SS18A - Atoms, Isotopes and Ions
... In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers ...
... In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... can create two of the same elements with different mass #’s, which is the reason we have an atomic mass. ...
... can create two of the same elements with different mass #’s, which is the reason we have an atomic mass. ...
Name_________________________________
... under General Sites. Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers. 1) All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of ____________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ______________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter ...
... under General Sites. Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers. 1) All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of ____________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ______________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different c ...
... one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different c ...
Chemical Formulas
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
TEK 8.5D: Chemical Formulas
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... made up of? Are all atoms of silver the same? What part of Dalton’s theory supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
... made up of? Are all atoms of silver the same? What part of Dalton’s theory supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
Atomic Structure
... • John Dalton was the next scientist to propose a theory about the atom in the 19th century ...
... • John Dalton was the next scientist to propose a theory about the atom in the 19th century ...
Chapter 5 - Effingham County Schools
... The periodic table organizes the atoms of the elements by properties and atomic number. ---copy the information under the red heading “Reading the Periodic Table” on page 147 – The elements in a column are known as a group and they are labeled by a number at the top of the column. Elements in a grou ...
... The periodic table organizes the atoms of the elements by properties and atomic number. ---copy the information under the red heading “Reading the Periodic Table” on page 147 – The elements in a column are known as a group and they are labeled by a number at the top of the column. Elements in a grou ...
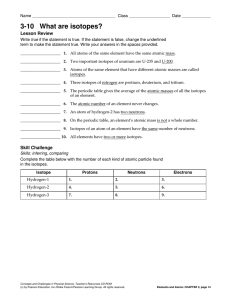
3-10 What are isotopes?
... 4. For which isotopes have scientists not been able to determine the atomic mass? Can you think of a reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According t ...
... 4. For which isotopes have scientists not been able to determine the atomic mass? Can you think of a reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According t ...
levels of organization and the atom
... Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. ...
... Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. ...
chapter_four
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE. Democritus thought of the world as being composed of very tiny "uncuttable" particles, which he called "atomoz" or atoms. These tiny, invisible particles were thought to be separated ...
... The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE. Democritus thought of the world as being composed of very tiny "uncuttable" particles, which he called "atomoz" or atoms. These tiny, invisible particles were thought to be separated ...
Development of atomic theory
... atomic theory. About 1807 he performed a great number of analyses of chemical compounds, and showed so many examples of the law of definite proportions that it could no longer be doubted. He also set about determining atomic weights and his first table, published in 1828, compared favourably with to ...
... atomic theory. About 1807 he performed a great number of analyses of chemical compounds, and showed so many examples of the law of definite proportions that it could no longer be doubted. He also set about determining atomic weights and his first table, published in 1828, compared favourably with to ...
Name ____ Date
... Recognize the origin and distribution of elements in the universe. Summarize the major experimental evidence that led to the development of various atomic models, both historic and current. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ...
... Recognize the origin and distribution of elements in the universe. Summarize the major experimental evidence that led to the development of various atomic models, both historic and current. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. • An Ion is an element with a number of electrons that differ from its number of protons. An ion is a charged atom. – Cation is ...
... number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. • An Ion is an element with a number of electrons that differ from its number of protons. An ion is a charged atom. – Cation is ...
Answers
... (d) Her claim is incorrect. [1] Lithium and sodium have similar but not the same chemical properties, as they only have the same number of outermost shell electrons, not the same number of electrons. [1] (e) Sodium melted into a silvery ball [1] which moved about very quickly on the water surface, [ ...
... (d) Her claim is incorrect. [1] Lithium and sodium have similar but not the same chemical properties, as they only have the same number of outermost shell electrons, not the same number of electrons. [1] (e) Sodium melted into a silvery ball [1] which moved about very quickly on the water surface, [ ...
Atoms have a structure that determines their properties.
... • Some groups of elements have characteristic sets of common physical and chemical properties, and are called chemical families. • The Periodic Table organizes elements in the following way: • Metals are found on the left side, non-metals on the right, and metalloids in between. • Chemical families ...
... • Some groups of elements have characteristic sets of common physical and chemical properties, and are called chemical families. • The Periodic Table organizes elements in the following way: • Metals are found on the left side, non-metals on the right, and metalloids in between. • Chemical families ...
10B Atoms and Isotopes
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called isotopes. Example: Sometimes the mass number for an element is included in its symbo ...
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called isotopes. Example: Sometimes the mass number for an element is included in its symbo ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
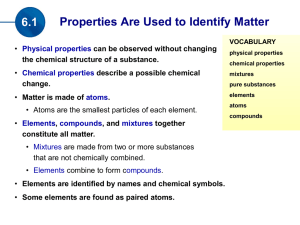
... ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the same substance after the change. _________________________ ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances ...
... ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the same substance after the change. _________________________ ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances ...
General_Chemistry_Text_Assignments_-_HOLT
... The chemical reaction where elements react (bond together) to form a compound is called synthesis. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The elements in a compound can only be separated by a chemical reaction. This reaction breaks the bonds between the eleme ...
... The chemical reaction where elements react (bond together) to form a compound is called synthesis. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The elements in a compound can only be separated by a chemical reaction. This reaction breaks the bonds between the eleme ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... When two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element in these compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... When two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element in these compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...