Gamma-ray imaging in medicine
... (for example, the total X-ray attenuation along each line through a slice of the body). Then image reconstruction is used to determine the contribution (eg attenuation coefficient) at each point within the slice. The line is specified by its angle θ and its offset x′. In terms of the (x,y) coordinat ...
... (for example, the total X-ray attenuation along each line through a slice of the body). Then image reconstruction is used to determine the contribution (eg attenuation coefficient) at each point within the slice. The line is specified by its angle θ and its offset x′. In terms of the (x,y) coordinat ...
Chapter 19 Radioactive Material An Isotope is an element with a
... 5. Electron Capture: when one of the inner orbital electrons is pulled into the nucleus. Causes no change in mass number but a decrease in the atomic number. Does not happen very often. Particle -‐1 ...
... 5. Electron Capture: when one of the inner orbital electrons is pulled into the nucleus. Causes no change in mass number but a decrease in the atomic number. Does not happen very often. Particle -‐1 ...
Radioactivity & Medicine I
... • Gamma ray detectors surround the patient and detect the coincident gamma rays. • These detected gamma rays give spatial information about the active metabolic site. ...
... • Gamma ray detectors surround the patient and detect the coincident gamma rays. • These detected gamma rays give spatial information about the active metabolic site. ...
AP Chem
... (A) Alpha particles < gamma rays < beta particles (B) Alpha particles < beta particles < gamma rays (C) Beta particles < alpha particles < gamma rays (D) Beta particles < gamma rays < alpha particles (E) Gamma rays < alpha particles < beta particles ...
... (A) Alpha particles < gamma rays < beta particles (B) Alpha particles < beta particles < gamma rays (C) Beta particles < alpha particles < gamma rays (D) Beta particles < gamma rays < alpha particles (E) Gamma rays < alpha particles < beta particles ...
Alpha decay
... element all have the same number of protons Atoms of the same element may have different neutrons and therefore mass numbers (p+ + n0) ...
... element all have the same number of protons Atoms of the same element may have different neutrons and therefore mass numbers (p+ + n0) ...
What is “Radiation”?
... Stopped by a layer of clothing or less than an inch of a substance (e.g. plastic) ...
... Stopped by a layer of clothing or less than an inch of a substance (e.g. plastic) ...
TERM 2 Unit 3 YR 9 SCI It is elementary
... reaction, and are able to list and describe the possible changes that can be observed during a chemical reaction. Students will be able to use the particle theory of matter to explain what is happening during a chemical reaction, and relate this to the Law of conservation of matter. They identify th ...
... reaction, and are able to list and describe the possible changes that can be observed during a chemical reaction. Students will be able to use the particle theory of matter to explain what is happening during a chemical reaction, and relate this to the Law of conservation of matter. They identify th ...
nuclear force
... release of gamma rays alone do not affect the identity of the atom since they have no mass and no charge. But, gamma radiation may be released along with release of an alpha or beta particle. Beta Particle ...
... release of gamma rays alone do not affect the identity of the atom since they have no mass and no charge. But, gamma radiation may be released along with release of an alpha or beta particle. Beta Particle ...
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity
... It was found that magnetic field splits the radiation from radioactive materials into 3 parts. Alpha () particles positively charged Beta () particles negatively charged electrons Gamma () particles (rays) no charge - decay: the nucleus composition does not change. -decay occurs in larg ...
... It was found that magnetic field splits the radiation from radioactive materials into 3 parts. Alpha () particles positively charged Beta () particles negatively charged electrons Gamma () particles (rays) no charge - decay: the nucleus composition does not change. -decay occurs in larg ...
particle - Uplift North Hills
... ionized an atom requires about 10 eV, so each particle can ionize 105 atoms before they have run out of energy. When radiation ionizes atoms that are part of a living cell, it can effect the ability of the cell to carry out its function or even cause the cell wall to be ruptured. If a large number o ...
... ionized an atom requires about 10 eV, so each particle can ionize 105 atoms before they have run out of energy. When radiation ionizes atoms that are part of a living cell, it can effect the ability of the cell to carry out its function or even cause the cell wall to be ruptured. If a large number o ...
Chapter 9
... GAMMA RADIATION In gamma radiation, • energy is emitted from an unstable nucleus, indicated by m following the mass number. • the mass number and the atomic number of the new nucleus are the same. 99mTc ...
... GAMMA RADIATION In gamma radiation, • energy is emitted from an unstable nucleus, indicated by m following the mass number. • the mass number and the atomic number of the new nucleus are the same. 99mTc ...
Glossary of Technical Terms - Institute for Energy and Environmental
... fission product Any isotope created by the fission of a heavy element. Fission products are usually radioactive. fission The splitting of the nucleus of an element into fragments. Heavy elements such as uranium or plutonium release energy when fissioned. fissile material A material consisting of ato ...
... fission product Any isotope created by the fission of a heavy element. Fission products are usually radioactive. fission The splitting of the nucleus of an element into fragments. Heavy elements such as uranium or plutonium release energy when fissioned. fissile material A material consisting of ato ...
File
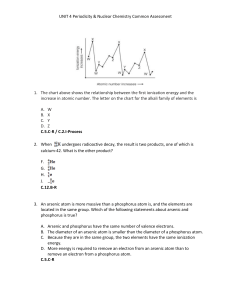
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
Waves notes section 5 - Nuclear radiation
... 1. The fuel rods are made of uranium which produces energy by fission. 2. The moderator, normally made of graphite slows down neutrons that are produced in fission, since a nucleus is split more easily by slow moving neutrons. 3. The control rods are made of boron, and absorb neutrons when lowered ...
... 1. The fuel rods are made of uranium which produces energy by fission. 2. The moderator, normally made of graphite slows down neutrons that are produced in fission, since a nucleus is split more easily by slow moving neutrons. 3. The control rods are made of boron, and absorb neutrons when lowered ...
SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES
... higher element and a mass number that equal to the reactant because the beta particle emitted was an electron) ...
... higher element and a mass number that equal to the reactant because the beta particle emitted was an electron) ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... 36. The diagnostic and therapeutic uses of radiopharmaceuticals are dependent on the accumulation of the material in the “organ of interest.” According to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) definition, the part of the body that is most susceptible to radiation damage under the specific condit ...
... 36. The diagnostic and therapeutic uses of radiopharmaceuticals are dependent on the accumulation of the material in the “organ of interest.” According to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) definition, the part of the body that is most susceptible to radiation damage under the specific condit ...
nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... 4. Electron capture (EC) – one of the electrons in an atom is captured by the nucleus of the atom ...
... 4. Electron capture (EC) – one of the electrons in an atom is captured by the nucleus of the atom ...
Nuclear Notes Introduction
... Radioactivity: is the act of emitting radiation spontaneously with the resulting emission of radiation resulting in the formation of a new nuclei. a. Does not need a source to travel through space and penetrate another material ...
... Radioactivity: is the act of emitting radiation spontaneously with the resulting emission of radiation resulting in the formation of a new nuclei. a. Does not need a source to travel through space and penetrate another material ...
Nuclear Decay
... Alpha Decay • Step 1. A nucleus releases an alpha particle (2 neutrons and 2 protons) decreasing the mass number of the nucleus • What does that mean? – The original atom is no longer the same – The atomic number is decreased by 2 ...
... Alpha Decay • Step 1. A nucleus releases an alpha particle (2 neutrons and 2 protons) decreasing the mass number of the nucleus • What does that mean? – The original atom is no longer the same – The atomic number is decreased by 2 ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
Rhenium isotopes in geochronology Stable isotope Relative atomic
... electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of pr ...
... electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of pr ...
Snímek 1
... organs along the specific path, much in the same manner that an Xray radiograph is a superposition of all anatomical structures from three dimensions into two dimensions. A SPECT study consists of ...
... organs along the specific path, much in the same manner that an Xray radiograph is a superposition of all anatomical structures from three dimensions into two dimensions. A SPECT study consists of ...
Half Life
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
... 19. An element that emits rays is said to be contaminated. 20. Unstable isotopes of elements are called radioisotopes. 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artifi ...
Chapter 21 - Richsingiser.com
... with isotopes that emit gamma radiation coupled to organic molecules that are taken up specifically in target organs. • Modern scanners use gamma ray cameras that take measurements at thousands of different locations. • Computerized tomography is often abbreviated CT and referred to as a CT scan. ...
... with isotopes that emit gamma radiation coupled to organic molecules that are taken up specifically in target organs. • Modern scanners use gamma ray cameras that take measurements at thousands of different locations. • Computerized tomography is often abbreviated CT and referred to as a CT scan. ...
Technetium-99m

Technetium-99m is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope.Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 140 keV gamma rays (these 8.8pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The ""short"" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the isotope suitable only for diagnostic but never therapeutic use.Technetium-99m was discovered as a product of cyclotron bombardment of molybdenum. This procedure produced molybdenum-99, a radionuclide with a longer half-life (2.75 days), which decays to Tc-99m. At present, molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) is used commercially as the easily transportable source of medically used Tc-99m. In turn, this Mo-99 is usually created commercially by fission of highly enriched uranium in aging research and material testing nuclear reactors in several countries.