Summative Assessment Review!
... material has enough mass to sustain a chain reaction. This amount is called the critical mass. • Nuclear Fission is what occurs in Nuclear Reactors and Atomic Bombs. • The Nuclear reactor is a controlled fission reaction, the bomb is not. ...
... material has enough mass to sustain a chain reaction. This amount is called the critical mass. • Nuclear Fission is what occurs in Nuclear Reactors and Atomic Bombs. • The Nuclear reactor is a controlled fission reaction, the bomb is not. ...
Topic 6 – Benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive materials
... (alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays) – this is a random process o As unstable nuclei emit ionising radiation, they lose (release) energy and decay to become more stable The ‘activity’ of any radioactive substance is the number of nuclear decays (i.e the number of unstable nuclei that emi ...
... (alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays) – this is a random process o As unstable nuclei emit ionising radiation, they lose (release) energy and decay to become more stable The ‘activity’ of any radioactive substance is the number of nuclear decays (i.e the number of unstable nuclei that emi ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... necessary for one-half of the radioactive material to decay. For example, the radioactive element bismuth (210Bi) can undergo alpha decay to form the element thallium (206Tl) with a reaction half-life equal to five days. • If we begin an experiment starting with 100 g of bismuth in a sealed lead con ...
... necessary for one-half of the radioactive material to decay. For example, the radioactive element bismuth (210Bi) can undergo alpha decay to form the element thallium (206Tl) with a reaction half-life equal to five days. • If we begin an experiment starting with 100 g of bismuth in a sealed lead con ...
DIAGNOSTIC PERFORMANCE OF LOW-DOSE ATTENUATION-CORRECTED REST/STRESS Tc-99m TETROFOSMIN
... DNM 530c SPECT to conventional SPECT, some patients with breast attenuation noted in the anterior wall on conventional SPECT had no loss of counts on D530c SPECT. Instead some of these patients had a mild count loss in the inferior wall.1 Attenuation correction may be performed on the DNM 530c by re ...
... DNM 530c SPECT to conventional SPECT, some patients with breast attenuation noted in the anterior wall on conventional SPECT had no loss of counts on D530c SPECT. Instead some of these patients had a mild count loss in the inferior wall.1 Attenuation correction may be performed on the DNM 530c by re ...
Radioactivity Notes Day 1 and 2 Apr 23 and Apr 24
... Radioactivity and Its History • Radiation is everywhere, but can be difficult to detect. ...
... Radioactivity and Its History • Radiation is everywhere, but can be difficult to detect. ...
Radiation Questions March 4th
... (a) A radiation detector and counter were used to detect and measure the radiation emitted from a weak source. The graph shows how the number of counts recorded in one minute changed with time. ...
... (a) A radiation detector and counter were used to detect and measure the radiation emitted from a weak source. The graph shows how the number of counts recorded in one minute changed with time. ...
AP Chem
... 11. The iodine that enters the body is stored in the thyroid gland from which it is released to control growth and metabolism. The thyroid can be imaged if iodine-131 is injected into the body. In larger doses I-131 is also used as a means of treating cancer of the thyroid. I-131 has a half-life of ...
... 11. The iodine that enters the body is stored in the thyroid gland from which it is released to control growth and metabolism. The thyroid can be imaged if iodine-131 is injected into the body. In larger doses I-131 is also used as a means of treating cancer of the thyroid. I-131 has a half-life of ...
atomic number = ZE = Element symbol
... decays to produce a proton and an electron. In this case, the parent and daughter are of different elements but the mass remains the same. ...
... decays to produce a proton and an electron. In this case, the parent and daughter are of different elements but the mass remains the same. ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... The decay reaction and T½ of a substance are specific to the isotope of the element undergoing radioactive decay. For example, Bi210 can undergo decay to Tl206 with a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of ...
... The decay reaction and T½ of a substance are specific to the isotope of the element undergoing radioactive decay. For example, Bi210 can undergo decay to Tl206 with a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • Example: Beta decay process is the decay of iodine- 131 into xenon131 by beta-particle emission • The mass number of the product nucleus is the same as that of the original nucleus ( they are both 131), but its atomic number has increased by 1 (54 instead of 53). This changed in atomic number, and ...
... • Example: Beta decay process is the decay of iodine- 131 into xenon131 by beta-particle emission • The mass number of the product nucleus is the same as that of the original nucleus ( they are both 131), but its atomic number has increased by 1 (54 instead of 53). This changed in atomic number, and ...
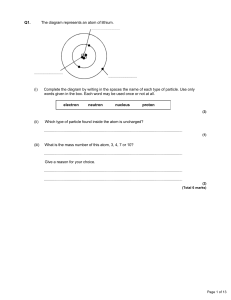
Revision of Atomic Structure and Nuclide Notations Nuclide
... number can vary depending on how many neutrons there are. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...
... number can vary depending on how many neutrons there are. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...
Half-life and Radioactive Decay guided notes
... takes for the amount of radioactive material to decrease from 1.0 to 0.5 is the same as the amount of time it takes to decrease from 0.25 to 0.125. This time interval, marked as t½ on the graph, represents the half-life of this radioactive substance and is independent of the amount of radioactive su ...
... takes for the amount of radioactive material to decrease from 1.0 to 0.5 is the same as the amount of time it takes to decrease from 0.25 to 0.125. This time interval, marked as t½ on the graph, represents the half-life of this radioactive substance and is independent of the amount of radioactive su ...
Chapter 25 – Types of Radiation 1. Alpha Radiation Alpha decay
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
File
... dedicated to the compounding and dispensing radiopharmaceuticals for use in nuclear medicine procedures. ...
... dedicated to the compounding and dispensing radiopharmaceuticals for use in nuclear medicine procedures. ...
nuclear radiation
... transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that was discovered later is called: ...
... transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that was discovered later is called: ...
SPECT/CT Preparation
... A Nuclear Medicine SPECT/CT Scan provides your doctor information about your body that is not available with other imaging methods such as x-ray, CT, or MRI. ...
... A Nuclear Medicine SPECT/CT Scan provides your doctor information about your body that is not available with other imaging methods such as x-ray, CT, or MRI. ...
Single-proton emission computed tomography (SPECT) differs from
... Sharon White, PhD University of Alabama-Birmingham, Birmingham, AL ...
... Sharon White, PhD University of Alabama-Birmingham, Birmingham, AL ...
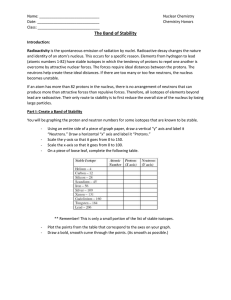
The Band of Stability
... produce more than attractive forces than repulsive forces. Therefore, all isotopes of elements beyond lead are radioactive. Their only route to stability is to first reduce the overall size of the nucleus by losing large particles. Part I: Create a Band of Stability You will be graphing the proton a ...
... produce more than attractive forces than repulsive forces. Therefore, all isotopes of elements beyond lead are radioactive. Their only route to stability is to first reduce the overall size of the nucleus by losing large particles. Part I: Create a Band of Stability You will be graphing the proton a ...
PowerPoint - Institute of Particle and Nuclear Physics
... the heart in systole. The use of two x-ray units makes possible the use of dual energy imaging, which allows an estimate of the average atomic number in a voxel, as well as the total attenutaion. This permits automatic differentiation of calcium (e.g. in bone, or diseased arteries) from iodine (in c ...
... the heart in systole. The use of two x-ray units makes possible the use of dual energy imaging, which allows an estimate of the average atomic number in a voxel, as well as the total attenutaion. This permits automatic differentiation of calcium (e.g. in bone, or diseased arteries) from iodine (in c ...
nuclear chemistry
... Most nuclei are stable. Radionuclides are unstable and spontaneously emit particles and/or electromagnetic radiation U-238 is radioactive o It emits alpha particles(Helium-4 particles) When a nucleus decomposes in this manner, we say it has decayed In nuclear equations, the total number of n ...
... Most nuclei are stable. Radionuclides are unstable and spontaneously emit particles and/or electromagnetic radiation U-238 is radioactive o It emits alpha particles(Helium-4 particles) When a nucleus decomposes in this manner, we say it has decayed In nuclear equations, the total number of n ...
Year 11 PHYSICS revision notes
... Universe began 10-20 billion years ago at a single point that was infinitely hot & dense. As it cooled down, energy turned into matter, forming particles which began to clump together. Since then, space has been expanding, pushing galaxies further apart (redshift). In the future, the universe could: ...
... Universe began 10-20 billion years ago at a single point that was infinitely hot & dense. As it cooled down, energy turned into matter, forming particles which began to clump together. Since then, space has been expanding, pushing galaxies further apart (redshift). In the future, the universe could: ...
3rd year - Module MPY301
... crystal, and is improved with larger hole sizes and smaller length septa. Sensitivity is independent of distance from the collimator face. Therefore resolution and sensitivity are conflicting parameters and different collimators need to be available , the choice of which to use depending on which pa ...
... crystal, and is improved with larger hole sizes and smaller length septa. Sensitivity is independent of distance from the collimator face. Therefore resolution and sensitivity are conflicting parameters and different collimators need to be available , the choice of which to use depending on which pa ...
Technetium-99m

Technetium-99m is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope.Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 140 keV gamma rays (these 8.8pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The ""short"" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the isotope suitable only for diagnostic but never therapeutic use.Technetium-99m was discovered as a product of cyclotron bombardment of molybdenum. This procedure produced molybdenum-99, a radionuclide with a longer half-life (2.75 days), which decays to Tc-99m. At present, molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) is used commercially as the easily transportable source of medically used Tc-99m. In turn, this Mo-99 is usually created commercially by fission of highly enriched uranium in aging research and material testing nuclear reactors in several countries.