mutation. Different environments lead to the increase or decrease of these traits through natural selection. ...
Evolution of Populations
... Relative frequencies within the gene pool change as some phenotypes are selected for (or some are ...
... Relative frequencies within the gene pool change as some phenotypes are selected for (or some are ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... all living things derive from a _____________________________________. 15) Restriction enzymes are like “molecular scissors” that cut _______ molecules. ...
... all living things derive from a _____________________________________. 15) Restriction enzymes are like “molecular scissors” that cut _______ molecules. ...
05 Evolutionary Mechanisms
... Genetic mutations create new alleles or change an existing one into another, thereby changing the frequency of both alleles. Gene duplications are the main source of new genetic material, as extra copies they are free to mutate with less likelihood of causing harm. Mutations occur as 1 in 10000 in a ...
... Genetic mutations create new alleles or change an existing one into another, thereby changing the frequency of both alleles. Gene duplications are the main source of new genetic material, as extra copies they are free to mutate with less likelihood of causing harm. Mutations occur as 1 in 10000 in a ...
Evolutionary biology
... Variation arise by chance and evolution proceeds through the natural selectionsame as Darwianism ...
... Variation arise by chance and evolution proceeds through the natural selectionsame as Darwianism ...
How Evolution Works
... Variation and Selection Variation from two sources 1) New mutations = new allele types 2) Gene shuffling = new allele combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
... Variation and Selection Variation from two sources 1) New mutations = new allele types 2) Gene shuffling = new allele combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
Evolutionary Biology Key Terms
... larger population. Functional adaptations -‐ traits that involve the internal functions or chemistry of an organism. Gametic isolation – sperm and egg are incompatible and no fertilization can occur. ...
... larger population. Functional adaptations -‐ traits that involve the internal functions or chemistry of an organism. Gametic isolation – sperm and egg are incompatible and no fertilization can occur. ...
MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION
... – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total n ...
... – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total n ...
Evolution WKS - Sardis Secondary
... 5. Identify the 4 conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg principle that must be met to maintain genetic equilibrium. ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Explain how population ...
... 5. Identify the 4 conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg principle that must be met to maintain genetic equilibrium. ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Explain how population ...
Lecture Ch 23 The evolution of populations
... organism, but can be beneficial when the environment is changing. Mutations’ effects can be seen in faster reproducing species (bacteria, insects) 6. Nonrandom mating a. Inbreeding-mating between closely-related partners b. assortative mating-individuals select partners that are like themselves and ...
... organism, but can be beneficial when the environment is changing. Mutations’ effects can be seen in faster reproducing species (bacteria, insects) 6. Nonrandom mating a. Inbreeding-mating between closely-related partners b. assortative mating-individuals select partners that are like themselves and ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 1
... Artificial selection-Selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in the offspring Thomas Malthus- Contended human suffering is the consequence of human population increasing faster than food and other resources Gregory Mendel- Made groundbreaki ...
... Artificial selection-Selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in the offspring Thomas Malthus- Contended human suffering is the consequence of human population increasing faster than food and other resources Gregory Mendel- Made groundbreaki ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... restriction fragments, gene therapy, DNA ligase, gel electrophoresis, what is PCR and how is it used?, RFLP, applications of RFLP, forensic uses of DNA technology, DNA fingerprinting, agricultural uses of DNA technology, safety and ethical issues (p.422-423) and other areas of this chapter), genomic ...
... restriction fragments, gene therapy, DNA ligase, gel electrophoresis, what is PCR and how is it used?, RFLP, applications of RFLP, forensic uses of DNA technology, DNA fingerprinting, agricultural uses of DNA technology, safety and ethical issues (p.422-423) and other areas of this chapter), genomic ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... • Change in an organisms DNA that creates a new allele which leads to new phenotypes. • The source of genetic variability. • Need to be recombined • Rare; take long time to develop, can reduce fitness • (e.g.) Sickle cell anemia ...
... • Change in an organisms DNA that creates a new allele which leads to new phenotypes. • The source of genetic variability. • Need to be recombined • Rare; take long time to develop, can reduce fitness • (e.g.) Sickle cell anemia ...
Evolution - Canyon ISD
... Natural selection -acts on phenotypes not individuals. Evolution acts on populations not individuals. ...
... Natural selection -acts on phenotypes not individuals. Evolution acts on populations not individuals. ...
01 - greinerudsd
... can evolve. 2. Natural selection can act only on ______________________ variation that exists in a population. 3. ______________________ is the formation of new species as a result of evolution. 4. Changes in the genes of populations are known as ______________________, whereas speciation is part of ...
... can evolve. 2. Natural selection can act only on ______________________ variation that exists in a population. 3. ______________________ is the formation of new species as a result of evolution. 4. Changes in the genes of populations are known as ______________________, whereas speciation is part of ...
Biological ideas relating to genetic modification
... The characteristics of an organism produced by a particular genotype. ...
... The characteristics of an organism produced by a particular genotype. ...
Evolution and Genetic Engineering Keystone Vocabulary
... 24. Migration (Genetics) 25. Mutation 26. Natural Selection ...
... 24. Migration (Genetics) 25. Mutation 26. Natural Selection ...
Class Starter
... • Certain offspring may be born with a combination of genes that is more successful than his/her parents or siblings. • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
... • Certain offspring may be born with a combination of genes that is more successful than his/her parents or siblings. • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
Evolution by natural selection - BioGeoWiki-4ESO
... Example of natural selection leading to speciation. Can no longer ...
... Example of natural selection leading to speciation. Can no longer ...
Document
... A gas produced by cattle and paddy fields of rice, which causes the greenhouse effect more strongly than carbon dioxide. Mutation A random change in the base sequence of a gene which may lead to harmful or beneficial effects on the organism which carries it. These are essential as sources of variati ...
... A gas produced by cattle and paddy fields of rice, which causes the greenhouse effect more strongly than carbon dioxide. Mutation A random change in the base sequence of a gene which may lead to harmful or beneficial effects on the organism which carries it. These are essential as sources of variati ...
part - MOCKSTER.NET!
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
Mechanisms of Evolution part 2
... Macroevolution refers to the sum total of many changes that transform organisms over a long period of time. Macroevolution leads to speciation or the creation of a new species. When an evolving population can no longer interbreed with the original population, a new species is formed. ...
... Macroevolution refers to the sum total of many changes that transform organisms over a long period of time. Macroevolution leads to speciation or the creation of a new species. When an evolving population can no longer interbreed with the original population, a new species is formed. ...
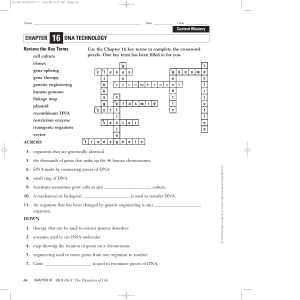
chapter dna technology - Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
Goal 3.05 Examine the Theory of Evolution by Natural
... CROPS like corn. It is a form of ASEXUAL reproduction. 12.Two advantages of producing transgenic plants:contain genes that produce: 1) natural insecticides, 2) resist weed killing chemicals, 3) resist rot & food spoilage, 4) may produce human antibodies. Another name for these plants is GENETICALLY ...
... CROPS like corn. It is a form of ASEXUAL reproduction. 12.Two advantages of producing transgenic plants:contain genes that produce: 1) natural insecticides, 2) resist weed killing chemicals, 3) resist rot & food spoilage, 4) may produce human antibodies. Another name for these plants is GENETICALLY ...