Radiology (Medical Imaging)
... This involves treatment by ionising radiations produced by superficial and deep X-ray machines, linear accelerators, betatrons and so on, or ionising radiations produced spontaneously by radium, radio-cobalt, radio-phosphorus, radio-iodine and other radioactive isotopes. This type of therapy is comm ...
... This involves treatment by ionising radiations produced by superficial and deep X-ray machines, linear accelerators, betatrons and so on, or ionising radiations produced spontaneously by radium, radio-cobalt, radio-phosphorus, radio-iodine and other radioactive isotopes. This type of therapy is comm ...
What do these food items have in common?
... • The radiation breaks down the chemical bonds found within the DNA of the food material and any contaminating microbes or insects. • Contaminating organisms are not able to repair DNA and reproduce. ...
... • The radiation breaks down the chemical bonds found within the DNA of the food material and any contaminating microbes or insects. • Contaminating organisms are not able to repair DNA and reproduce. ...
Introduction to Radiation and Radioactivity
... – Of course. Many of the elements found in everyday items include radioactive isotopes. – Concern is about radioactivity over and above what occurs naturally; a question of amount, not presence. ...
... – Of course. Many of the elements found in everyday items include radioactive isotopes. – Concern is about radioactivity over and above what occurs naturally; a question of amount, not presence. ...
Health Effects of Radiation
... of lead can stop penetration of medical x-rays. How can alpha particles affect people’s health? The health effects of alpha particles depend heavily upon how exposure takes place. External exposure (external to the body) is of far less concern than internal exposure, because alpha particles lack the ...
... of lead can stop penetration of medical x-rays. How can alpha particles affect people’s health? The health effects of alpha particles depend heavily upon how exposure takes place. External exposure (external to the body) is of far less concern than internal exposure, because alpha particles lack the ...
Document
... Nuclear Chemistry: the study of nuclear reactions Learning goals and key skills: Write balanced nuclear equations Know the difference between fission and fusion Predict nuclear stability in terms of neutron-to-proton ratio Calculate ages of objects or amounts of materials from data on nuclea ...
... Nuclear Chemistry: the study of nuclear reactions Learning goals and key skills: Write balanced nuclear equations Know the difference between fission and fusion Predict nuclear stability in terms of neutron-to-proton ratio Calculate ages of objects or amounts of materials from data on nuclea ...
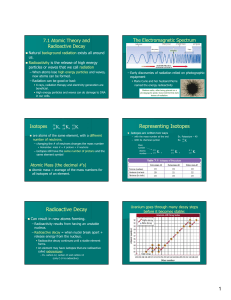
Radioactivity
... whatever you like to it - and you won't affect the rate of decay in the slightest. ...
... whatever you like to it - and you won't affect the rate of decay in the slightest. ...
1412-PracticeExam4
... Carbon-11 is a radioactive isotope of carbon. Its half-life is 20.3 minutes. What fraction of the initial number of carbon-11 atoms in a sample will remain after 81 minutes? ...
... Carbon-11 is a radioactive isotope of carbon. Its half-life is 20.3 minutes. What fraction of the initial number of carbon-11 atoms in a sample will remain after 81 minutes? ...
Powerpoint Slides
... – Differentiate between fusion and fission – Describe the processes involved in radioactive decays (alpha, beta, and gamma) ...
... – Differentiate between fusion and fission – Describe the processes involved in radioactive decays (alpha, beta, and gamma) ...
AP Exam Questions: Nuclear
... A beta particle, , or electron, has a single negative charge and is attracted to the positive side of the electric field, but since it is much lighter and faster than an alpha it would not be as strongly deflected. Gamma, , rays are not charged and, therefore, not deflected by the electric field. ...
... A beta particle, , or electron, has a single negative charge and is attracted to the positive side of the electric field, but since it is much lighter and faster than an alpha it would not be as strongly deflected. Gamma, , rays are not charged and, therefore, not deflected by the electric field. ...
Nuclear - PEO Scarborough Chapter
... FIGURE 1: ALPHA DECAY OF A URANIUM-238 NUCLEUS In beta decay, a neutron is converted into a proton and a high velocity electron is ejected to attain atomic stability. There are two types of beta decay: 1. Positive - release of positively charged particle called positron and neutrino 2. Negative - re ...
... FIGURE 1: ALPHA DECAY OF A URANIUM-238 NUCLEUS In beta decay, a neutron is converted into a proton and a high velocity electron is ejected to attain atomic stability. There are two types of beta decay: 1. Positive - release of positively charged particle called positron and neutrino 2. Negative - re ...
Radioactivity & Medicine II
... Background Image courtesy of Dr. Bill Moore, Dept. of Radiology, Stony Brook Hospital ...
... Background Image courtesy of Dr. Bill Moore, Dept. of Radiology, Stony Brook Hospital ...
Nuc Chem PP - Liberty Union High School District
... energy that is released. • Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves. • They have no mass. • Gamma radiation has no charge. – Most Penetrating, can be stopped by 1m thick concrete or a several cm thick sheet of lead. ...
... energy that is released. • Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves. • They have no mass. • Gamma radiation has no charge. – Most Penetrating, can be stopped by 1m thick concrete or a several cm thick sheet of lead. ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost always accompany alpha and beta radiation. • X rays are a form of high-energy electr ...
... • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost always accompany alpha and beta radiation. • X rays are a form of high-energy electr ...
CARESTREAM OnSight 3D Extremity System
... A CT scan for arms and legs Allows for weight bearing examination Installed at preferred location ...
... A CT scan for arms and legs Allows for weight bearing examination Installed at preferred location ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
1 0 +1 0 - davis.k12.ut.us
... 9. There are some elements within the periodic table that do not occur in nature, can you list a few? Technetium, neptunium, elements 93 and up… 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? Bombarding an atom with a neutron or alpha particle. 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .6 ...
... 9. There are some elements within the periodic table that do not occur in nature, can you list a few? Technetium, neptunium, elements 93 and up… 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? Bombarding an atom with a neutron or alpha particle. 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .6 ...
Average Atomic Mass
... one element changing into an atom of another element. These reactions, which involve a change in an atom’s nucleus, are called nuclear reactions. ...
... one element changing into an atom of another element. These reactions, which involve a change in an atom’s nucleus, are called nuclear reactions. ...
Document
... - no change of A or Z (element) - release of photon - usually occurs in conjunction with other decay ...
... - no change of A or Z (element) - release of photon - usually occurs in conjunction with other decay ...
Chapter 16 Notes - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... F. Producing radioactive isotopes. 1. Commonly, technetium-99m is used as a gamma emitter because it has a short half-life. 2. Radioisotopes can be made by a process named transmutation, where a stable nucleus is bombarded by a high-speed particle, such as alpha particles, protons, neutrons and oth ...
... F. Producing radioactive isotopes. 1. Commonly, technetium-99m is used as a gamma emitter because it has a short half-life. 2. Radioisotopes can be made by a process named transmutation, where a stable nucleus is bombarded by a high-speed particle, such as alpha particles, protons, neutrons and oth ...
clinical applications of spect with special reference to oncology
... used in nuclear medicine since the early 1960’s when Kuhl and Edwards developed a rectilinear scanning system for use in neuronuclear medicine. Tomography is now used extensi vely for diagnosis by ultrasound, x-ray CT scanning and magnetic resonance imaging. The improvement in quality of the images ...
... used in nuclear medicine since the early 1960’s when Kuhl and Edwards developed a rectilinear scanning system for use in neuronuclear medicine. Tomography is now used extensi vely for diagnosis by ultrasound, x-ray CT scanning and magnetic resonance imaging. The improvement in quality of the images ...
HSC Physics 9.6 Medical Physics Example Questions
... Answers could include: To be medically useful, radioactive isotopes must have a half-life that is long enough to allow them to accumulate in the target organ, so that an image can be produced, yet short enough so that the exposure of the person to radioactivity is minimised to reduce harm to the pat ...
... Answers could include: To be medically useful, radioactive isotopes must have a half-life that is long enough to allow them to accumulate in the target organ, so that an image can be produced, yet short enough so that the exposure of the person to radioactivity is minimised to reduce harm to the pat ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
Technetium-99m

Technetium-99m is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope.Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 140 keV gamma rays (these 8.8pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The ""short"" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the isotope suitable only for diagnostic but never therapeutic use.Technetium-99m was discovered as a product of cyclotron bombardment of molybdenum. This procedure produced molybdenum-99, a radionuclide with a longer half-life (2.75 days), which decays to Tc-99m. At present, molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) is used commercially as the easily transportable source of medically used Tc-99m. In turn, this Mo-99 is usually created commercially by fission of highly enriched uranium in aging research and material testing nuclear reactors in several countries.