48 Nervous System PowerPoint
... eye, nervous system (neural tube), mouth and rectum Digestive tract lining, respiratory system lining, many organs Notochord, skeleton, muscles, circulatory systems, reproductive system, excretory system ...
... eye, nervous system (neural tube), mouth and rectum Digestive tract lining, respiratory system lining, many organs Notochord, skeleton, muscles, circulatory systems, reproductive system, excretory system ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
Detox - Wellness Trading Post
... Symptoms are usually felt in the first few days, and are due to the increase of circulating toxins in the body. The symptoms dissipate as the toxins are excreted from the body. ...
... Symptoms are usually felt in the first few days, and are due to the increase of circulating toxins in the body. The symptoms dissipate as the toxins are excreted from the body. ...
WAP 217 Introduction - Midlands State University
... Memory, learning, and conscious thought are a few aspects of the functions of the nervous system. Maintaining autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions are performed by some of the parts of this system. Endocrine System works with the nervous system to c ...
... Memory, learning, and conscious thought are a few aspects of the functions of the nervous system. Maintaining autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions are performed by some of the parts of this system. Endocrine System works with the nervous system to c ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... sensory to motor neuron C. Motor neuron: receives message (response) and tells effectors (muscles) what to do ...
... sensory to motor neuron C. Motor neuron: receives message (response) and tells effectors (muscles) what to do ...
Second exam study questions
... 3. What are the general pathways by which input from skin receptors gets carried to the cerebral cortex? What are dorsal root ganglia? How is skin sensory input organized in the cerebral cortex? 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are ...
... 3. What are the general pathways by which input from skin receptors gets carried to the cerebral cortex? What are dorsal root ganglia? How is skin sensory input organized in the cerebral cortex? 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
... Motor neurons – passes impulse to muscles or glands to respond to a stimulus, found attached to muscles or glands ...
... Motor neurons – passes impulse to muscles or glands to respond to a stimulus, found attached to muscles or glands ...
Chapter 13 - Nervous Tissue
... Most (99%) neurons in the body are multipolar. Bipolar neurons are rare and occur in special sense organs of ear, nose and eye. Unipolar neurons begin as bipolar but processes fuse into one. They are primarily sensory neurons. ...
... Most (99%) neurons in the body are multipolar. Bipolar neurons are rare and occur in special sense organs of ear, nose and eye. Unipolar neurons begin as bipolar but processes fuse into one. They are primarily sensory neurons. ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... Most (99%) neurons in the body are multipolar. Bipolar neurons are rare and occur in special sense organs of ear, nose and eye. Unipolar neurons begin as bipolar but processes fuse into one. They are primarily sensory neurons. ...
... Most (99%) neurons in the body are multipolar. Bipolar neurons are rare and occur in special sense organs of ear, nose and eye. Unipolar neurons begin as bipolar but processes fuse into one. They are primarily sensory neurons. ...
3cf1482f14bbaf7
... Descending Spinal Pathways extrapyramidal system - Coordination of head & eye movements, - Coordinated function of trunk & extremity musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
... Descending Spinal Pathways extrapyramidal system - Coordination of head & eye movements, - Coordinated function of trunk & extremity musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
The movement, the motor system, muscles and nervous – part 2
... Motor systems, including muscle function and nervous reflexes related to the movement ...
... Motor systems, including muscle function and nervous reflexes related to the movement ...
PowerPoint: Physiology Overview
... a. Students know how the complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. b. Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with ...
... a. Students know how the complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. b. Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
unit 1 notes
... • If deviation outside normal occurs, this feedback _____________________________. ...
... • If deviation outside normal occurs, this feedback _____________________________. ...
Chapter 29 Nervous and Endocrine System
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
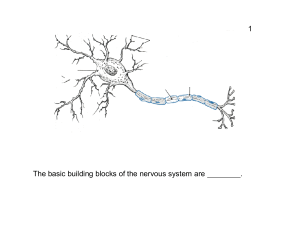
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... • Muscles are classified as being voluntary or involuntary – Voluntary muscles are those that can be contracted or relaxed at will – Involuntary muscles are regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems ...
... • Muscles are classified as being voluntary or involuntary – Voluntary muscles are those that can be contracted or relaxed at will – Involuntary muscles are regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems ...
Nervous System Part I Flashcards
... carries impulse FROM Central Nervous System (CNS) to muscle or gland ...
... carries impulse FROM Central Nervous System (CNS) to muscle or gland ...
True or False: Write “True” or “False”
... organized and represented in the brain. Marshall showed that even though the different systems carry different types of information and end up in different regions of the cerebral cortex, they share a common logic in their organization: all sensory information is organized topographically in the bra ...
... organized and represented in the brain. Marshall showed that even though the different systems carry different types of information and end up in different regions of the cerebral cortex, they share a common logic in their organization: all sensory information is organized topographically in the bra ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.