Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... formula for salt, sugar, and oxygen gas – Salt NaCl; Sugar C6H12O6; ...
... formula for salt, sugar, and oxygen gas – Salt NaCl; Sugar C6H12O6; ...
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE chapter three
... _____ electrons are located in the outermost energy level of an atom. They determine the chemical properties of an element. ...
... _____ electrons are located in the outermost energy level of an atom. They determine the chemical properties of an element. ...
File
... • Heterogeneous Mixture-a mixture in which the presence of a t least two different substances is visible to the eye. • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbo ...
... • Heterogeneous Mixture-a mixture in which the presence of a t least two different substances is visible to the eye. • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbo ...
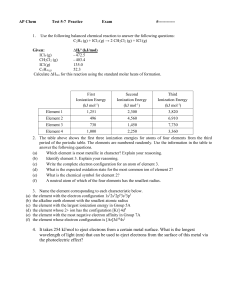
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... 3. Name the element corresponding to each characteristic below. the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 th ...
... 3. Name the element corresponding to each characteristic below. the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 th ...
Extra Credit Test Review
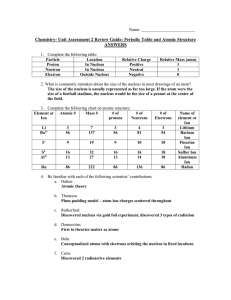
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum Numbers (n,l,ml,ms), when they are allowed, how they describe the electron state, and how they relate to: Energy levels, orbitals (number allowed, shapes, sizes), elec ...
... Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum Numbers (n,l,ml,ms), when they are allowed, how they describe the electron state, and how they relate to: Energy levels, orbitals (number allowed, shapes, sizes), elec ...
Chemical Bonding
... • Atoms are the smallest units of matter. They are the building blocks of everything. • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
... • Atoms are the smallest units of matter. They are the building blocks of everything. • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
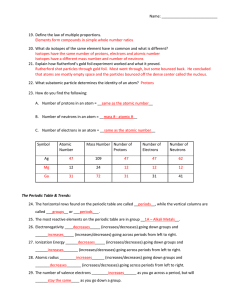
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
Chemical Change
... Negatively charged particles with almost no mass that circle the nucleus at different energy levels ...
... Negatively charged particles with almost no mass that circle the nucleus at different energy levels ...
19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 13. Moseley arranged elements by increasing atomic number but Mendeleev arranged elements by increasing atomic mass. 14. If Fluorine gained a proton, it would be called Neon. If it gained an electron, it would be called a Fluorine ion or F-. 15. Metals tend to give away electrons when bonding, formi ...
... 13. Moseley arranged elements by increasing atomic number but Mendeleev arranged elements by increasing atomic mass. 14. If Fluorine gained a proton, it would be called Neon. If it gained an electron, it would be called a Fluorine ion or F-. 15. Metals tend to give away electrons when bonding, formi ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element. ...
... The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element. ...
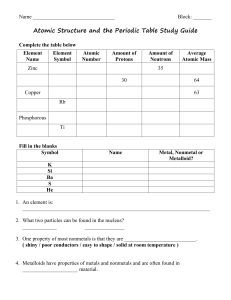
Chemistry Test Review – 8th Science Vocabulary: Element atom
... The difference between mass number and atomic mass The charge and location of each type of subatomic particle (proton, neutron, electron) Electrons Which ones have the most energy Which ones have the least energy Trends in the Periodic Table Atomic Radius Valence electrons Characteristics of Metals ...
... The difference between mass number and atomic mass The charge and location of each type of subatomic particle (proton, neutron, electron) Electrons Which ones have the most energy Which ones have the least energy Trends in the Periodic Table Atomic Radius Valence electrons Characteristics of Metals ...
CHAPTER6_MEET_THE_ELEMENTS
... Extraction - is the mechanical and chemical processes used to remove metals from the minerals and ores and that contain them. There are 2 main components of extraction: 1. Concentration – removing as much rock as possible, so that the remaining mixture contains as much of the mineral as possible. Th ...
... Extraction - is the mechanical and chemical processes used to remove metals from the minerals and ores and that contain them. There are 2 main components of extraction: 1. Concentration – removing as much rock as possible, so that the remaining mixture contains as much of the mineral as possible. Th ...
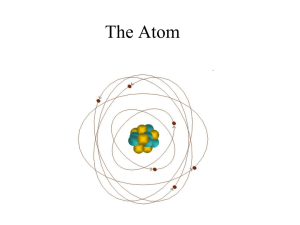
The Atom - Riverside City College
... • Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule: a molecule made of two atoms that are different elements – NO ...
... • Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule: a molecule made of two atoms that are different elements – NO ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
Chapter 2
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
Page 233 - ClassZone
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...