Slide 1
... There are many other variations of these and other systems • Whisker barrels in rodents (mechano) • Polarized light (vision: e.g. insects, fishes, turtles) • Mechano and chemo sensors on arthropods ...
... There are many other variations of these and other systems • Whisker barrels in rodents (mechano) • Polarized light (vision: e.g. insects, fishes, turtles) • Mechano and chemo sensors on arthropods ...
Course Expectations
... 2. The sensory organ provide the means for all interaction with the world around us Know: ...
... 2. The sensory organ provide the means for all interaction with the world around us Know: ...
Glossary of commonly used Occupational Therapy terms
... Fight-Or-Flight Response: The instinctive reaction to defend oneself from real or perceived danger by becoming aggressive or by withdrawing. Figure-Ground Perception: The ability to perceive a figure in the foreground from a rival background. Fine Motor: Referring to movement of the muscles in the f ...
... Fight-Or-Flight Response: The instinctive reaction to defend oneself from real or perceived danger by becoming aggressive or by withdrawing. Figure-Ground Perception: The ability to perceive a figure in the foreground from a rival background. Fine Motor: Referring to movement of the muscles in the f ...
Human Nerve Chapter
... respond to changes in the external environment. In vertebrates, these functions are controlled by two organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and exter ...
... respond to changes in the external environment. In vertebrates, these functions are controlled by two organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and exter ...
SNC2D BIOLOGY: ORGAN SYSTEMS WS#8
... Organs that function together form organ systems, such as the nervous system or the muscular system. Each organ system consists of a group of organs that work together to carry out specific duties in the body. Biologists categorize organ systems according to their main functions. There are 11 main o ...
... Organs that function together form organ systems, such as the nervous system or the muscular system. Each organ system consists of a group of organs that work together to carry out specific duties in the body. Biologists categorize organ systems according to their main functions. There are 11 main o ...
02.422-03.2 Functional Anatomy
... cleanses the body by carrying toxic materials to the kidneys and sweat glands for excretion. Digestive system – takes the food ingested and converts it into a form that can be used. Nervous system – essential for all of the systems to function properly, the movements and processes have to be con ...
... cleanses the body by carrying toxic materials to the kidneys and sweat glands for excretion. Digestive system – takes the food ingested and converts it into a form that can be used. Nervous system – essential for all of the systems to function properly, the movements and processes have to be con ...
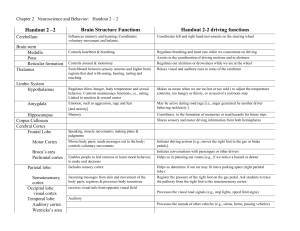
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Regulates thirst, hunger, body temperature and sexual behavior. Controls maintenance functions, i.e., eating; Linked to emotion & reward center ...
... Regulates thirst, hunger, body temperature and sexual behavior. Controls maintenance functions, i.e., eating; Linked to emotion & reward center ...
The Nervous System - AP Psychology-NWHS
... hemispheres (left and right), regulates most complex behaviors, cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness Thalamus: relays and translates incoming messages from the ...
... hemispheres (left and right), regulates most complex behaviors, cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness Thalamus: relays and translates incoming messages from the ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... A) Somatic nervous system – Conscious control of skeletal muscles B) Autonomic nervous system (ANS) e.g. Regulate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... A) Somatic nervous system – Conscious control of skeletal muscles B) Autonomic nervous system (ANS) e.g. Regulate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
Central nervous system
... •Myelin will get laid down in segments along the axon, leaving unmyelinated gaps known as “nodes of Ranvier” ...
... •Myelin will get laid down in segments along the axon, leaving unmyelinated gaps known as “nodes of Ranvier” ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology • Introduction to Physiology
... What is Human Physiology? • Physiology is the study of how normal body works to maintain life. • Physiology is an integrative discipline that utilizes biology, chemistry and physics to explain: • Functions of the human body • Mechanisms (physical and chemical processes) of these functions (cells, ti ...
... What is Human Physiology? • Physiology is the study of how normal body works to maintain life. • Physiology is an integrative discipline that utilizes biology, chemistry and physics to explain: • Functions of the human body • Mechanisms (physical and chemical processes) of these functions (cells, ti ...
Nervous System
... Your nervous system controls all of your body’s actions and functions. It senses changes not only within your body but also outside of it in your environment Enables you to respond within fractions of a second. ...
... Your nervous system controls all of your body’s actions and functions. It senses changes not only within your body but also outside of it in your environment Enables you to respond within fractions of a second. ...
psychology_midterm_review
... information relayed from the spinal cord regarding the position of various body parts and how they are moving. This middle area of the brain can also be used to relay information from the sense of touch, including pain or pressure which is affecting different portions of the body. The Thalamus: is l ...
... information relayed from the spinal cord regarding the position of various body parts and how they are moving. This middle area of the brain can also be used to relay information from the sense of touch, including pain or pressure which is affecting different portions of the body. The Thalamus: is l ...
Body Systems
... The blood contains nutrients from digestive system and the red blood cells carry the oxygen. Arteries move blood away from the heart. Blood pressure is highest in the veins which are small and lowest in the arteries which are larger. ...
... The blood contains nutrients from digestive system and the red blood cells carry the oxygen. Arteries move blood away from the heart. Blood pressure is highest in the veins which are small and lowest in the arteries which are larger. ...
FinalStudyGuide
... What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system? What do they “connect”? How do the divisions work together (synergistic or antagonistic?) What are the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system? What are the actions of the sympathetic nervous system? Be able to give names of bo ...
... What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system? What do they “connect”? How do the divisions work together (synergistic or antagonistic?) What are the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system? What are the actions of the sympathetic nervous system? Be able to give names of bo ...
document
... impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – Slow action, uses chemicals called HORMONES released into the blood. Changes by this system tend to be slow but long lasting. ...
... impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – Slow action, uses chemicals called HORMONES released into the blood. Changes by this system tend to be slow but long lasting. ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
Document
... • Bringing nutrients and water into the body and removal of wastes. • It is basically a long tube with some accessory organs that pump in enzymes to help break food down into smaller particles for assimilation into the blood. ...
... • Bringing nutrients and water into the body and removal of wastes. • It is basically a long tube with some accessory organs that pump in enzymes to help break food down into smaller particles for assimilation into the blood. ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... 1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. _____ 2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as the activation of skeletal muscles. ______ 3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves and ganglia. ____ 4. Subd ...
... 1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. _____ 2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as the activation of skeletal muscles. ______ 3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves and ganglia. ____ 4. Subd ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.