Sensation and Perception - Shannon Deets Counseling
... Transfer of Information through CNS • Coding translates the physical properties of a stimulus into neural activity • Sensory nerves transfer coded activity to the brain (Thalamus) • Coded information for all senses except smell goes to the Thalamus • Thalamus does some initial processing and sends ...
... Transfer of Information through CNS • Coding translates the physical properties of a stimulus into neural activity • Sensory nerves transfer coded activity to the brain (Thalamus) • Coded information for all senses except smell goes to the Thalamus • Thalamus does some initial processing and sends ...
Review
... o Purpose of clavicle Know the locations of the bones of the upper and lower extremities (ex. Humerus, radius, fibula, femur, etc.) Three bones of the pelvic girdle o Ilium, ishium, pubis o Purpose of pubic symphysis ...
... o Purpose of clavicle Know the locations of the bones of the upper and lower extremities (ex. Humerus, radius, fibula, femur, etc.) Three bones of the pelvic girdle o Ilium, ishium, pubis o Purpose of pubic symphysis ...
E4-D5-12
... Superior oblique eye muscle Muscles of mastication Lateral rectus eye muscle Muscles of facial ...
... Superior oblique eye muscle Muscles of mastication Lateral rectus eye muscle Muscles of facial ...
Document
... Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A Functions of the Nervous System 1.Sensory input • Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
... Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A Functions of the Nervous System 1.Sensory input • Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
... Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A Functions of the Nervous System 1.Sensory input • Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
... Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A Functions of the Nervous System 1.Sensory input • Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... Nervous System 5 Functions 1. Sensory function = receptors monitor external & internal body changes; providing input ...
... Nervous System 5 Functions 1. Sensory function = receptors monitor external & internal body changes; providing input ...
General Neurophysiology
... Two pairs of wings Each pair beat in synchrony but the rear wings lead the front wings in the beat cycle by about ...
... Two pairs of wings Each pair beat in synchrony but the rear wings lead the front wings in the beat cycle by about ...
The Human Body - Teacher Bulletin
... me in my mother’s womb. I will praise you because I am fearfully and wonderfully made. Wonderful are Your works. ...
... me in my mother’s womb. I will praise you because I am fearfully and wonderfully made. Wonderful are Your works. ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... force • Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system • In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… – Agonist muscle causing it to relax – Antagonist muscle causing it to contract ...
... force • Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system • In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… – Agonist muscle causing it to relax – Antagonist muscle causing it to contract ...
The Nervous System
... • The Nervous System controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and “responds” to internal and external stimuli – “Your nervous system is how your body communicates within itself and with the outside world” ...
... • The Nervous System controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and “responds” to internal and external stimuli – “Your nervous system is how your body communicates within itself and with the outside world” ...
nervous system power point
... Pain, Proprioception, Controls movement • Integrative function – that which goes on between reception of impulse and a response • Consciousness – state of awareness (coma, REM sleep, anesthesia, ASC), Memory (long term, short term) • Language – usually controlled by the left hemisphere • Emotions – ...
... Pain, Proprioception, Controls movement • Integrative function – that which goes on between reception of impulse and a response • Consciousness – state of awareness (coma, REM sleep, anesthesia, ASC), Memory (long term, short term) • Language – usually controlled by the left hemisphere • Emotions – ...
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
to view the powerpoint
... Quick facts about the muscular system: • Functions of this system include movement, protection, assistance of blood flow, produce heat, and stability/posture. • Three distinct types of muscles: Cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscles are connected to one another by intercalated disc wh ...
... Quick facts about the muscular system: • Functions of this system include movement, protection, assistance of blood flow, produce heat, and stability/posture. • Three distinct types of muscles: Cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscles are connected to one another by intercalated disc wh ...
Human Body
... defends people against germs and microorganisms every day. In most cases, the immune system does a great job of keeping people healthy and preventing infections. But sometimes problems with the immune system can lead to illness and infection. http://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystem s/immunesystem/ ...
... defends people against germs and microorganisms every day. In most cases, the immune system does a great job of keeping people healthy and preventing infections. But sometimes problems with the immune system can lead to illness and infection. http://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystem s/immunesystem/ ...
SC.6.L.14.5 PowerPoint on Human Body and Homeostasis
... defends people against germs and microorganisms every day. In most cases, the immune system does a great job of keeping people healthy and preventing infections. But sometimes problems with the immune system can lead to illness and infection. http://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystem s/immunesystem/ ...
... defends people against germs and microorganisms every day. In most cases, the immune system does a great job of keeping people healthy and preventing infections. But sometimes problems with the immune system can lead to illness and infection. http://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystem s/immunesystem/ ...
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
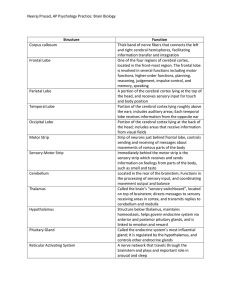
... the head, and receives sensory input for touch and body position Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes auditory areas; Each temporal lobe receives information from the opposite ear Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that recei ...
... the head, and receives sensory input for touch and body position Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes auditory areas; Each temporal lobe receives information from the opposite ear Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that recei ...
lec---20
... coordinates and controls actions of internal organs and body systems. Memory, learning, and conscious thought are the functions of the nervous system. Maintaining autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions. ...
... coordinates and controls actions of internal organs and body systems. Memory, learning, and conscious thought are the functions of the nervous system. Maintaining autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions. ...
File
... bilateral projections from the retina to the pretectum and projections from the pretectum to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. Neurons in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus terminate in the ciliary ganglion, and neurons in the ciliary ganglion innervate the pupillary constrictor muscles. Notice that the affer ...
... bilateral projections from the retina to the pretectum and projections from the pretectum to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. Neurons in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus terminate in the ciliary ganglion, and neurons in the ciliary ganglion innervate the pupillary constrictor muscles. Notice that the affer ...
Human Body Systems Study Guide
... out waste products from the blood. The kidney does this and then it is removed from the body as liquid waste. The reproductive system produces hormones that are carried throughout the body by the blood. These hormones help to regulate growth and development as well as maintain homeostasis. ...
... out waste products from the blood. The kidney does this and then it is removed from the body as liquid waste. The reproductive system produces hormones that are carried throughout the body by the blood. These hormones help to regulate growth and development as well as maintain homeostasis. ...
answerKey
... excretory system works with the circulatory system to help filter out waste products from the blood. The kidney does this and then it is removed from the body as liquid waste. The reproductive system produces hormones that are carried throughout the body by the blood. These hormones help to regulate ...
... excretory system works with the circulatory system to help filter out waste products from the blood. The kidney does this and then it is removed from the body as liquid waste. The reproductive system produces hormones that are carried throughout the body by the blood. These hormones help to regulate ...
The Nervous System
... – An axon terminal will abut another cell, a neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. – This is the site of the conversion of an electrical signal into a ...
... – An axon terminal will abut another cell, a neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. – This is the site of the conversion of an electrical signal into a ...
Chapter 48: Nervous Systems Overview: Command and Control
... • The brainstem consists of three parts: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain • The medulla oblongata contains centers that control several visceral functions • The pons also participates in visceral functions • The midbrain contains centers for the receipt and integration of several ty ...
... • The brainstem consists of three parts: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain • The medulla oblongata contains centers that control several visceral functions • The pons also participates in visceral functions • The midbrain contains centers for the receipt and integration of several ty ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.