File
... providing the optimum conditions for the small intestine enzymes to fructose is sweeter than glucose less is needed to give the work at. ...
... providing the optimum conditions for the small intestine enzymes to fructose is sweeter than glucose less is needed to give the work at. ...
Topic 2 Notes
... Toxicity primarily results from cellular hypoxia caused by impedance of oxygen delivery. CO reversibly binds hemoglobin, resulting in relative anemia. Because it binds hemoglobin 230-270 times more avidly than oxygen, even small concentrations can result in significant levels of carboxyhemoglobin (H ...
... Toxicity primarily results from cellular hypoxia caused by impedance of oxygen delivery. CO reversibly binds hemoglobin, resulting in relative anemia. Because it binds hemoglobin 230-270 times more avidly than oxygen, even small concentrations can result in significant levels of carboxyhemoglobin (H ...
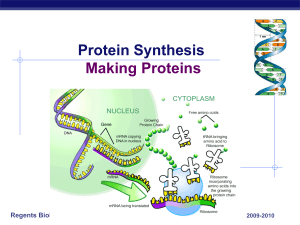
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms enzymes ...
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms enzymes ...
13 Protein Synthesis Making a Sentence Activity Key
... 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus with the transcribed code and goes to the cytoplasm (the rest of the classroom) to find the ribosome (the student desks). (1 point) 4. The m-RNA and the ribosome tell the t-RNA which anti-codons are needed (cards around the room). The ribosome writes the anti-codon in ...
... 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus with the transcribed code and goes to the cytoplasm (the rest of the classroom) to find the ribosome (the student desks). (1 point) 4. The m-RNA and the ribosome tell the t-RNA which anti-codons are needed (cards around the room). The ribosome writes the anti-codon in ...
12C Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels
... Respiration, burning of fossil fuels, volcanic activity: adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere Effect of deforestation Increased use of fossil fuels by humans adds a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Trees are some of the only organisms to remove the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Howeve ...
... Respiration, burning of fossil fuels, volcanic activity: adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere Effect of deforestation Increased use of fossil fuels by humans adds a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Trees are some of the only organisms to remove the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Howeve ...
Biology Review
... 4. How does the shape of an enzyme relate to enzyme function? 5. A nucleotide is made of a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a ___________. 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes repro ...
... 4. How does the shape of an enzyme relate to enzyme function? 5. A nucleotide is made of a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a ___________. 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes repro ...
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
... Now it is time to put all of the elements of transcription together. Write an essay below to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and underline each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3', termination, initiation RNA, polymer ...
... Now it is time to put all of the elements of transcription together. Write an essay below to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and underline each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3', termination, initiation RNA, polymer ...
Flashcard pictures hsa
... – Include: catalyst, enzyme substrate complex, enzyme, substrate, product, and denature ...
... – Include: catalyst, enzyme substrate complex, enzyme, substrate, product, and denature ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... Water – Helps maintain HOMEOSTASIS Polar, it has oppositely charged regions that allow soluble substances to be pulled apart (dissolved). Water and sugar are polar, oil is NONpolar. Universal Solvent – able to dissolve ALL polar molecules High Heat Capacity – water takes longer to cool down and heat ...
... Water – Helps maintain HOMEOSTASIS Polar, it has oppositely charged regions that allow soluble substances to be pulled apart (dissolved). Water and sugar are polar, oil is NONpolar. Universal Solvent – able to dissolve ALL polar molecules High Heat Capacity – water takes longer to cool down and heat ...
C: CHON F: C: energy Store,Supply,Structure P: Structural
... recycled, link metabolic pathways that need to take place in sequence (1st enzyme product becomes 2nd enzyme’s substrate…final enzyme’s product is 1st enzyme’s substrate/non comp inhibitor so end product doesn’t build up) o Prosthetic group- co e, permanent part of enzyme ...
... recycled, link metabolic pathways that need to take place in sequence (1st enzyme product becomes 2nd enzyme’s substrate…final enzyme’s product is 1st enzyme’s substrate/non comp inhibitor so end product doesn’t build up) o Prosthetic group- co e, permanent part of enzyme ...
Biology Review
... 4. How does the shape of an enzyme relate to enzyme function? 5. A nucleotide is made of a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a ___________. 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes repro ...
... 4. How does the shape of an enzyme relate to enzyme function? 5. A nucleotide is made of a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a ___________. 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes repro ...
Unit 2 The Chemistry of Life
... Amino acids are referred to as the “building blocks” of proteins. We use 20 different amino acids to build proteins in our bodies. Your body makes 12 and the others need to be ingested through meat, beans, and nuts. All have similar structures: hydrogen atom, an amino group (NH2), and a carb ...
... Amino acids are referred to as the “building blocks” of proteins. We use 20 different amino acids to build proteins in our bodies. Your body makes 12 and the others need to be ingested through meat, beans, and nuts. All have similar structures: hydrogen atom, an amino group (NH2), and a carb ...
Page 1 Edexcel 2011 Biology B2 Topic 1 The building blocks of
... cell research 1.22 Describe how the order of bases in a section of DNA decides the order of amino acids in the protein 1.23 Demonstrate an understanding of the stages of protein synthesis, including transcription and translation: a the production of complementary mRNA strand in the nucleus b the att ...
... cell research 1.22 Describe how the order of bases in a section of DNA decides the order of amino acids in the protein 1.23 Demonstrate an understanding of the stages of protein synthesis, including transcription and translation: a the production of complementary mRNA strand in the nucleus b the att ...
Biology Core Vocabulary List
... As matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization of living systems—cells, organs, organisms, and communities—and between living systems and the physical environment, chemical elements are recombined in different ways. Each recombination results in storage and dissipation of ...
... As matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization of living systems—cells, organs, organisms, and communities—and between living systems and the physical environment, chemical elements are recombined in different ways. Each recombination results in storage and dissipation of ...
Biology Core Vocabulary List
... As matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization of living systems—cells, organs, organisms, and communities—and between living systems and the physical environment, chemical elements are recombined in different ways. Each recombination results in storage and dissipation of ...
... As matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization of living systems—cells, organs, organisms, and communities—and between living systems and the physical environment, chemical elements are recombined in different ways. Each recombination results in storage and dissipation of ...
Bio 5, Physiology
... Physiological processes based upon properties and interactions of atoms, ions, and molecules. Water is the major constituent (compound) of the body (65-75% of body weight). 2/3 water intracellular; 1/3 extracellular (lymph, blood plasma, interstitial fluid, urine, saliva, etc..). I. Elements and Ato ...
... Physiological processes based upon properties and interactions of atoms, ions, and molecules. Water is the major constituent (compound) of the body (65-75% of body weight). 2/3 water intracellular; 1/3 extracellular (lymph, blood plasma, interstitial fluid, urine, saliva, etc..). I. Elements and Ato ...
Protein Synthesis
... which genes will be expressed (used to make a protein). This can be affected by the cell’s history and/or environment (g+e=p) Proteins may be overproduced, underproduced or produced at incorrect times ...
... which genes will be expressed (used to make a protein). This can be affected by the cell’s history and/or environment (g+e=p) Proteins may be overproduced, underproduced or produced at incorrect times ...
Cells - Dr Magrann
... Functions of Golgi complex: • When the proteins have finished their journey in the RER, their edges are exposed, and are vulnerable to oxidative damage. Therefore, they first go to the Golgi complex, which puts chemical bonds on the ends of the proteins. • Thus, in the Golgi complex, the proteins ar ...
... Functions of Golgi complex: • When the proteins have finished their journey in the RER, their edges are exposed, and are vulnerable to oxidative damage. Therefore, they first go to the Golgi complex, which puts chemical bonds on the ends of the proteins. • Thus, in the Golgi complex, the proteins ar ...
name date ______ period
... E-mail: [email protected] *** Reminder: If you are absent, you School Website: www.esperanzahs.com have three school days to Look for Freeman under “Teachers” make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 1 WEEK 16 TOPICS: BIOCHEMISTRY CA State Standards Covere ...
... E-mail: [email protected] *** Reminder: If you are absent, you School Website: www.esperanzahs.com have three school days to Look for Freeman under “Teachers” make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 1 WEEK 16 TOPICS: BIOCHEMISTRY CA State Standards Covere ...
File - SCIENTIST CINDY
... that lightening sparked chemical reactions in Earth’s early atmosphere. Some studies have speculated that lightning activity played a crucial role in the development of not only Earth's early atmosphere, but also early life. Scientists hypothesize that this created a “soup” of organic ...
... that lightening sparked chemical reactions in Earth’s early atmosphere. Some studies have speculated that lightning activity played a crucial role in the development of not only Earth's early atmosphere, but also early life. Scientists hypothesize that this created a “soup” of organic ...
Answer Key for Activity #1 - Center for Occupational Research and
... 2. True/False: DNA leaves the nucleus to be translated into proteins. False, DNA never leaves the nucleus. Only RNA will leave the nucleus. 3. Proteins are made in: a. The nucleus b. On the RNA c. Ribosomes d. Outside the cell Answer: C 4. True/False: Cells contain only the DNA that is relevant to t ...
... 2. True/False: DNA leaves the nucleus to be translated into proteins. False, DNA never leaves the nucleus. Only RNA will leave the nucleus. 3. Proteins are made in: a. The nucleus b. On the RNA c. Ribosomes d. Outside the cell Answer: C 4. True/False: Cells contain only the DNA that is relevant to t ...
RDM Day One Interpretation Questions 1.
... 4. Compare and contrast today's agarose gel electrophoresis with the SDSPAGE we did in PBC by stating whether the two are SIMILAR or DIFFERENT based on the following properties of SDS-PAGE: a. We used SDS-PAGE to separate molecules by size, such that the larger ones ran slower through the gel than t ...
... 4. Compare and contrast today's agarose gel electrophoresis with the SDSPAGE we did in PBC by stating whether the two are SIMILAR or DIFFERENT based on the following properties of SDS-PAGE: a. We used SDS-PAGE to separate molecules by size, such that the larger ones ran slower through the gel than t ...
Introduction: Key Ideas, Central Dogma and Educational Philosophy
... The relationship between the particular set of traits of an organism and its reproductive success is termed fitness. Darwin's famous dictum, “Survival of the fittest,” emphasizes the high stakes and inherent competition involved in differential reproductive success. Of course, “fitness” is a very co ...
... The relationship between the particular set of traits of an organism and its reproductive success is termed fitness. Darwin's famous dictum, “Survival of the fittest,” emphasizes the high stakes and inherent competition involved in differential reproductive success. Of course, “fitness” is a very co ...
An Introduction to Cells
... • Charges are separated creating a potential difference • Unequal charge across the plasma membrane is transmembrane potential • Resting potential ranges from –10 mV to –100 mV, depending on cell type ...
... • Charges are separated creating a potential difference • Unequal charge across the plasma membrane is transmembrane potential • Resting potential ranges from –10 mV to –100 mV, depending on cell type ...
B.4.A compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... Coevolution – the concurrent evolution of two species completely dependent on each other For example, if a plant is pollinated by one type of insect. If the insect population evolves, the plant population must evolve to maintain its existence. Adaptation – an inherited characteristic that allows for ...
... Coevolution – the concurrent evolution of two species completely dependent on each other For example, if a plant is pollinated by one type of insect. If the insect population evolves, the plant population must evolve to maintain its existence. Adaptation – an inherited characteristic that allows for ...