Document
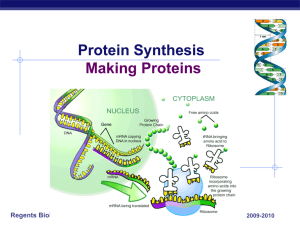
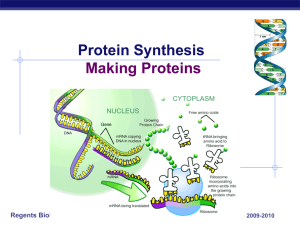
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
Amino acids and prot..
... form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimer) twisted around each other forming triplet-helix molecule. • ⅓ of st ...
... form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimer) twisted around each other forming triplet-helix molecule. • ⅓ of st ...
Lipids
... There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the ...
... There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the ...
CHAPTER 2: THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... unsaturated fats: a. have one or more double bond between the carbons in their fatty acid chains; b. are liquid at RT (oils); c. are plant fats; d. include corn and olive oil, e. are nutritionally "GOOD" fat; ...
... unsaturated fats: a. have one or more double bond between the carbons in their fatty acid chains; b. are liquid at RT (oils); c. are plant fats; d. include corn and olive oil, e. are nutritionally "GOOD" fat; ...
DNA repair
... effects of even tiny changes to the DNA Red Blood Cells Hemoglobin Has a large protein component 2 beta globin chains A single base change -substitution causes the disease ...
... effects of even tiny changes to the DNA Red Blood Cells Hemoglobin Has a large protein component 2 beta globin chains A single base change -substitution causes the disease ...
57 chapter summary
... 4. Jimmy, a 12-year-old boy, was awakened suddenly by a loud crash. As he sat up in bed, straining to listen, his fright was revealed by his rapid breathing (hyperventilation), a breathing pattern effective in ridding the blood of CO2. At this point, was his blood pH rising or falling? 5. After you ...
... 4. Jimmy, a 12-year-old boy, was awakened suddenly by a loud crash. As he sat up in bed, straining to listen, his fright was revealed by his rapid breathing (hyperventilation), a breathing pattern effective in ridding the blood of CO2. At this point, was his blood pH rising or falling? 5. After you ...
chap1_SBI4U
... Cholesterol is a steroid that is: A component of cell membranes Present in the blood of animals The precursor of several other steroids, such as sex hormones testosterone and estrogen. Testosterone regulates sexual function and aids in building bone and muscle mass Estrogen regulates sex ...
... Cholesterol is a steroid that is: A component of cell membranes Present in the blood of animals The precursor of several other steroids, such as sex hormones testosterone and estrogen. Testosterone regulates sexual function and aids in building bone and muscle mass Estrogen regulates sex ...
WYSE – “Academic Challenge” - Worldwide Youth in Science and
... Please read the following instructions carefully. This is a timed test; any instructions from the test supervisor should be followed promptly. The test supervisor will give instructions for filling in any necessary information on the answer sheet. Most Academic Challenge sites will ask you to indica ...
... Please read the following instructions carefully. This is a timed test; any instructions from the test supervisor should be followed promptly. The test supervisor will give instructions for filling in any necessary information on the answer sheet. Most Academic Challenge sites will ask you to indica ...
Objective 2: demonstrate an understanding of the organization of
... Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of (ATP) adenosine triphosphate, used as a source of the chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in a range of other processes, such as signali ...
... Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of (ATP) adenosine triphosphate, used as a source of the chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in a range of other processes, such as signali ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Biochemistry
... the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans (e.g., crabs, lobsters and shrimps) and insects, the radula or tongues of mollusks, and the beaks and internal shells of cephalopods, including squid and octopuses. In terms of structure, chitin may be compared to the polysaccharide cellulose. The ...
... the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans (e.g., crabs, lobsters and shrimps) and insects, the radula or tongues of mollusks, and the beaks and internal shells of cephalopods, including squid and octopuses. In terms of structure, chitin may be compared to the polysaccharide cellulose. The ...
Biology Mrs. Riney 2009-2010
... Safety procedures are important when working a. in a laboratory. b. in the field. c. with animals. d. all of the above ...
... Safety procedures are important when working a. in a laboratory. b. in the field. c. with animals. d. all of the above ...
Ch 12.DNA and RNA.Biology.Landis
... 25. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promot ...
... 25. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promot ...
Chapter 2
... Carbon: unique element for basic building block of molecules of life • Carbon has 4 valence electrons: Can form four covalent bonds – Can form single , double, triple bonds. – Can form large, complex, branching molecules and rings. – Carbon atoms easily bond to C, N, O, H, P, S. • Huge variety of m ...
... Carbon: unique element for basic building block of molecules of life • Carbon has 4 valence electrons: Can form four covalent bonds – Can form single , double, triple bonds. – Can form large, complex, branching molecules and rings. – Carbon atoms easily bond to C, N, O, H, P, S. • Huge variety of m ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... functions depend on cellular functions that, in turn, result from chemical changes. B. Biochemistry is the study of chemistry in living organisms. II. Structure of Matter A. Elements and Atoms 1. Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space. 2. All matter is composed of elements. 3. Example ...
... functions depend on cellular functions that, in turn, result from chemical changes. B. Biochemistry is the study of chemistry in living organisms. II. Structure of Matter A. Elements and Atoms 1. Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space. 2. All matter is composed of elements. 3. Example ...
4. Bases are substances that combine with hydrogen ions.
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen an ...
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen an ...
1. Hydrogen ion concentration is typically measured in grams of ions
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, an ...
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, an ...
Chapter 2
... • Organic Substances= contains the atoms carbon (and hydrogen) • Small molecules (monomers or building blocks) are covalently bonded together to form large polymers or macromolecules • Water is usually involved in the formation and breakage of bonds between monomers – Dehydration Synthesis = removal ...
... • Organic Substances= contains the atoms carbon (and hydrogen) • Small molecules (monomers or building blocks) are covalently bonded together to form large polymers or macromolecules • Water is usually involved in the formation and breakage of bonds between monomers – Dehydration Synthesis = removal ...
1999 AP Biology Exam - Speedway High School
... (B) Chemiosmotic coupling (D) Photolysis (D) Fixation of CO2 (E) Transport of sugars 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved i ...
... (B) Chemiosmotic coupling (D) Photolysis (D) Fixation of CO2 (E) Transport of sugars 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved i ...
Hydrogen Bonds
... • When 2 amino acids are joined, the N from one’s amino group attaches to the C of the other’s carboxyl group. • Forms a peptide bond. • What is this process called? • What is released? • To join 3 amino acids, how many water are released? ...
... • When 2 amino acids are joined, the N from one’s amino group attaches to the C of the other’s carboxyl group. • Forms a peptide bond. • What is this process called? • What is released? • To join 3 amino acids, how many water are released? ...
Glossary - HDBuzz - Huntington`s disease research news.
... A description of HD and other diseases that are caused by abnormal expansion of stretches of DNA containing the sequence CAG repeated many times. Too many CAGs in a gene results in proteins with too many ‘glutamine’ building blocks, and glutamine is represented by the symbol Q. ...
... A description of HD and other diseases that are caused by abnormal expansion of stretches of DNA containing the sequence CAG repeated many times. Too many CAGs in a gene results in proteins with too many ‘glutamine’ building blocks, and glutamine is represented by the symbol Q. ...
Quiz 3 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... Last part of Ch. 21 (DNA and Biotechnology) Most of Ch. 4 (Body Organization, Homeostasis, and the Integumentary System) First part of Ch. 5 (The Skeletal System) ...
... Last part of Ch. 21 (DNA and Biotechnology) Most of Ch. 4 (Body Organization, Homeostasis, and the Integumentary System) First part of Ch. 5 (The Skeletal System) ...
To Do” List
... Read Chapter- 3.2–3.6 Bring any ?’s you have to class Watch CARBOHYDRATES part of BIOMOLECULES Powerpoint video by MON 9/19 BILL Carb modeling IN CLASS Carbohydrate comparison Carb ?’s DUE MON 9/22 Watch the LIPIDS part of Biomolecules Powerpoint video by WED 9/21 BILL Lipid modeling IN CLASS WED 9/ ...
... Read Chapter- 3.2–3.6 Bring any ?’s you have to class Watch CARBOHYDRATES part of BIOMOLECULES Powerpoint video by MON 9/19 BILL Carb modeling IN CLASS Carbohydrate comparison Carb ?’s DUE MON 9/22 Watch the LIPIDS part of Biomolecules Powerpoint video by WED 9/21 BILL Lipid modeling IN CLASS WED 9/ ...
Click here for powerpoint
... Once a copy is made in the nucleus mRNA goes to the ribosome TRANSLATION: ribosome decodes the instructions on mRNA and makes a protein ...
... Once a copy is made in the nucleus mRNA goes to the ribosome TRANSLATION: ribosome decodes the instructions on mRNA and makes a protein ...
Serrétia is made up of pure pharmaceutical grade
... on the silkworm’s living tissue. The powerful protein-dissolving properties of serrapeptase break down the protein molecules that make up the silk cocoon, allowing the silkworm larvae to escape unharmed. Enzymes are extremely specific and only target certain natural mediums. Serrapeptase is actively ...
... on the silkworm’s living tissue. The powerful protein-dissolving properties of serrapeptase break down the protein molecules that make up the silk cocoon, allowing the silkworm larvae to escape unharmed. Enzymes are extremely specific and only target certain natural mediums. Serrapeptase is actively ...