CHAPTER 13 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... B. Two parts of the nervous system 1. central nervous system = brain and spinal cord (CNS) ...
... B. Two parts of the nervous system 1. central nervous system = brain and spinal cord (CNS) ...
Slide ()
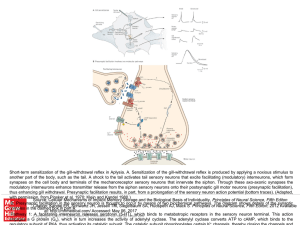
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
28.1_Responses
... nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example of one with a complex sensory system ...
... nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example of one with a complex sensory system ...
A.P. Psychology 4 (E)
... o The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts ...
... o The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts ...
Annexure `AAB-CD-01b` Course Title: ANATOMY AND
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... • Convey incoming messages toward cell body as graded potentials (short distance signals) ...
... • Convey incoming messages toward cell body as graded potentials (short distance signals) ...
Muscle Synergies for Motor Control
... recorded during reaching in different directions, with different speeds, and to targets whose location suddenly changes is captured by the linear combination of a small number of muscle synergies, coordinated recruitment of groups of muscles. These results suggest that muscle synergies are basic mod ...
... recorded during reaching in different directions, with different speeds, and to targets whose location suddenly changes is captured by the linear combination of a small number of muscle synergies, coordinated recruitment of groups of muscles. These results suggest that muscle synergies are basic mod ...
1 - U-System
... of temporal/parietal lobes (frontal eye fields may be involved) - vertical movements triggered bilaterally - unilateral cortical damage impairs horizontal pursuit movements in both directions, but impairment is greater when looking to ipsilateral side - pathway from cortex to abducens involves flocc ...
... of temporal/parietal lobes (frontal eye fields may be involved) - vertical movements triggered bilaterally - unilateral cortical damage impairs horizontal pursuit movements in both directions, but impairment is greater when looking to ipsilateral side - pathway from cortex to abducens involves flocc ...
Phylum Arthropods člán kono
... - muscle attached inside of the exosceleton - arthropodes moult when they grow because the exoskeleton won´t expand ...
... - muscle attached inside of the exosceleton - arthropodes moult when they grow because the exoskeleton won´t expand ...
File
... adjustments to occur (sweating or cardiovascular changes) - prepares the body for emergencies (fight/flight) 2. Parasympathetic System - returns body to normal after sympathetic response ...
... adjustments to occur (sweating or cardiovascular changes) - prepares the body for emergencies (fight/flight) 2. Parasympathetic System - returns body to normal after sympathetic response ...
11.4: The Peripheral Nervous System
... 1. (a) Answers may vary. Students should include the following: The somatic system is the mainly conscious and voluntary part of the nervous system that controls body movements and carries signals from the CNS to skeletal muscles. The somatic system consists of 31 sets of spinal nerves. The autonomi ...
... 1. (a) Answers may vary. Students should include the following: The somatic system is the mainly conscious and voluntary part of the nervous system that controls body movements and carries signals from the CNS to skeletal muscles. The somatic system consists of 31 sets of spinal nerves. The autonomi ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... What is the nervous system? It is a communication system that gathers information, interprets that information, and makes either conscious or ...
... What is the nervous system? It is a communication system that gathers information, interprets that information, and makes either conscious or ...
Bodyworks Test Review Things to know: Functions of body systems
... ___ 4. This pump works every minute of life. ___ 5. This moves food from the mouth into the stomach. ___ 6. This system helps our body absorb nutrients ___ 7. Air passes through these just before it reaches the lungs ___ 8. This system gives the body structure and protects organs ___ 9. This stretch ...
... ___ 4. This pump works every minute of life. ___ 5. This moves food from the mouth into the stomach. ___ 6. This system helps our body absorb nutrients ___ 7. Air passes through these just before it reaches the lungs ___ 8. This system gives the body structure and protects organs ___ 9. This stretch ...
Neuromuscular and Neurological Systems
... The base is as wide as the shoulder width Foot placement is accurate Walk is smooth, even and well-balanced Associated movements, such as arm swing, are present. ...
... The base is as wide as the shoulder width Foot placement is accurate Walk is smooth, even and well-balanced Associated movements, such as arm swing, are present. ...
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS FINAL PROJECT
... Rubric: Papers hand written will not be graded. All projects must be typed. All papers must be either emailed to yourself or saved to a thumb drive to be saved to the classroom desktop computer on February 24, 2017. If you are absent on this date the project must be emailed to your teacher in order ...
... Rubric: Papers hand written will not be graded. All projects must be typed. All papers must be either emailed to yourself or saved to a thumb drive to be saved to the classroom desktop computer on February 24, 2017. If you are absent on this date the project must be emailed to your teacher in order ...
human body systems final project
... Rubric: Papers hand written will not be graded. All projects must be typed. All papers must be either emailed to yourself or saved to a thumb drive to be saved to the classroom desktop computer on February 24, 2017. If you are absent on this date the project must be emailed to your teacher in order ...
... Rubric: Papers hand written will not be graded. All projects must be typed. All papers must be either emailed to yourself or saved to a thumb drive to be saved to the classroom desktop computer on February 24, 2017. If you are absent on this date the project must be emailed to your teacher in order ...
Reflexes
... -receptors are specialized muscle cells embedded within whole muscles: intrafusal muscle fibers -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron ending ...
... -receptors are specialized muscle cells embedded within whole muscles: intrafusal muscle fibers -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron ending ...
Homeostasis Review Definitions
... • A negative feedback system stops the response that the body had to being out of equilibrium. For example, when one goes from dehydrated to hydrated vasopressin causes the kidneys to absorb more water. Once the person is hydrated, negative feedback tells the hypothalamus to stop producing ...
... • A negative feedback system stops the response that the body had to being out of equilibrium. For example, when one goes from dehydrated to hydrated vasopressin causes the kidneys to absorb more water. Once the person is hydrated, negative feedback tells the hypothalamus to stop producing ...
CHAPTER 1 Lecture
... Homeostasis • The body communicates through neural and hormonal control systems • Control Mechanism: • The receptor responds to changes in the environment and sends information to the control center (brain). • The control center determines the set point (98.6) and determines the appropriate respons ...
... Homeostasis • The body communicates through neural and hormonal control systems • Control Mechanism: • The receptor responds to changes in the environment and sends information to the control center (brain). • The control center determines the set point (98.6) and determines the appropriate respons ...
The Nervous System - riverridge210.org
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
File
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...
Unit10 Nervous Wk 1
... works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and digest response) » Sympathetic nervous system works in actions that do require a fast response (fight or fight response) ...
... works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and digest response) » Sympathetic nervous system works in actions that do require a fast response (fight or fight response) ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
... and left portions. 2. A transverse section divides the body into superior and inferior portions. It is often called a “cross section”. 3. A coronal section divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. ...
... and left portions. 2. A transverse section divides the body into superior and inferior portions. It is often called a “cross section”. 3. A coronal section divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.