Keystone Countdown
... 1. Organic compounds are made primarily of atoms of which element? 2. What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer? 3. What is another name for a large polymer? 4. In order to link monomers together to form a polymer, what type of reaction must take place? (2 names) 5. To break down a poly ...
... 1. Organic compounds are made primarily of atoms of which element? 2. What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer? 3. What is another name for a large polymer? 4. In order to link monomers together to form a polymer, what type of reaction must take place? (2 names) 5. To break down a poly ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • What type of bond is a peptide bond? Where can one be found? • What are two types of secondary structure in proteins? What causes the formation of each? • What types of bonds and what level of structure is destroyed when a protein is denatured? ...
... • What type of bond is a peptide bond? Where can one be found? • What are two types of secondary structure in proteins? What causes the formation of each? • What types of bonds and what level of structure is destroyed when a protein is denatured? ...
UNIT 2 -BASIC PRINCIPLES OF BODY CHEMISTRY
... B. Covalent Bonding 1. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electron pairs by two or more atoms. 2. A single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of one pair of electrons. 3. A double covalent bond is formed by the sharing of two pairs of electrons. 4. A triple covalent bond is formed by the sharing ...
... B. Covalent Bonding 1. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electron pairs by two or more atoms. 2. A single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of one pair of electrons. 3. A double covalent bond is formed by the sharing of two pairs of electrons. 4. A triple covalent bond is formed by the sharing ...
BIO 181 Unity of Life I - Coconino Community College
... 12. Identify and define the functional operation of organelles found in eukaryotic structures 13. Compare and contrast in detail photosynthesis and respiration 14. Compare and contrast in written detail asexual/ mitotic reproduction with sexual/ meiotic reproduction 15. Outline Mendel’s laws and app ...
... 12. Identify and define the functional operation of organelles found in eukaryotic structures 13. Compare and contrast in detail photosynthesis and respiration 14. Compare and contrast in written detail asexual/ mitotic reproduction with sexual/ meiotic reproduction 15. Outline Mendel’s laws and app ...
File - G. Scott`s Bio Page
... – Organic because contains carbon – Made up of CHON – Made up of amino acids (monomer) – Polypeptide chain or amino acid chain (polymer) ex enzymes – Builds muscle and bones, enzymes = catalysts (speed up reactions) ...
... – Organic because contains carbon – Made up of CHON – Made up of amino acids (monomer) – Polypeptide chain or amino acid chain (polymer) ex enzymes – Builds muscle and bones, enzymes = catalysts (speed up reactions) ...
review for Bio. I HSA
... How do enzymes lower the activation energy? Explain at the molecular level. A. Body temperature cannot be too great so there isn’t enough activation energy to get chemical reactions to go so enzymes must lower the activation energy B. If reactions could happen on their own (if body temperature provi ...
... How do enzymes lower the activation energy? Explain at the molecular level. A. Body temperature cannot be too great so there isn’t enough activation energy to get chemical reactions to go so enzymes must lower the activation energy B. If reactions could happen on their own (if body temperature provi ...
1.3.1 Function of Food
... amino acids There are 20 common and several rare amino acids found in proteins More amino acids are found in cells and tissues but are not in proteins Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds This results in the formation of polypeptide chains ...
... amino acids There are 20 common and several rare amino acids found in proteins More amino acids are found in cells and tissues but are not in proteins Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds This results in the formation of polypeptide chains ...
MCAS Biology Review Packet Answer Key
... 12. Complete the following monohybrid cross. Two parents that are heterozygous for brown eyes. Be sure to identify the genotypes of the parents, complete the punnett square, identify the phentoypes with genotypes and the ratio of the phenotypes. What percent of the ...
... 12. Complete the following monohybrid cross. Two parents that are heterozygous for brown eyes. Be sure to identify the genotypes of the parents, complete the punnett square, identify the phentoypes with genotypes and the ratio of the phenotypes. What percent of the ...
What is Food Chemistry
... glycerol molecule. This compound is an important source of energy for the human body. ...
... glycerol molecule. This compound is an important source of energy for the human body. ...
MCAS Biology - Fall River Public Schools
... 3. Elements join together by chemical bonds to form compounds. Name the 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. There are 4 major categories of organic molecules that are made up of the SPONCH elements. Complete the following chart on the macromolecules of life. ...
... 3. Elements join together by chemical bonds to form compounds. Name the 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. There are 4 major categories of organic molecules that are made up of the SPONCH elements. Complete the following chart on the macromolecules of life. ...
EOC review packet answers Biology EOC
... 2. How does a hypothesis become a theory? Repeated testing. Give an example of how new information can change a theory. 3. What are some safety concerns for students working in the lab? Goal 2: Learner will develop an understanding of the physical, chemical and cellular basis of life. 4. What is the ...
... 2. How does a hypothesis become a theory? Repeated testing. Give an example of how new information can change a theory. 3. What are some safety concerns for students working in the lab? Goal 2: Learner will develop an understanding of the physical, chemical and cellular basis of life. 4. What is the ...
UNIT 2 -BASIC PRINCIPLES OF BODY CHEMISTRY
... 1. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electron pairs by two or more atoms. 2. A single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of one pair of electrons. 3. A double covalent bond is formed by the sharing of two pairs of electrons. 4. A triple covalent bond is formed by the sharing of three pairs elec ...
... 1. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electron pairs by two or more atoms. 2. A single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of one pair of electrons. 3. A double covalent bond is formed by the sharing of two pairs of electrons. 4. A triple covalent bond is formed by the sharing of three pairs elec ...
MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMIN
... Engineering, Sports and Sciences Academic Group BEng (Hons)/MEng Biomedical Engineering Semester Two Examinations 2014/2015 Fundamentals of Systems and Synthetic Biology Module No. BME4006 SECTION A: Answer ALL questions in this section; 1 mark per question, 35 marks in total. ...
... Engineering, Sports and Sciences Academic Group BEng (Hons)/MEng Biomedical Engineering Semester Two Examinations 2014/2015 Fundamentals of Systems and Synthetic Biology Module No. BME4006 SECTION A: Answer ALL questions in this section; 1 mark per question, 35 marks in total. ...
PhD Project Template
... The main aim of the DNA Damage Response group led by Dr. Carty is to elucidate the molecular basis of the response of human primary cells and cancer cells to DNA damaging agents, with a specific interest in cancer therapeutics such as platinum-based drugs that interfere with DNA replication. Title & ...
... The main aim of the DNA Damage Response group led by Dr. Carty is to elucidate the molecular basis of the response of human primary cells and cancer cells to DNA damaging agents, with a specific interest in cancer therapeutics such as platinum-based drugs that interfere with DNA replication. Title & ...
TAKS biology review
... • The bits train your immune system to recognize and attack when they see that protein or virus. • But some viruses change proteins too quickly for us to keep up… like colds, and HIV ...
... • The bits train your immune system to recognize and attack when they see that protein or virus. • But some viruses change proteins too quickly for us to keep up… like colds, and HIV ...
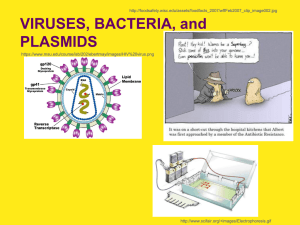
Virus Bacteria Plasmids 1
... human colon (large intestines) 2 x 1010 (billion) new E. coli each day! spontaneous mutations for 1 gene, only ~1 mutation in 10 million replications each day, ~2,000 bacteria develop mutation in that ...
... human colon (large intestines) 2 x 1010 (billion) new E. coli each day! spontaneous mutations for 1 gene, only ~1 mutation in 10 million replications each day, ~2,000 bacteria develop mutation in that ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... 1. Chemicals that contain carbon and hydrogen are ____________________________. 2. Chemicals that generally do not contain carbon and hydrogen are _______________. 3. Many organic chemicals have long chains or ring structures that can be formed because of a carbon atom’s ability to ________________ ...
... 1. Chemicals that contain carbon and hydrogen are ____________________________. 2. Chemicals that generally do not contain carbon and hydrogen are _______________. 3. Many organic chemicals have long chains or ring structures that can be formed because of a carbon atom’s ability to ________________ ...
HB Unit 1 Foundations of Biology
... Unit 1: Foundations of Biology Section 1: The World of Biology Section 2: Themes in Biology Section 3: The Study of Biology Section 4: Tools and Techniques ...
... Unit 1: Foundations of Biology Section 1: The World of Biology Section 2: Themes in Biology Section 3: The Study of Biology Section 4: Tools and Techniques ...
EXPLORING PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but they can be joined together in many different combinations to form the diverse range of proteins that ex ...
... down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but they can be joined together in many different combinations to form the diverse range of proteins that ex ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... In animals, the egg-producing gonad of the female. In flowering plants, the enlarged base of the pistil. In which seeds develop Single celled protists- animal- like characteristics- cilia surround the cell Vascular plant tissue composed of tubular cells joined end to end; transports sugars from the ...
... In animals, the egg-producing gonad of the female. In flowering plants, the enlarged base of the pistil. In which seeds develop Single celled protists- animal- like characteristics- cilia surround the cell Vascular plant tissue composed of tubular cells joined end to end; transports sugars from the ...
Protein - Canon-MacFCS
... Create and regulate hormones: proteins are one component of hormones that help regulate the systems of the body including blood sugar and metabolism. Create antibodies: proteins made by the body are necessary to destroy foreign substances and prevent illness. Energy source: last choice of energy ...
... Create and regulate hormones: proteins are one component of hormones that help regulate the systems of the body including blood sugar and metabolism. Create antibodies: proteins made by the body are necessary to destroy foreign substances and prevent illness. Energy source: last choice of energy ...
Which is the odd one out and why?
... makes 13, the 9 other amino acids come from proteins in food. It is essential for the body to eat proteins. • Protein is a major functional and structural component of all our cells. They provide the body with roughly 10-15% of all our dietary energy and is needed for growth and repair. ...
... makes 13, the 9 other amino acids come from proteins in food. It is essential for the body to eat proteins. • Protein is a major functional and structural component of all our cells. They provide the body with roughly 10-15% of all our dietary energy and is needed for growth and repair. ...
Final Exam Review Packet (Scary, Isn`t It?) Date: Time: Room
... ___Prokaryotic (BACTERIA)- contains DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall (NO membrane bound organelles); Eukaryotic cell (ANIMAL, PLANT, FUNGI, PROTISTS)- more complex with membrane bound organelles and DNA contained in a nucleus_____ 3. What is the difference between a unicellular a ...
... ___Prokaryotic (BACTERIA)- contains DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall (NO membrane bound organelles); Eukaryotic cell (ANIMAL, PLANT, FUNGI, PROTISTS)- more complex with membrane bound organelles and DNA contained in a nucleus_____ 3. What is the difference between a unicellular a ...