Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... 12. What is the most common cause for spinal cord injuries? a. Car crashes 13. In some reflex actions, skeletal muscles contract without the involvement of the ____________. a. Brain 14. When you feel thirsty, what body process is the nervous system helping to carry out? a. Maintaining Homeostasis ...
... 12. What is the most common cause for spinal cord injuries? a. Car crashes 13. In some reflex actions, skeletal muscles contract without the involvement of the ____________. a. Brain 14. When you feel thirsty, what body process is the nervous system helping to carry out? a. Maintaining Homeostasis ...
Human Body Systems
... our body - Ca helps our heart and muscles work - P helps our cells produce and store energy - When stored in our bones, Ca and P help make bones stronger ...
... our body - Ca helps our heart and muscles work - P helps our cells produce and store energy - When stored in our bones, Ca and P help make bones stronger ...
Body Systems Powerpoint Slideshow
... Bronchi – the two large passageways that lead from the trachea to your lungs (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles. Bronchioles lead to air sac clusters of alveoli. -- capillaries surrounding each alveolus is where the exchange of gases with the blood occurs The ...
... Bronchi – the two large passageways that lead from the trachea to your lungs (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles. Bronchioles lead to air sac clusters of alveoli. -- capillaries surrounding each alveolus is where the exchange of gases with the blood occurs The ...
Spastic cerebral palsy (spasticity) This is caused by impairment in
... leading to a decreased range of movement in the joints. The effects may increase with anxiety or increased effort, leading to excessive fatigue. Athetoid or dystonic, also known as dyskinetic cerebral palsy (athetosis) This is caused by impairment in the basal ganglia area of the brain. It is charac ...
... leading to a decreased range of movement in the joints. The effects may increase with anxiety or increased effort, leading to excessive fatigue. Athetoid or dystonic, also known as dyskinetic cerebral palsy (athetosis) This is caused by impairment in the basal ganglia area of the brain. It is charac ...
The Nervous System funtions and neuron
... Classification of the Neuron • Neurons of classified based on ...
... Classification of the Neuron • Neurons of classified based on ...
Substance Abuse Terminology (April 2014)
... of pain and other functions (e.g., morphine, heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone). Physical Dependence: An adaptive physiological state that occurs with regular drug use and results in a withdrawal syndrome when drug use is stopped; often occurs with tolerance. Physical dependence can happen with chronic ...
... of pain and other functions (e.g., morphine, heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone). Physical Dependence: An adaptive physiological state that occurs with regular drug use and results in a withdrawal syndrome when drug use is stopped; often occurs with tolerance. Physical dependence can happen with chronic ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... • The _________ ________ ___ __________ and function within the human body. • Though all cells ____________ ______ ____________ that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. • Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. Tissues: • A ________ ____ _____ ...
... • The _________ ________ ___ __________ and function within the human body. • Though all cells ____________ ______ ____________ that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. • Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. Tissues: • A ________ ____ _____ ...
notes Ch. 40 tissues
... Respiratory-gas exchange Reproductive-reproduction Skeletal-support; protection ...
... Respiratory-gas exchange Reproductive-reproduction Skeletal-support; protection ...
Neuroscience Insights on Radicalization and
... relatively new field not well studied; Neuroscience research is conducted in laboratories – not all findings are easily generalized to operational settings. Neuroscience has not been traditionally applied to national security. Neuroscience literature may not be easily accessible. ...
... relatively new field not well studied; Neuroscience research is conducted in laboratories – not all findings are easily generalized to operational settings. Neuroscience has not been traditionally applied to national security. Neuroscience literature may not be easily accessible. ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... Impulse sent to the CNS, sensory Sense of smell doesn’t pass through here Part of the CNS, provides 2-way communication Looks like a butterfly in the spinal cord ...
... Impulse sent to the CNS, sensory Sense of smell doesn’t pass through here Part of the CNS, provides 2-way communication Looks like a butterfly in the spinal cord ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System The nervous system coordinates the activities of all of the body’s organ systems so that they work in concert with one another What systems must cooperate during exercise? What do we use to respond to changes in the external environment? Do the senses operate individually? ...
... Nervous System The nervous system coordinates the activities of all of the body’s organ systems so that they work in concert with one another What systems must cooperate during exercise? What do we use to respond to changes in the external environment? Do the senses operate individually? ...
The Nervous System
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
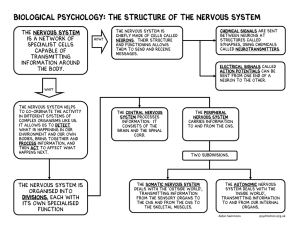
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... The nervous system helps to co-ordinate the activity in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and then ACT TO AFFECT WHAT HAPPENS NEXT. ...
... The nervous system helps to co-ordinate the activity in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and then ACT TO AFFECT WHAT HAPPENS NEXT. ...
The Nervous System
... heat, cold, pain, touch, and body position in space. The occipital lobe contains the sense of vision. The temporal lobe contains the senses of hearing and smell as well as memory, thought, and judgment. ...
... heat, cold, pain, touch, and body position in space. The occipital lobe contains the sense of vision. The temporal lobe contains the senses of hearing and smell as well as memory, thought, and judgment. ...
Human-Anatomy-Syllab..
... Lesson 1: The Skeletal System-Students will be introduced to the 206 bones of the body. They will learn their function in the body and be able to name and know the location of the major bones of the body. Lesson 2: The Muscular System-Students will be introduced to the major types of muscles in the ...
... Lesson 1: The Skeletal System-Students will be introduced to the 206 bones of the body. They will learn their function in the body and be able to name and know the location of the major bones of the body. Lesson 2: The Muscular System-Students will be introduced to the major types of muscles in the ...
best
... Which human body system performs these functions? A. skeletal B. digestive C. circulatory D. respiratory ...
... Which human body system performs these functions? A. skeletal B. digestive C. circulatory D. respiratory ...
Chapter 13 and 16
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
File
... one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its responsibilities. What does MS stand for and what is it? Multiple sclerosis – this is ...
... one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its responsibilities. What does MS stand for and what is it? Multiple sclerosis – this is ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in numbe ...
... function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in numbe ...
nervous system
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
B 11.A
... Central Nervous System The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord and relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information. ...
... Central Nervous System The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord and relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information. ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
... the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
Lecture in Linköping 23/9 Music, the Brain and Multimodal
... Are these principles important for how music can be used in multimodal communication? Let us discuss this for film music. 1. The principle of unification: Because of unification we know what to look for when we hear a sound. Sounds direct the gaze. The eye is looking for the sound source. And in doi ...
... Are these principles important for how music can be used in multimodal communication? Let us discuss this for film music. 1. The principle of unification: Because of unification we know what to look for when we hear a sound. Sounds direct the gaze. The eye is looking for the sound source. And in doi ...
7-3.2 Notes
... An organ of the central nervous system, which has three distinct parts that all serve to control and coordinate the activities of the body. The cerebrum controls thoughts, voluntary actions, and the sensations related to the five senses. The cerebellum helps with balance and coordination. The ...
... An organ of the central nervous system, which has three distinct parts that all serve to control and coordinate the activities of the body. The cerebrum controls thoughts, voluntary actions, and the sensations related to the five senses. The cerebellum helps with balance and coordination. The ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.