What is the average % of protein in Grade 1 oats
... -Spare protein being metabolized for energy -Important source of energy in mare’s milk -Increases tastiness of food supplements -Increases stamina in performance horses ...
... -Spare protein being metabolized for energy -Important source of energy in mare’s milk -Increases tastiness of food supplements -Increases stamina in performance horses ...
Protein - PBworks
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
Protein in meats and how it helps your body
... Meats • Protein is an important sours for our body but you can get protein in several foods and shacks steak, squirrel, eggs and other meats. All foods contain some protein but many foods like those of plant origin lack certain amino acids but that’s why ...
... Meats • Protein is an important sours for our body but you can get protein in several foods and shacks steak, squirrel, eggs and other meats. All foods contain some protein but many foods like those of plant origin lack certain amino acids but that’s why ...
The Living World
... functional groups Organisms are primarily made of four kinds of molecules ...
... functional groups Organisms are primarily made of four kinds of molecules ...
Table - BioMed Central
... Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-binding protein that plays a role in proliferation and/or differentiation GRID2 belongs to the family of ionotropic glutamate receptors which are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain. Plays a role in neuronal apoptotic death. The ...
... Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-binding protein that plays a role in proliferation and/or differentiation GRID2 belongs to the family of ionotropic glutamate receptors which are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain. Plays a role in neuronal apoptotic death. The ...
Protein Structures
... The sequence of the nucleotide determines the amino acid. The amino acid sequence determines the protein shape. The protein shape determines it function. ...
... The sequence of the nucleotide determines the amino acid. The amino acid sequence determines the protein shape. The protein shape determines it function. ...
Protein Structure
... Amyloids - a collection of improperly folded protein aggregates found in the human body. When misfolded, they are insoluble and contribute to some twenty human diseases including important neurological ones involving prions. Amyloid diseases include (affected protein in parentheses) - ...
... Amyloids - a collection of improperly folded protein aggregates found in the human body. When misfolded, they are insoluble and contribute to some twenty human diseases including important neurological ones involving prions. Amyloid diseases include (affected protein in parentheses) - ...
Protein Misfolding and Degenerative Diseases
... genome are very similar to a highly compressed digital file, such as an MP3, in which a lot of information is packed very efficiently. How is this possible? The Nobel laureate Christian B. Anfinsen postulated an answer. He proposed that all the information needed for a protein to fold into its three ...
... genome are very similar to a highly compressed digital file, such as an MP3, in which a lot of information is packed very efficiently. How is this possible? The Nobel laureate Christian B. Anfinsen postulated an answer. He proposed that all the information needed for a protein to fold into its three ...
Chapter 6 questions
... 1. Identify the body's working proteins. 2. Identify the body's structural proteins. 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustr ...
... 1. Identify the body's working proteins. 2. Identify the body's structural proteins. 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustr ...
Soybean Meal - International Feed
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
Structural Studies of Sgt2, a Component of the GET Pathway that
... Structural Studies of Sgt2, a Component of the GET Pathway that Mediates the Sorting of Tail-anchored Proteins to the ER Membrane. Nuri Sung, Sukyeong Lee, Amadeo B. Biter, and Francis T.F. Tsai Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, One ...
... Structural Studies of Sgt2, a Component of the GET Pathway that Mediates the Sorting of Tail-anchored Proteins to the ER Membrane. Nuri Sung, Sukyeong Lee, Amadeo B. Biter, and Francis T.F. Tsai Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, One ...
Chapter 6: Protein 1. Identify the body's working proteins.
... 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustrate an example. 7. Globular shaped proteins are __________ proteins and are _________ ...
... 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustrate an example. 7. Globular shaped proteins are __________ proteins and are _________ ...
Ch. 5. Protein Purification and Characterization Techniques
... Paul D. Adams • University of Arkansas ...
... Paul D. Adams • University of Arkansas ...
Structure Reveals How Cells `Sugar
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE CLASSIFICATION
... Low sequence similarity may yield very similar structures Sometimes high sequence similarity yields different structures ...
... Low sequence similarity may yield very similar structures Sometimes high sequence similarity yields different structures ...
Episode 23 0 Proetin: Structure and Function
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
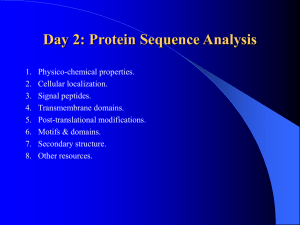
Day 2: Protein Sequence Analysis
... Can include the cleavage of the pro- region to release the active protein, the removal of the signal peptide and numerous covalent modifications such as, acetylations, glycosylations, hydroxylations, methylations and phosphorylations. Posttranslational modifications may alter the molecular weight of ...
... Can include the cleavage of the pro- region to release the active protein, the removal of the signal peptide and numerous covalent modifications such as, acetylations, glycosylations, hydroxylations, methylations and phosphorylations. Posttranslational modifications may alter the molecular weight of ...
Abstract: The backbone chain of a protein (called its fold) can be
... Abstract: The backbone chain of a protein (called its fold) can be considered as a simple directed chain with one point representing each amino acid in the sequence. Repeated local smoothing of the chain coordinate set (without chain passage) leads to a simple method to detect knots in open chains. ...
... Abstract: The backbone chain of a protein (called its fold) can be considered as a simple directed chain with one point representing each amino acid in the sequence. Repeated local smoothing of the chain coordinate set (without chain passage) leads to a simple method to detect knots in open chains. ...
Lecture 19 - phys.protres.ru
... must become more and more stable for hierarchic folding. This cannot provide a simultaneous explanation to (i) folding within non-astronomical time; (ii) “all-or-none” transition, i.e., co-existence of only native and denatured molecules in visible amount; (iii) the same 3D structure resulting from ...
... must become more and more stable for hierarchic folding. This cannot provide a simultaneous explanation to (i) folding within non-astronomical time; (ii) “all-or-none” transition, i.e., co-existence of only native and denatured molecules in visible amount; (iii) the same 3D structure resulting from ...
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
Protein folding

Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil.Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma). Experiments beginning in the 1980s indicate the codon for an amino acid can also influence protein structure.The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins may remain unfolded, so that protein dynamics is important. Failure to fold into native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances misfolded proteins have modified or toxic functionality. Several neurodegenerative and other diseases are believed to result from the accumulation of amyloid fibrils formed by misfolded proteins. Many allergies are caused by incorrect folding of some proteins, because the immune system does not produce antibodies for certain protein structures.