* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 0 +1 0 - davis.k12.ut.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
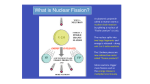
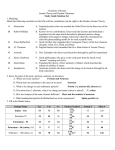
CE Nuclear Review Name_____________________ You need to know this to do well on the TEST!!!!!! 1. Fill in the table: Alpha Beta Gamma positron neutron rays rays rays symbol e. An isotope of Curium containing 150 neutrons is bombarded with and captures a proton. f. Pm-142 undergoes electron capture. actual particle representation charges g. 142 61𝑃𝑚 h. ________ → 142 60𝑁𝑑 + __________ 0 +1𝑒 226 86𝑅𝑛 + 2. Which nuclear particle has the greatest mass? Least mass? 3. What will stop the following particles? Star the least penetrating power. alpha 5. How much fissionable material is required to have a selfsustaining reaction? 6. Define Happens in Stars or with Nuclear Energy/power? Fission beta Fusion gamma 4. Write the nuclear equation for each word equation. a. Radon – 222 is an alpha emitter. b. ___ is produced when thorium -234 emits an alpha particle. 7. Draw a magnetic field with a positive plate on the top and a negative plate on the bottom. Show how the alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays are affected by the charged plates. c. The decay of 32P to 32S occurs through the emission of ___. d. Einsteinium – 253 is bombarded by an alpha particle. It will release one neutron. 8. What is the main difference between a nuclear reaction and a chemical reaction? What part of the atom is involved in these types of reactions? 9. There are some elements within the periodic table that do not occur in nature, can you list a few? 17. What is the difference between hydrogen-3 and hydrogen-1? 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? 18. Write the nuclear symbol for Iron-56. ______________ 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .63 g. How much time has passed if Lead-210 has a half-life of 22 years? How many Protons?__________ 12. The half-life of radium-226 is 1600 years. How many grams of a 0.25g sample will remain after 4800 years? How many electrons? __________ How many neutrons? __________ 19. What kinds of emissions can cause radiation sickness? 13. Sodium-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How much sodium-24 will remain in an 18.0g sample after 60 hours? 20. Define Free Radicals and describe why they are dangerous. 14. The half-life of radon-222 is 3.823 days. What was the original mass if 0.050g remains after 7.646 days? 21. List the characteristics of a diagnostic tracer. 15. The half-life of tritium ( 31𝐻 ) is 12.5 years. Suppose you have a sample containing .020 moles of tritium. How many years would be required to reduce your sample to 3.125 x 10-4 moles? 16. How many neutrons are produced in each of the following fission reactions? 90 147 1 1 a. 239 94𝑃𝑢 + 0𝑛 38𝑆𝑟 + 56𝐵𝑎 1 + _____ 0𝑛 b. 235 1 92𝑈+ 0𝑛 72 30𝑍𝑛 1 + 160 62𝑆𝑚 + _____ 0𝑛 22. List the characteristics that are important for radioisotope dating. Review Nuclear Name______Key__ 1. Fill in the table: Alpha Particle symbol α Beta Particle 𝟒 𝟐𝑯𝒆 𝟎 −𝟏𝒆 actual particle representation Charges +2 Gamma radiation positron 𝟐𝟒𝟔 𝟗𝟔𝑪𝒎 neutron γ β -1 e. An isotope of Curium containing 150 neutrons is bombarded with and captures a proton. f. Pm-142 undergoes electron capture. 𝟏𝟒𝟐 𝟔𝟏𝑷𝒎 n 𝟎 𝟎𝜸 0 𝟎 +𝟏𝒆 +1 𝟏 𝟎𝒏 0 2. Which nuclear particle has the greatest mass? Alpha Least mass? Gamma rays 3. What will stop the following particles? Star the least penetrating power. alpha Paper/ skin beta 0.5 cm lead gamma Thick lead or 6 feet concrete 4. Write the nuclear equation for each word equation. a. Radon – 222 emits an alpha particle. 𝟐𝟐𝟐 𝟖𝟔𝑹𝒏 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟐𝟏𝟖 𝟖𝟒𝑷𝒐 𝟐𝟑𝟒 𝟗𝟎𝑻𝒉 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟐𝟑𝟎 𝟖𝟖𝑹𝒂 + 𝟏𝟏𝑯 𝟐𝟒𝟕 𝟗𝟕𝑩𝒌 + 𝟎 𝟏𝟒𝟐 −𝟏𝒆 𝟔𝟎𝑵𝒅 g. 142 61𝑃𝑚 h. 𝟐𝟐𝟔 𝟖𝟕𝑭𝒓 → 142 60𝑁𝑑 0 +1𝑒 + +𝟏𝟎𝒆 + 226 86𝑅𝑛 5. How much fissionable material is required to have a selfsustaining reaction? Critical mass 6. Fission Splitting of Nuclear energy/power Fusion atoms Putting atoms together plants Sun and stars 7. Draw a magnetic field with a positive plate on the top and a negative plate on the bottom. Show how the alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays are affected by the charged plates. b. _______ is produced them thorium -234 emits an alpha particle. c. The decay of 𝟑𝟐 𝟏𝟓𝑷 −𝟏𝟎𝒆 + 𝟑𝟐 𝟏𝟔𝑺 d. Einsteinium – 253 is bombarded by an alpha particle. It will release one neutron. 𝟐𝟓𝟑 𝟗𝟗𝑬𝒔 + 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 𝟏𝟎𝒏 + 𝟐𝟓𝟔 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝑴𝒅 8. What is the main difference between a nuclear reaction and a chemical reaction? What part of the atom is involved in these types of reactions? Nuclear rxns happen in the nucleus, releasing lots of energy as the nucleus splits or fuses. Chemical reactions happen with the electrons, bonds are being broken or formed. 9. There are some elements within the periodic table that do not occur in nature, can you list a few? Technetium, neptunium, elements 93 and up… 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? Bombarding an atom with a neutron or alpha particle. 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .63 g. How much time has passed if Lead-210 has a half-life of 22 years? 65.7 or approximately 66 years 12. The half-life of radium-226 is 1600 years. How many grams of a 0.25g sample will remain after 4800 years? 0.031g 13. Sodium-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How much sodium-24 will remain in an 18.0g sample after 60 hours? 1.13 g 17. What is the difference between hydrogen-3 and hydrogen-1? 2 neutrons more in the hydrogen-3 18. Write the nuclear symbol for Iron-56. How many Protons?____26______ 𝟓𝟔 𝟐𝟔𝑭𝒆 How many neutrons? ___30_______ How many electrons? ___26_______ 19. What kinds of emissions can cause radiation sickness? Alpha, beta, gamma 20. Define Free Radicals and describe why they are dangerous. Electron deficient, very reactive 21. List the characteristics of a diagnostic tracer. Short ½-life, nontoxic daughter 14. The half-life of radon-222 is 3.823 days. What was the original mass if 0.050g remains after 7.646 days? .2 g 15. The half-life of tritium ( 31𝐻 ) is 12.5 years. Suppose you have a sample containing .020 moles of tritium. How many years would be required to reduce your sample to 3.125 x 10-4 moles? 75 years 16. How many neutrons are produced in each of the following fission reactions? 90 147 1 1 a. 239 94𝑃𝑢 + 0𝑛 38𝑆𝑟 + 56𝐵𝑎 1 + 3 0𝑛 b. 235 1 92𝑈+ 0𝑛 72 30𝑍𝑛 1 + 160 62𝑆𝑚 + 4 0𝑛 22. List the characteristics that are important for radioisotope dating. Long ½-life