* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1 notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
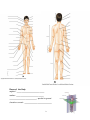
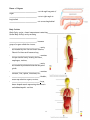
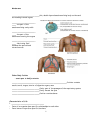
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology – Unit 1 So what will we study? 1. anatomy – ___________________________________________ 2. physiology – _________________________________________ The Body Plan anatomical position: ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ supine: ___________________________ prone: ___________________________ Body Orientation and Directional Terms Superior (cranial): toward the ___________________________ __________________________away from head, below Example: The forehead is ___________________________ to the nose. __________________________ toward the front, in front of Posterior (dorsal): toward the __________________________ Example: The heart is ___________________________to the sternum. Medial: toward the ___________________________ of the body, on the inner side ___________________________: away from the midline of the body, on the outer side ___________________________: between a more medial and a more lateral structure. Example: The eye is __________________________ to the bridge of the nose. 1 NOTE: USED FOR APPENDAGES ONLY!!! ___________________________: closer to the point of limb attachment ___________________________: farther from the point of limb attachment Example: The elbow is ___________________________to the wrist. ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________- belly ___________________________– back ___________________________– close to surface of body ___________________________ – toward interior of body ___________________________= shoulder to elbow ___________________________ = elbow to wrist ___________________________ = hip to knee ___________________________ = knee to ankle trunk ▫ ___________________________ ▫ ___________________________ ▫ ___________________________ ___________________________: making up the main axis of the body (head, neck, trunk) ___________________________: consisting of appendages or limbs 2 Planes of the Body sagittal – ___________________________ median – ___________________________ ___________________________– parallel to ground frontal or coronal – ___________________________ 3 Planes of Organs ___________________________: cut through long axis of organ ___________________________: cut at right angle to longitudinal ___________________________: cut across longitudinal Body Cavities Body Cavity: major, closed compartment containing ___________________________ Dorsal Body Cavity: cavity encasing ___________________________ ___________________________: houses a group of organs called the viscera. ▫ ___________________________: cavity surrounded by the ribs and chest muscles. Pleural Cavities: each houses a lung ▫ ___________________________: contains the pericardial cavity housing the heart, esophagus, trachea... ▫ ___________________________: cavity surrounded by abdominal muscles and pelvic girdle. ▫ ___________________________: contains stomach, liver, spleen, intestines, etc... ▫ ___________________________: bladder, some reproductive organs, rectum... ▫ ___________________________: large, dome-shaped muscle separating the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities. 4 Membranes ___________________________thin, double-layered membrane lining body cavities and surrounding internal organs. _______________________ ____: the part of the membrane lining cavity walls _______________________ ____: the part of the membrane covering the organs _______________________ ____: lubricating fluid between the parietal and visceral serosa Other Body Cavities – most open to body’s exterior ______________________________________________________Cavities: contains mouth, teeth, tongue, interior of digestive organs, anus ___________________________Cavity: part of the passages of the respiratory system ___________________________Cavity: houses the eyes ___________________________Cavities: contains bones Characteristics of Life 1. ________________________________ ▫ Parts of an organism have specific relationships to each other. ▫ Parts interact to perform specific functions. 5 ▫ Cell is basic structural and functional unit of an organism. levels of structural organization atoms ________________ _____________ organs ________________ ________________ ________________ 2. ________________________________ ▫ ability to use ___________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________ ▫ ability to ___________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________ ▫ increase in size or all or part of the organism 5. ________________________________ ▫ changes an organism undergoes over time ▫ ___________________________________________________ ▫ ___________________________________________________ 6. ________________________________ ▫ formation of new cells or organisms ▫ allows for growth and tissue repair 7. ________________________________ ▫ obtaining and using oxygen ▫ removal of toxic waste 8. ________________________________ ▫ 9. passage of digestive products through membranes ________________________________ ▫ movement of substances from place to place 10. ________________________________ 11. ▫ supplies cells with nutrients ▫ changes them to substances the body needs ________________________________ ▫ removal of wastes produced by body parts Maintenance of Life ________________________________ 1. __________________________ 6 Metabolic processes are carried out in water. 2. __________________________ 3. energy source source of vitamins, minerals that regulate vital chemical reactions _________________________ releases energy from food substances 4. _________________________ released from chemical reactions 5. __________________________ pressing or compressing action Homeostasis existence and maintenance of constant environment ▫ within the body variables: ▫ _________________________________________ __________ ▫ MUST be within normal value (set point); normal range ▫ Homeostasis is a dynamic condition in response to changing conditions. ▫ __________________________________ _______help control the internal environment, i.e. removing wastes, getting nutrients. Negative feedback system Any deviation from the set point is made smaller or resisted. • ______________________________________ • maintains variation within normal 1. __________________ – monitors value of variable 2. __________________– establishes set point around which variable is maintained 3. __________________ – can change value of variable 7 Positive feedback system • If deviation outside normal occurs, this feedback _____________________________. • __________________ • rare in healthy people Dehydration Mild to moderate causes: • ___________________________ • sleepiness or tiredness • ___________________________ • decreased urine output (8 hours or more w/out urination) • ___________________________ • muscle weakness • ___________________________ • • dizziness or lightheadedness Severe can cause: • ___________________________ • extreme fussiness or sleepiness in children • ___________________________ • very dry mouth, skin and mucous membranes • ___________________________ • little or no urination (urine will be dark yellow or amber) • ___________________________ • shriveled and dry skin that lacks elasticity • ___________________________ • low blood pressure • ___________________________ • fever • ______________________________________________________ 8 9