* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - G. Scott`s Bio Page
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
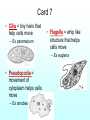
• Water’s structure Card 1 – Partial positive and negative charge = polar – This causes water to stick to other water molecules = cohesion - Causes water to stick to other substances = adhesion (think of adhesive band aid) – Allows water to dissolve most substances = universal solvent – Water is less dense when it freezes, so ponds do not freeze from the bottom up; only the top freezes Continued on next slide Card 1 continued – Surface tension = water sticks to its self (cohesion) and forms a film on top of the water, which allows insects to walk on it (adhesion) – Capillary action = water sticks to is self (cohesion) and is pulled up the vascular tissue in plants (adhesion) – Hydrogen bonds holds individual water molecules together Card 2 • The pH scale measures how acidic or basic something is – Acids are 0-7 on the scale – Neutral is 7 (water) – Bases are 7-14 on the scale – Remember that A comes before B. Acid___________________Base 0 7 14 Card 3 • Carbohydrate – Organic because contains carbon – Made up of CHO (in a ration of 1-2-1) – Made up of monosaccharide (monomer) ex glucose – Polysaccharide (polymer) ex starch – Provides short term energy, makes up cell wall in plants • Lipid – Organic – Made up of CHO (no specific ratio) – Made up of fatty acids (monomer) – Chain of fatty acids (polymer) ex fats – Provides long term energy storage, makes up the cell membrane Card 4 • Protein – Organic because contains carbon – Made up of CHON – Made up of amino acids (monomer) – Polypeptide chain or amino acid chain (polymer) ex enzymes – Builds muscle and bones, enzymes = catalysts (speed up reactions) • Nucleic acid – Organic – Made up of CHONP – Made up of nucleotide (monomer) – DNA and RNA – Transmits and stores genetic information Card 5 • The lock and key model – An enzyme is a protein that speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required to start a reaction – Enzymes are reused after reactions; stays the same Card 6 • Prokaryote – Does not contain a nucleus or any other membrane bound organelles – Has ribosomes, cell membrane, and some times cell wall, and DNA loose inside cell – Ex bacteria • Eukaryote (Euks have nukes) – Has a nucleus that contains DNA and other membrane bound organelles – Ribosomes = make protein – Plant cells have cell wall and chloroplast Card 7 • Cilia = tiny hairs that help cells move – Ex paramecium • Flagella = whip like structure that helps cells move – Ex euglena • Pseudopodia = movement of cytoplasm helps cells move – Ex amobea Card 8 • Respiratory – Made up of lungs, trachea, nose – Where exchange of gases takes place • Breathes out carbon dioxide and takes in oxygen • Circulatory – Made up of heart, blood, blood vessels – Transports nutrients and blood through out the body Card 9 • Digestive – Made up of mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, liver, and large intestines – Where nutrients are broken down and absorbed by the body • Excretory – Made up of blood, kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder – Where blood is filtered and waste is eliminated from the body Card 10 • Nervous – Made up of brain, spinal cord, nerves – Controls movement in the body (coordination) and communication • Endocrine – Made up of hormones, hormone secreting glands (thyroid, pituitary) – Regulates processes in the body Card 11 • Diffusion – Movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration – Form of passive transport because it does not require energy • Osmosis – Movement of water from high concentration to low concentration – Form of diffusion; passive transport because it does not require energy • Hypertonic = more water inside the cell (less solute) • Hypotonic = more water outside the cell ( less solute) • Isotonic = equilibrium; same concentration of water in and out of cell Card 12 • Mitochondria – Cellular respiration (power house of cell) – ATP is created (energy) • Chloroplast – Photosynthesis – Use sunlight to make their own food (glucose) – Takes place in all organism (bacteria, plants and animals) – Takes place in plants – O2 + C6H12O6 → CO2 + H2O + ATP – CO2 + H2O + Sunlight → O2 + C6H12O6 Card 13 • DNA structure – Watson and Crick discovered its shape as a Double Helix, which has a sugar and phosphate backbone with nitrogen bases in the center (rungs) – Made up of individual nucleotides – Base pairing rules (complimentary) • A–T • C-G