Unit #12: Nuclear Chemistry
... Artificial Nuclear Reactions New elements or new isotopes of known elements are produced by bombarding an atom with a subatomic particle such as a proton or neutron -or even a much heavier particle such as 4He and 11B. Reactions using neutrons are called ...
... Artificial Nuclear Reactions New elements or new isotopes of known elements are produced by bombarding an atom with a subatomic particle such as a proton or neutron -or even a much heavier particle such as 4He and 11B. Reactions using neutrons are called ...
Foldable - Georgetown ISD
... Nuclear Reactions (*produce far more energy compared to chemical): ...
... Nuclear Reactions (*produce far more energy compared to chemical): ...
Chapter 1
... Cancer Therapy Using Radiation • Based on the fact that high-energy gamma rays cause damage to biological molecules • Tumor cells are more susceptible than normal cells • Example: cobalt-60 • Gamma radiation can cure cancer, but can also cause cancer ...
... Cancer Therapy Using Radiation • Based on the fact that high-energy gamma rays cause damage to biological molecules • Tumor cells are more susceptible than normal cells • Example: cobalt-60 • Gamma radiation can cure cancer, but can also cause cancer ...
By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic
... Carbon-14 has a half-life of approximately 5,700 years. Analysis of the carbon in a piece of charred wood found in an excavation revealed that the carbon has 25 percent of the amount of carbon-14 that is found in the carbon of living trees. Which of the following is most nearly the age of the excava ...
... Carbon-14 has a half-life of approximately 5,700 years. Analysis of the carbon in a piece of charred wood found in an excavation revealed that the carbon has 25 percent of the amount of carbon-14 that is found in the carbon of living trees. Which of the following is most nearly the age of the excava ...
12 · Nuclear Chemistry
... Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many neutrons in hydrogen-1? ...
... Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many neutrons in hydrogen-1? ...
Nuclear Medicine for Diagnosis and Treatment
... a short distance in the body, thereby minimizing unwanted side effects and damage to other organs or nearby structures. Ensuring safety when using nuclear medicine Apprehensions about radiation exposure are common among the general public, but nuclear medicine procedures are safe. Moreover, these pr ...
... a short distance in the body, thereby minimizing unwanted side effects and damage to other organs or nearby structures. Ensuring safety when using nuclear medicine Apprehensions about radiation exposure are common among the general public, but nuclear medicine procedures are safe. Moreover, these pr ...
Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic
... 7. Potassium-42 has a half-life of 12.4 hours. How much of an 848 g sample of potassium-42 will be left after 62.0 hours? 8. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 y. How much of a 144 g sample of carbon-14 will remain after 1.719 x 104 y? 9. If the half-life of uranium-235 is 7.04 x 108 y and 12.5 ...
... 7. Potassium-42 has a half-life of 12.4 hours. How much of an 848 g sample of potassium-42 will be left after 62.0 hours? 8. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 y. How much of a 144 g sample of carbon-14 will remain after 1.719 x 104 y? 9. If the half-life of uranium-235 is 7.04 x 108 y and 12.5 ...
Concept Lecture Outline – Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... b. Either 2 or 3 neutrons are also produced with the products. c. These neutrons act as "bullets" to ram into other unstable nuclei and split them, resulting in a chain reaction. d. All nuclear reactors in the world are fission reactors. 1) They cannot "blow up" like an atom bomb. 2) They produce ra ...
... b. Either 2 or 3 neutrons are also produced with the products. c. These neutrons act as "bullets" to ram into other unstable nuclei and split them, resulting in a chain reaction. d. All nuclear reactors in the world are fission reactors. 1) They cannot "blow up" like an atom bomb. 2) They produce ra ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Radioactivity
... • When an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy • When these particles are emitted, the element changes to another isotope or to a different element • Nuclear radiation refers to radiation resulting from nuclear changes ...
... • When an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy • When these particles are emitted, the element changes to another isotope or to a different element • Nuclear radiation refers to radiation resulting from nuclear changes ...
nuclear powperpoint
... give off rays and particles. • Radiation – penetrating rays and particles emitted by a radioactive substance. • Radioisotopes – unstable nuclei ...
... give off rays and particles. • Radiation – penetrating rays and particles emitted by a radioactive substance. • Radioisotopes – unstable nuclei ...
Nuclear Chemistry - VCC Library
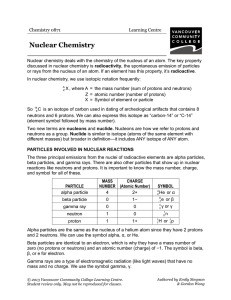
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
Review of Nuclear Chemistry
... How does the enriching process for uranium work? What technique is used? What is the starting material and what is achieved in the process? What are the aftereffects of Chernobyl? What are some of the benefits of nuclear chemistry and what are some of the drawbacks? How do breeder reactors work? Why ...
... How does the enriching process for uranium work? What technique is used? What is the starting material and what is achieved in the process? What are the aftereffects of Chernobyl? What are some of the benefits of nuclear chemistry and what are some of the drawbacks? How do breeder reactors work? Why ...
MAIN SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS Maximum number of slices 160
... to acquire dynamic volume data in whole-brain perfusion studies*. The analysis software performs 3D perfusion processing and 3D CT DSA using the same scan data. ...
... to acquire dynamic volume data in whole-brain perfusion studies*. The analysis software performs 3D perfusion processing and 3D CT DSA using the same scan data. ...
Medical Imaging and You
... internal pictures to help identify what’s wrong. Imaging tests can use simple x-rays or more complex techniques. ...
... internal pictures to help identify what’s wrong. Imaging tests can use simple x-rays or more complex techniques. ...
Chapter 10
... 10.8 Measurement of Radiation 11 Nuclear Imaging • Isotope is administered. • Isotope begins to concentrate in the organ. • Photographs (nuclear images) are taken at ...
... 10.8 Measurement of Radiation 11 Nuclear Imaging • Isotope is administered. • Isotope begins to concentrate in the organ. • Photographs (nuclear images) are taken at ...
Positron Emission Tomography - PET
... • For a lytic lesion to be visualized by radiography localized demineralization of 30-50% must occur • Bone scans usually demonstrate metastatic lesions much earlier than radiography • False negative bone scan: ...
... • For a lytic lesion to be visualized by radiography localized demineralization of 30-50% must occur • Bone scans usually demonstrate metastatic lesions much earlier than radiography • False negative bone scan: ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
radioactivity-ppt
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
Radioactivity
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
Positron Emission Tomography - PET
... image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy ...
... image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy ...
Technetium-99m

Technetium-99m is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope.Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 140 keV gamma rays (these 8.8pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The ""short"" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the isotope suitable only for diagnostic but never therapeutic use.Technetium-99m was discovered as a product of cyclotron bombardment of molybdenum. This procedure produced molybdenum-99, a radionuclide with a longer half-life (2.75 days), which decays to Tc-99m. At present, molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) is used commercially as the easily transportable source of medically used Tc-99m. In turn, this Mo-99 is usually created commercially by fission of highly enriched uranium in aging research and material testing nuclear reactors in several countries.