The Shroedinger/Modern Model of the Atom
... • The act of observing changes an object. • To see things, we must bounce light off of them. • To observe an electron, we have to bounce light off of it. • The light would move the electron so much that we would not be able to tell where it was, or how fast it was going. • Think of hot tea and a col ...
... • The act of observing changes an object. • To see things, we must bounce light off of them. • To observe an electron, we have to bounce light off of it. • The light would move the electron so much that we would not be able to tell where it was, or how fast it was going. • Think of hot tea and a col ...
The Fine Structure Constant and Electron (g‐2) Factor: Questions
... The third term in the expression for E(n,ms) is the leading relativistic correction to the energy levels, and δ is defined as ...
... The third term in the expression for E(n,ms) is the leading relativistic correction to the energy levels, and δ is defined as ...
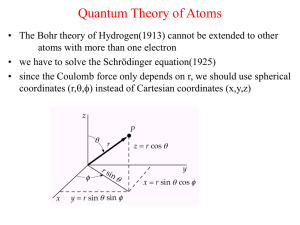
Quantum Theory of Atoms
... m= -l,(-l+1),…0,1,2,…,l => 2l+1 values of m for a given l • n is the principal quantum number and is associated with the distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum numbe ...
... m= -l,(-l+1),…0,1,2,…,l => 2l+1 values of m for a given l • n is the principal quantum number and is associated with the distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum numbe ...
ppt - HEP Educational Outreach
... small, that perhaps in the course of the hour one of the atomsdecays, but also, with equal probability, perhaps none; if it happens, the counter tube discharges andthrough a relay releases a hammer which shatters a small flask of hydrocyanic acid. If one has left thisentire system to itself for an h ...
... small, that perhaps in the course of the hour one of the atomsdecays, but also, with equal probability, perhaps none; if it happens, the counter tube discharges andthrough a relay releases a hammer which shatters a small flask of hydrocyanic acid. If one has left thisentire system to itself for an h ...
Triggered entangled photon-pairs from single quantum dots and
... During the last few years remarkable progress has been achieved in the development of single and coupled semiconductor quantum dots and high-quality micro-cavities which might open the way for new applications in the field of quantum information processing. Here we demonstrate triggered polarization ...
... During the last few years remarkable progress has been achieved in the development of single and coupled semiconductor quantum dots and high-quality micro-cavities which might open the way for new applications in the field of quantum information processing. Here we demonstrate triggered polarization ...
Chap 2 Solns
... 2.4 (a) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (b) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ...
... 2.4 (a) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (b) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.