EOC Review Part 1
... Proteins are made of Amino acids held together by peptide bonds. Important Proteins: Enzymes (see enzymes in this packet) Hemoglobin- a protein in a blood cell that helps carry oxygen in the blood. Insulin- a protein in the body which helps maintain proper blood sugar levels. If there are problems m ...
... Proteins are made of Amino acids held together by peptide bonds. Important Proteins: Enzymes (see enzymes in this packet) Hemoglobin- a protein in a blood cell that helps carry oxygen in the blood. Insulin- a protein in the body which helps maintain proper blood sugar levels. If there are problems m ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... Negative feedback – deviation from set point progressively lessens Positive feedback – deviation from set point gets progressively greater ...
... Negative feedback – deviation from set point progressively lessens Positive feedback – deviation from set point gets progressively greater ...
Biology STAAR Review #4 – Body systems
... The endocrine system makes certain hormones. Blood in the circulatory system carries them to the skeletal system to control the amount of calcium released from bones. Nervous system detects levels. Food is broken down in the stomach mechanically by the muscular system (churns food) and chemically by ...
... The endocrine system makes certain hormones. Blood in the circulatory system carries them to the skeletal system to control the amount of calcium released from bones. Nervous system detects levels. Food is broken down in the stomach mechanically by the muscular system (churns food) and chemically by ...
MOLECULES OF LIFE
... 3. PROTEINS are molecules that make up most of our body. Our hair, nails, tissues, ligaments, cartilage, bone, tendons, muscles, and organs are made of proteins. Other proteins we have are enzymes, which function to speed up metabolic reactions and break down larger molecules into smaller ones. In o ...
... 3. PROTEINS are molecules that make up most of our body. Our hair, nails, tissues, ligaments, cartilage, bone, tendons, muscles, and organs are made of proteins. Other proteins we have are enzymes, which function to speed up metabolic reactions and break down larger molecules into smaller ones. In o ...
Name: Period: ___ Date
... What is Translation (include type(s) of RNA, location of the process, and the name given to the triplet of bases on the tRNA strand? mRNA--tRNA--proteins. mRNA attaches to ribosome, tRNA (anticodon) brings amino acids to mRNA to form proteins ...
... What is Translation (include type(s) of RNA, location of the process, and the name given to the triplet of bases on the tRNA strand? mRNA--tRNA--proteins. mRNA attaches to ribosome, tRNA (anticodon) brings amino acids to mRNA to form proteins ...
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
... 3. Most common type of fat molecule, with three fatty acids bound to a glycerol molecule. 4. Fatty acid that contains only single covalent bonds between the carbon atoms. 5. Believed to be the best type of fat in the diet. ...
... 3. Most common type of fat molecule, with three fatty acids bound to a glycerol molecule. 4. Fatty acid that contains only single covalent bonds between the carbon atoms. 5. Believed to be the best type of fat in the diet. ...
EOCT Review Sheet
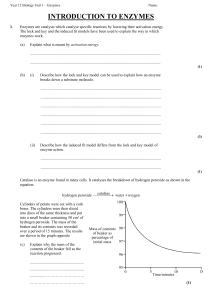
... A Bacteria that cause food spoilage are killed by these low temperatures. B Bacteria that cause food spoilage multiply rapidly at these temperatures. C The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are not active at these temperatures. D The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are denatu ...
... A Bacteria that cause food spoilage are killed by these low temperatures. B Bacteria that cause food spoilage multiply rapidly at these temperatures. C The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are not active at these temperatures. D The enzymes in bacteria that cause food spoilage are denatu ...
digestion and excretion notes
... Unsaturated fats are less likely to cause heart disease than saturated fats ...
... Unsaturated fats are less likely to cause heart disease than saturated fats ...
Organic Macromolecules: Biological macromolecules
... • Glucose is a carbohydrate monomer. Glucose is the molecule that is needed for cellular respiration. starch, glycogen and cellulose. Proteins have a number of important functions. These include their roles in structures, transport, storage, hormonal proteins and enzymes. A protein consists of monom ...
... • Glucose is a carbohydrate monomer. Glucose is the molecule that is needed for cellular respiration. starch, glycogen and cellulose. Proteins have a number of important functions. These include their roles in structures, transport, storage, hormonal proteins and enzymes. A protein consists of monom ...
Presentation - Asian and Pacific Centre for Transfer of Technology
... Design of GMP bio-containment facilities for pharmaceutical and vaccine production Risk and impact assessment Impact on operation ...
... Design of GMP bio-containment facilities for pharmaceutical and vaccine production Risk and impact assessment Impact on operation ...
here - The University of Sydney
... Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a highly conserved biological process required for the removal of unwanted, damaged or infected cells. The central regulators of apoptotic programmed cell death belong to the BCL‐2 family of proteins. A delicate interplay ...
... Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a highly conserved biological process required for the removal of unwanted, damaged or infected cells. The central regulators of apoptotic programmed cell death belong to the BCL‐2 family of proteins. A delicate interplay ...
Semester 1 study guide answer key 2016 Biology Semester 1 Study
... 16. When a person grows from a baby to an adult, it is gaining mass. Where is that mass coming from? Biomolecules and CO2 17. What does our body use to transport sugar and oxygen into our cells? blood 18. Fill in the following table: Biomolecule Subunit Rich Food Source Carbohydrates Monosaccharide ...
... 16. When a person grows from a baby to an adult, it is gaining mass. Where is that mass coming from? Biomolecules and CO2 17. What does our body use to transport sugar and oxygen into our cells? blood 18. Fill in the following table: Biomolecule Subunit Rich Food Source Carbohydrates Monosaccharide ...
B2 revision questions
... A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein Two stands in a double helix linked by base pairs in hydrogen bonds Adenine (A) with Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) with Guanine (G) Franklin, Wilkins, Watson and Crick It was a collaboration between many scientists around the world which lead to a better ...
... A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein Two stands in a double helix linked by base pairs in hydrogen bonds Adenine (A) with Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) with Guanine (G) Franklin, Wilkins, Watson and Crick It was a collaboration between many scientists around the world which lead to a better ...
Enzymes and the Digestive system…
... – The outer cells are continuously rubbed away by friction (with the swallowed food), so the mucosa is folded. This also allows elastic expansion* . The ...
... – The outer cells are continuously rubbed away by friction (with the swallowed food), so the mucosa is folded. This also allows elastic expansion* . The ...
lecture 4
... Detection of allergens in food, e.g. peanuts. Detection of illegal drugs in humans. Detection of hormones, e.g. pregnancy ...
... Detection of allergens in food, e.g. peanuts. Detection of illegal drugs in humans. Detection of hormones, e.g. pregnancy ...
Chap02 ed11
... Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d. Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e. Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, temper ...
... Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d. Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e. Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, temper ...
function
... 1. Carbon forms covalent bonds (strong bonds) with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms (has 4 unpaired electrons in its outer energy level) 2. They can form large, complex molecules ...
... 1. Carbon forms covalent bonds (strong bonds) with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms (has 4 unpaired electrons in its outer energy level) 2. They can form large, complex molecules ...
Basic Chemistry
... slight changes in pH; and acid-base balance is carefully regulated by the kidneys, lungs, and a number of chemicals called buffers, which are present in body fluids. • Buffer - a substance or substances that help to stabilize the pH of a solution. ...
... slight changes in pH; and acid-base balance is carefully regulated by the kidneys, lungs, and a number of chemicals called buffers, which are present in body fluids. • Buffer - a substance or substances that help to stabilize the pH of a solution. ...
Biology Review Notes
... DNA DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick. DNA is the shape of a double helix ( which is a spiral staircase or twisted ladder) In eukaryotes, DNA is stored in the nucleus DNA is made up of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of deo ...
... DNA DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick. DNA is the shape of a double helix ( which is a spiral staircase or twisted ladder) In eukaryotes, DNA is stored in the nucleus DNA is made up of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of deo ...
Unit 1 – Cell Biology
... their DNA and the proteins they produce. For example your hair colour may be different to another person as your DNA carries a different sequence of bases, so the protein that makes your hair is also different. The production of these proteins is controlled by a variety of enzymes. ...
... their DNA and the proteins they produce. For example your hair colour may be different to another person as your DNA carries a different sequence of bases, so the protein that makes your hair is also different. The production of these proteins is controlled by a variety of enzymes. ...
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions 2008/09
... synthesis, degradation, activation, deactivation, and role in signaling pathways. 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways: cAMP, phosphatidylinositols, calcium, Ras/MAPKinases, connection to transcription factors. 9 ...
... synthesis, degradation, activation, deactivation, and role in signaling pathways. 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways: cAMP, phosphatidylinositols, calcium, Ras/MAPKinases, connection to transcription factors. 9 ...
Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
From Gene to Protein
... So, the language of DNA is a triplet code. How many unique triplets exist? ...
... So, the language of DNA is a triplet code. How many unique triplets exist? ...