* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
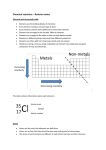
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide Key Vocabulary 1) atom 2) compound 3) period 4) neutralization 5) subscript 6) chemical formula 7) chemical reaction 8) conservation of mass 9) reactant 10) product 11)chemical equation 12) coefficient 13) proton 14) neutron 15) electron 16) ionic bond 17) covalent bond Content 1) difference between an element and compound – A compound is made of one or more elements that are bonded together; An element is a pure, single substance made of one type of atom. 2) examples of compounds – CO2, C6H12O6, NaCl, N2, O2, Fe2O3, H2O 3) where metals and nonmetals are found on the periodic table – Metals are to the left of the zig-zag line; Non-metals are to the right. 4) examples of physical and chemical properties – Physical Properties: Luster; Hardness; Color; Conductivity; Density; Malleable; Ductile; States of Matter; Boiling Point. Chemical: Ability to rust; Ability to Burn. 5) examples of physical changes – Breaking glass; melting ice; Cutting; Boiling 6) difference between physical and chemical changes – In a physical change, nothing new is formed. In a chemical change, a new substance is formed. 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have similar properties. 8) how to find elements on the periodic table – You can use the group and period that the element is in, it’s atomic number, or it’s atomic mass. 9) examples of heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures – heterogeneous: trail mix; chex mix; salad; fruit cups; skittles; Italian salad dressing. Homogeneous: Blood, air, salt water, coffee, sweet tea, kool aid. 10) properties of acids – Sour taste; pH below 7; Corrode metals; React with bases 11)properties of bases – Bitter taste; slippery; pH above 7; react with acids 12) pH scale - what is it and what does it tell us – tells how strongly acidic or basic or neutral a substance is. A scale from 0-14. 13) what it means when an equation is “balanced” – The number of atoms and types of atoms are the same on both sides. 14) symbols for common elements – see your study guide for quiz 2 15) formula for salt, sugar, and oxygen gas – Salt NaCl; Sugar C6H12O6; Oxygen O2 16) structure of chemical equations – reactants products (includes formula, coefficients, and subscripts) 17) where protons, neutrons (nucleus), and electrons (surrounding shells) are found in atoms 18) what information can you find in each block of the periodic table – atomic number, symbol, element name, atomic mass 19) balancing equations – see worksheet 20) how balanced equations support the law of conservation of mass – The laws says that no matter can be created or destroyed. Therefore, each side of the equation must be the same. 21) two differences between ionic (electrons are taken from metals and given to non-metal) and covalent (shared between non-metals) bonds 22) using subscripts to find the number of atoms – The subscript gives you the number of atoms of the element it comes directly after. H2O has 2 hydrogen atoms. 23) formula for volume – L x W x H 24) formula for density and units – M/V with g/mL for units 25) how to know if an object will float or sink – It will float if its density is less than the liquid. It will sink if its density is more than the liquid.