Transparancies for Feynman Graphs
... KG as old as QM, originally dismissed. No spin 0 particles known. Pion was only discovered in 1948. Dirac equation of 1928 described known spin ½ electron. Also described an anti-particle – Dirac boldly postulated existence of positron Discovered by Anderson in 1933 using a cloud chamber (C.Wilson) ...
... KG as old as QM, originally dismissed. No spin 0 particles known. Pion was only discovered in 1948. Dirac equation of 1928 described known spin ½ electron. Also described an anti-particle – Dirac boldly postulated existence of positron Discovered by Anderson in 1933 using a cloud chamber (C.Wilson) ...
final2012
... b) Which is the unstable isotope and why. c) Write down the decay mechanism that converts the unstable to the stable isotope. d) Calculate the nuclear radius for these isotopes given ...
... b) Which is the unstable isotope and why. c) Write down the decay mechanism that converts the unstable to the stable isotope. d) Calculate the nuclear radius for these isotopes given ...
Skill Assessment Sheet Modern Atomic Theory (Quantum Mechanics)
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
HWU4-21 QUESTION: The principal quantum number, n, describes
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
Consider the following solution to the hydrogen atom problem
... magnetic field, a result known as the Paschen-Bach effect is realized. In the PaschenBach effect the perturbation produced by the external magnetic field is large enough so that spin-orbit coupling can be ignored, but smaller than the Coulomb interaction, so the Paschen-Bach can be treated as a pert ...
... magnetic field, a result known as the Paschen-Bach effect is realized. In the PaschenBach effect the perturbation produced by the external magnetic field is large enough so that spin-orbit coupling can be ignored, but smaller than the Coulomb interaction, so the Paschen-Bach can be treated as a pert ...
HW Wk9 Solutions
... equal to that of the energy difference, “spin-flip” transitions can be induced. Find the wavelength of the photons needed for such transitions. Solution: (a) The difference in energy levels is !E = 2 µ B . The magnetic moment due to spin for the electron is µ = 5.79 ! 10 "5 eV T (Bohr magneton). Hen ...
... equal to that of the energy difference, “spin-flip” transitions can be induced. Find the wavelength of the photons needed for such transitions. Solution: (a) The difference in energy levels is !E = 2 µ B . The magnetic moment due to spin for the electron is µ = 5.79 ! 10 "5 eV T (Bohr magneton). Hen ...
Mass of electron m = 9.1. 10 kg
... Formulae and constants Mass of electron me = 9.1. 10 -31 kg Charge on electron = 1.6.10-19 C Planck’s Constant h= 6.626. 10-34 J.s =4.136. 10-15 eV.s h = h / 2! = 1.055.10 "34 J.s = 6.582.10 "16 eV.s ...
... Formulae and constants Mass of electron me = 9.1. 10 -31 kg Charge on electron = 1.6.10-19 C Planck’s Constant h= 6.626. 10-34 J.s =4.136. 10-15 eV.s h = h / 2! = 1.055.10 "34 J.s = 6.582.10 "16 eV.s ...
Chapter 7 -- Radiative Corrections: some formal developments Chapter 7:
... “We cheated four times in the last three chapters, stating (and sometimes motivating) a result but postponing its proof. Those results were: 1. decay rates 2. master formula 3. ward identity 4. subtraction for UV divergences ...
... “We cheated four times in the last three chapters, stating (and sometimes motivating) a result but postponing its proof. Those results were: 1. decay rates 2. master formula 3. ward identity 4. subtraction for UV divergences ...
Chapter 2 Part 1 ppt
... • When energy is absorbed, electrons move to higher orbits • When electrons move to lower orbits, energy is emitted • Equation predicted line spectra only for single-electron atoms • Adjustments were made to use elliptical orbits to better fit data • Ultimately failed - did not incorporate wave prop ...
... • When energy is absorbed, electrons move to higher orbits • When electrons move to lower orbits, energy is emitted • Equation predicted line spectra only for single-electron atoms • Adjustments were made to use elliptical orbits to better fit data • Ultimately failed - did not incorporate wave prop ...
DOC - 嘉義大學
... 3. (a) Explain why you observe two different types of diffraction patterns in the following two figures. (b) What does the observed spots or rings indicate? Explain briefly. (Hint: Exclude your answer for different materials) (20%) ...
... 3. (a) Explain why you observe two different types of diffraction patterns in the following two figures. (b) What does the observed spots or rings indicate? Explain briefly. (Hint: Exclude your answer for different materials) (20%) ...
Chemistry 681 Introduction to Quantum
... Chemistry 681 Introduction to Quantum Chemistry Fall 2003 ...
... Chemistry 681 Introduction to Quantum Chemistry Fall 2003 ...
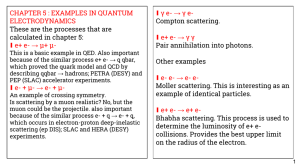
CHAPTER 5 : EXAMPLES IN QUANTUM γ e- → γ e- ∎ ELECTRODYNAMICS
... These were important experiments in the history of high-energy physics. From the particle data group, the figure shows the ratio R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. Neglecting QCD interactions we would just have R = cons ...
... These were important experiments in the history of high-energy physics. From the particle data group, the figure shows the ratio R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. Neglecting QCD interactions we would just have R = cons ...
Lecture notes, part 6
... What is the probability that one of the HO has a quantum number of 0? To answer this we use the fundamental postulate, which says that ...
... What is the probability that one of the HO has a quantum number of 0? To answer this we use the fundamental postulate, which says that ...
Notes
... There are various selection rules pertaining to how elections change orbits and produce spectral lines. For instance, if Δ 1 the transition is forbidden and occurs with very low probability. The photon carries away the angular momentum lost in the allowed transition as spin. For complex atoms, ...
... There are various selection rules pertaining to how elections change orbits and produce spectral lines. For instance, if Δ 1 the transition is forbidden and occurs with very low probability. The photon carries away the angular momentum lost in the allowed transition as spin. For complex atoms, ...
3.4oquantum.4u
... we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels during the emission of atomic spectra. ...
... we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels during the emission of atomic spectra. ...
Modern Physics
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
Chemistry 2000 Review: quantum mechanics of
... This equation was know to belong to a special class known as an eigenvector equation: an operator acts on a function (ψ) and generates a scalar times the same function Ψ is known as the wavefunction of the electron: there are an infinite number of such wavefunctions, each of which is characterized b ...
... This equation was know to belong to a special class known as an eigenvector equation: an operator acts on a function (ψ) and generates a scalar times the same function Ψ is known as the wavefunction of the electron: there are an infinite number of such wavefunctions, each of which is characterized b ...
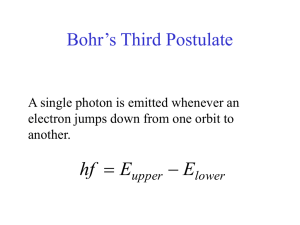
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... 2. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Zeta rays are charged particles or e/m waves? Could this experiment distinguish between neutral particles and an e/m wave? 3. If a metal surf ...
... 2. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Zeta rays are charged particles or e/m waves? Could this experiment distinguish between neutral particles and an e/m wave? 3. If a metal surf ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.