Powerpoint slides
... involves the relative movement of its two lobes to each other in a cooperative manner ...
... involves the relative movement of its two lobes to each other in a cooperative manner ...
Protein folding
... interactions between chaperonins, or inert, where chaperonines simply make a environment conducive to folding, is not known. It is however, required for the proper folding of many proteins. ...
... interactions between chaperonins, or inert, where chaperonines simply make a environment conducive to folding, is not known. It is however, required for the proper folding of many proteins. ...
TWO-DAY COURSE, Saturday and Sunday 12 Peptides and
... 12 Peptides and Proteins in Mass Spectrometry Instructors ...
... 12 Peptides and Proteins in Mass Spectrometry Instructors ...
Protein and Enzyme Check for Understanding
... Protein and Enzyme Check for Understanding: 1. What is the monomer of a protein? 2. What is the name of the bond between the amino acids in a protein? 3. Label the following parts: ...
... Protein and Enzyme Check for Understanding: 1. What is the monomer of a protein? 2. What is the name of the bond between the amino acids in a protein? 3. Label the following parts: ...
WSB2 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q01)
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
Shin-ichi Tate Research Group Activity ・ Protein dynamics and
... ・ Protein dynamics and function relationships revealed through nuclear spin relaxation analyses Protein dynamics, in the time regime in sec-msec, can be revealed by nuclear spin relaxations. Systematic analyses on the dynamical modulations caused by single site-directed mutation will give us experi ...
... ・ Protein dynamics and function relationships revealed through nuclear spin relaxation analyses Protein dynamics, in the time regime in sec-msec, can be revealed by nuclear spin relaxations. Systematic analyses on the dynamical modulations caused by single site-directed mutation will give us experi ...
influence of macromolecular crowding on protein stability
... more compact conformations, including the native state. Experimental studies intending to verify whether the proteins are stabilized by excluded volume effects were performed on test macromolecules in presence of polysaccharides such as Ficoll 70 or Dextran to mimic the crowding of the cytoplasm. Fl ...
... more compact conformations, including the native state. Experimental studies intending to verify whether the proteins are stabilized by excluded volume effects were performed on test macromolecules in presence of polysaccharides such as Ficoll 70 or Dextran to mimic the crowding of the cytoplasm. Fl ...
Protein Aggregation in High-Protein Caramel
... sugar (sucrose, corn syrup, lactose) continuous phase with fat globules homogeneously dispersed throughout. Lecithin is often used to help create small fat globules, although proteins and the high-viscosity amorphous phase help prevent lipid coalescence. By varying water content, caramels can be mad ...
... sugar (sucrose, corn syrup, lactose) continuous phase with fat globules homogeneously dispersed throughout. Lecithin is often used to help create small fat globules, although proteins and the high-viscosity amorphous phase help prevent lipid coalescence. By varying water content, caramels can be mad ...
CHEM F654
... exams will only be allowed with pre-approval of the instructor or with an acceptable, documented reason such as unexpected illness, family emergencies or other unavoidable events. The final exam could be an exclusive oral exam if students unanimously opt for this exam type. Presentations: Students w ...
... exams will only be allowed with pre-approval of the instructor or with an acceptable, documented reason such as unexpected illness, family emergencies or other unavoidable events. The final exam could be an exclusive oral exam if students unanimously opt for this exam type. Presentations: Students w ...
Lecture 7 Proteins 1. Which amino acids are considered as acidic
... sulphate is the most commonly used salt as it is cheap and sufficiently soluble. Other salts which can be used are ammonium acetate, sodium sulphate, and sodium citrate. 6. How to differentiate between secondary and tertiary structure of proteins? Answer: Tertiary protein structure refers to the com ...
... sulphate is the most commonly used salt as it is cheap and sufficiently soluble. Other salts which can be used are ammonium acetate, sodium sulphate, and sodium citrate. 6. How to differentiate between secondary and tertiary structure of proteins? Answer: Tertiary protein structure refers to the com ...
Biosynthesis and degradation of proteins
... A large conformational change in the serpin accompanies cleavage of its substrate loop. This leads to disordering of the protease active site, preventing completion of the reaction. The serpin remains covalently linked to the protease as an acylenzyme intermediate. ...
... A large conformational change in the serpin accompanies cleavage of its substrate loop. This leads to disordering of the protease active site, preventing completion of the reaction. The serpin remains covalently linked to the protease as an acylenzyme intermediate. ...
amino acids
... – polymer = polypeptide • protein can be two or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together via covalent and hydrogen bonds ...
... – polymer = polypeptide • protein can be two or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together via covalent and hydrogen bonds ...
Computational Prediction of Beta Structure from Amino Acid
... Sequence in a Class of Pathologically Relevant Proteins Abstract Objectives/Goals Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, th ...
... Sequence in a Class of Pathologically Relevant Proteins Abstract Objectives/Goals Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, th ...
Topic: DISORDERS OF PROTEIN METABOLISM. GOUT
... Topic: DISORDERS OF PROTEIN METABOLISM. GOUT Aim of the lesson: to study disorders of protein metabolism, mechanisms of protein insufficiency and gout development and their complications. ...
... Topic: DISORDERS OF PROTEIN METABOLISM. GOUT Aim of the lesson: to study disorders of protein metabolism, mechanisms of protein insufficiency and gout development and their complications. ...
... a simple spiral. At high speeds the protein would be held on the wall by centrifugal force but liquids entering at the top would not just pass down and out the tip but would rise up again when they reached the bottom. A vertical rotating column with a base would allow extracting liquids introduced t ...
HW #6 BP401/P475 Fall 2015 Assigned Fr 10/02/15: due: Thursday
... b. Explain in terms of what’s happening to the bonds (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) and in terms of H, S, G. c. A student asked me an interesting question. When you heat a protein, how much more energy are you giving a water molecule? The answer is surprisingly small. Yet we say that ...
... b. Explain in terms of what’s happening to the bonds (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) and in terms of H, S, G. c. A student asked me an interesting question. When you heat a protein, how much more energy are you giving a water molecule? The answer is surprisingly small. Yet we say that ...
Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
... common amino sugar D-glucosamine, occurs as its N-acetyl derivative-N-acetyl-Dglucosamine. These kind of amino sugar are usually joined by N link to a polypeptide at an aspargine residue. The N links of oligosaccharides to polypeptides occur most often where the polypeptide strand is following a ben ...
... common amino sugar D-glucosamine, occurs as its N-acetyl derivative-N-acetyl-Dglucosamine. These kind of amino sugar are usually joined by N link to a polypeptide at an aspargine residue. The N links of oligosaccharides to polypeptides occur most often where the polypeptide strand is following a ben ...
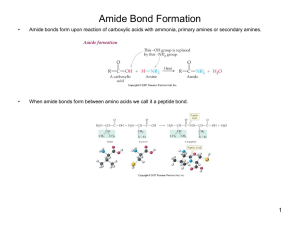
Amide Bond Formation
... Roles of proteins: – Gene expression is due to proteins – Almost all enzymes are proteins – Many hormones are proteins or peptides – Proteins form structural tissue – Storage and transportation of many molecules is possible due to proteins (think back to passive transport of hydrophilic molecules in ...
... Roles of proteins: – Gene expression is due to proteins – Almost all enzymes are proteins – Many hormones are proteins or peptides – Proteins form structural tissue – Storage and transportation of many molecules is possible due to proteins (think back to passive transport of hydrophilic molecules in ...
Slide 1
... • Is crystal state relevant? • Short answer: Yes – High solvent content; similar to cell plasma – Comparisons indicate OK ...
... • Is crystal state relevant? • Short answer: Yes – High solvent content; similar to cell plasma – Comparisons indicate OK ...
Chapt. 3-Proteins - University of New England
... • Definite 3D regions along a polypeptide with a precise function • Example: enzyme binding sites, substrate binding sites ...
... • Definite 3D regions along a polypeptide with a precise function • Example: enzyme binding sites, substrate binding sites ...
Document
... (2004) Folding of beta/alpha-unit scrambled forms of S. cerevisiae triosephosphate isomerase: Evidence for autonomy of substructure formation and plasticity of hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions in the core of the (beta/alpha)8-barrel. Proteins : Structure, Function & Bioinformatics 55, 5 ...
... (2004) Folding of beta/alpha-unit scrambled forms of S. cerevisiae triosephosphate isomerase: Evidence for autonomy of substructure formation and plasticity of hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions in the core of the (beta/alpha)8-barrel. Proteins : Structure, Function & Bioinformatics 55, 5 ...
Protein folding

Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil.Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma). Experiments beginning in the 1980s indicate the codon for an amino acid can also influence protein structure.The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins may remain unfolded, so that protein dynamics is important. Failure to fold into native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances misfolded proteins have modified or toxic functionality. Several neurodegenerative and other diseases are believed to result from the accumulation of amyloid fibrils formed by misfolded proteins. Many allergies are caused by incorrect folding of some proteins, because the immune system does not produce antibodies for certain protein structures.