CHEMISTRY The Molecular Science
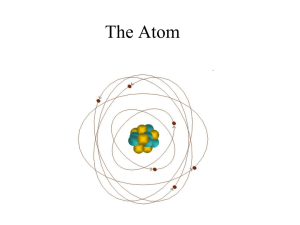
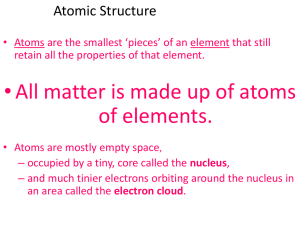
... • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of ea ...
... • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of ea ...
Lecture 2: Atoms - U of L Class Index
... Is there a simple reaction which only one isotope undergoes? What is the main difference between isotopes of an element? How can we take advantage of that difference? ...
... Is there a simple reaction which only one isotope undergoes? What is the main difference between isotopes of an element? How can we take advantage of that difference? ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Review Guide
... 1.1 Atoms are the smallest form of elements Answer each question. You may use your book, reading guides, or reinforcement guides to help you. Answers do not have to be in complete sentences. 1. What does the atomic number tell you? 2. Where are electrons located in an atom and what is their charge? ...
... 1.1 Atoms are the smallest form of elements Answer each question. You may use your book, reading guides, or reinforcement guides to help you. Answers do not have to be in complete sentences. 1. What does the atomic number tell you? 2. Where are electrons located in an atom and what is their charge? ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... What elements are made by small stars? What additional elements are made by large ...
... What elements are made by small stars? What additional elements are made by large ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... produces smaller and smaller groups of atoms, until you come to a single gold atom. Dividing that atom into two parts produces fragments that no longer have the properties of gold. ...
... produces smaller and smaller groups of atoms, until you come to a single gold atom. Dividing that atom into two parts produces fragments that no longer have the properties of gold. ...
Basic Chemistry Lesson - Agriculture Solutions
... Molecules are made up of two or more atoms that are held together by chemical bonds. Some molecules contain hundreds or even thousands of atoms that join together in chains that can attain considerable lengths. ...
... Molecules are made up of two or more atoms that are held together by chemical bonds. Some molecules contain hundreds or even thousands of atoms that join together in chains that can attain considerable lengths. ...
Thursday, October 31, 2013 D-day
... – Only group which has all three states of matter at STP. (what is STP?) – Most reactive nonmetals. – These elements are all brightly colored. ...
... – Only group which has all three states of matter at STP. (what is STP?) – Most reactive nonmetals. – These elements are all brightly colored. ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
What does an elements atomic mass tell us about the element?
... Atomic # = 19 Mass # = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
... Atomic # = 19 Mass # = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
chapter_3_study_guide
... Rutherford's Experiment Ernest Rutherford studied, among many other things, __________________ (α) particles. Alpha particles are made of two_____________________ and two ______________________. They can be emitted by radio active material and fly through the air. In Rutherford's experiment he bomba ...
... Rutherford's Experiment Ernest Rutherford studied, among many other things, __________________ (α) particles. Alpha particles are made of two_____________________ and two ______________________. They can be emitted by radio active material and fly through the air. In Rutherford's experiment he bomba ...
Chapter 5
... Charges are of two types: Positive and Negative Unlike charges attract and like charges repel Charges may be transferred by contact or induction The closer two object are, the greater the force of attraction ...
... Charges are of two types: Positive and Negative Unlike charges attract and like charges repel Charges may be transferred by contact or induction The closer two object are, the greater the force of attraction ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an
... __________; in particular, they all have the same _________. 3. Atoms of different elements are ____________; in particular, they have different masses. 4. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements in the compound are j ...
... __________; in particular, they all have the same _________. 3. Atoms of different elements are ____________; in particular, they have different masses. 4. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements in the compound are j ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... What elements are made by small stars? What additional elements are made by large ...
... What elements are made by small stars? What additional elements are made by large ...
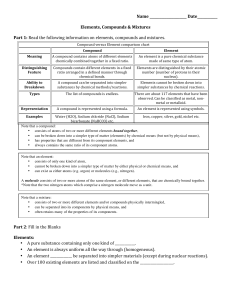
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
Elements Compounds Mixtures
... Subscript- tells the number of atoms in a compound ex. H2O CO2 Coefficient- tells the number of molecules ex. 2H2O Chemical Equation- describes the chemical reaction using symbols and formulas ...
... Subscript- tells the number of atoms in a compound ex. H2O CO2 Coefficient- tells the number of molecules ex. 2H2O Chemical Equation- describes the chemical reaction using symbols and formulas ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Synthesis – 2 substances (reactants) combine to form a new substance (product). – Substances are either atoms (elements) or compounds in this case. A + ...
... • Synthesis – 2 substances (reactants) combine to form a new substance (product). – Substances are either atoms (elements) or compounds in this case. A + ...
unit plan template
... What role do subatomic particles play with regard to mass, location, and charge? Explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity, mass, volume, and reactivity). Compare and contrast atoms of elements which exist as stable or unstable isotopes. What is the rol ...
... What role do subatomic particles play with regard to mass, location, and charge? Explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity, mass, volume, and reactivity). Compare and contrast atoms of elements which exist as stable or unstable isotopes. What is the rol ...
Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...