Quantum Atom
... Describes mathematically the properties of an electron Wave function (Ψ2) – series of solutions that describes the allowed energy levels for electrons Shows regions of probability of finding an electron Regions of high electron density have large values of Ψ2 ...
... Describes mathematically the properties of an electron Wave function (Ψ2) – series of solutions that describes the allowed energy levels for electrons Shows regions of probability of finding an electron Regions of high electron density have large values of Ψ2 ...
Lecture 5
... Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momentum, magnetic momentum (z-component of l), and spin quantum numbers of a single electron Orbital: specified by n and l Configuration - Assignment of electro ...
... Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momentum, magnetic momentum (z-component of l), and spin quantum numbers of a single electron Orbital: specified by n and l Configuration - Assignment of electro ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Outline for Concepts to Know 6.1 Wave
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
ppt
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS AND GRAVITATION
... the electronic charge in the Planck system of units (which treats Å and c as if they were both equal to 1, and ε0 as if it equaled 1/4π) - neither the charge nor the mass of the electron or any other other charged particle can actually be calculated in QED they have to be assumed. This is because th ...
... the electronic charge in the Planck system of units (which treats Å and c as if they were both equal to 1, and ε0 as if it equaled 1/4π) - neither the charge nor the mass of the electron or any other other charged particle can actually be calculated in QED they have to be assumed. This is because th ...
Quantum Theory 1 - Class Exercise 4
... Quantum Theory 1 - Class Exercise 4 1. Consider a Hamiltonian which describes a one dimensional system of two particles of masses m1 and m2 moving in a potential that depends only on the distance between them. Ĥ = ...
... Quantum Theory 1 - Class Exercise 4 1. Consider a Hamiltonian which describes a one dimensional system of two particles of masses m1 and m2 moving in a potential that depends only on the distance between them. Ĥ = ...
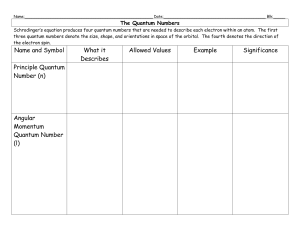
e-the-quantum-numberssv-2
... The Quantum Numbers Schrodinger’s equation produces four quantum numbers that are needed to describe each electron within an atom. The first three quantum numbers denote the size, shape, and orientations in space of the orbital. The fourth denotes the direction of the electron spin. ...
... The Quantum Numbers Schrodinger’s equation produces four quantum numbers that are needed to describe each electron within an atom. The first three quantum numbers denote the size, shape, and orientations in space of the orbital. The fourth denotes the direction of the electron spin. ...
Statistical description of systems of particles
... The evolution of a system in a microscopic state is completely deterministic both in quantum and classical mechanics. However, such information cannot be made available for a system with a large number of degrees of freedom. We consider a large number of identical systems (ensemble), all prepared su ...
... The evolution of a system in a microscopic state is completely deterministic both in quantum and classical mechanics. However, such information cannot be made available for a system with a large number of degrees of freedom. We consider a large number of identical systems (ensemble), all prepared su ...
7.2.4. Normal Ordering
... 7.2.4. Normal Ordering In the last section, we get rid of an infinite vacuum energy on the ground that only relative energies have physical meaning. However, if the structure of spacetime is to be determined by matter distribution, the vacuum must be at zero energy. Therefore, we must impose some ru ...
... 7.2.4. Normal Ordering In the last section, we get rid of an infinite vacuum energy on the ground that only relative energies have physical meaning. However, if the structure of spacetime is to be determined by matter distribution, the vacuum must be at zero energy. Therefore, we must impose some ru ...
Ch 6 Outline
... Quantum Calculate the energy of one photon of yellow light with a wavelength of 589nm. ...
... Quantum Calculate the energy of one photon of yellow light with a wavelength of 589nm. ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.