RAD 354 Chapt 3 Structure of Matter
... • The atom is the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of the element – 112 elements have been identified 92 are natural 20 were artificially produced ...
... • The atom is the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of the element – 112 elements have been identified 92 are natural 20 were artificially produced ...
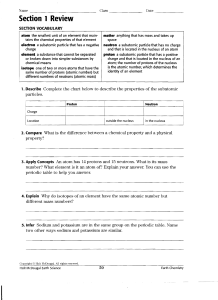
Section 1 Review
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
Test Review Answers File
... Unit 2.1 Test Review-Answer Key 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the first periodic table? By atomic mass 2. What did Mendeleev’s arrangement of the elements lead scientists to? Predict the properties of unknown elements 3. Study the element key boxes for Tellurium (Te) and Iodine (I). Tellurium is in G ...
... Unit 2.1 Test Review-Answer Key 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the first periodic table? By atomic mass 2. What did Mendeleev’s arrangement of the elements lead scientists to? Predict the properties of unknown elements 3. Study the element key boxes for Tellurium (Te) and Iodine (I). Tellurium is in G ...
Atomic Theory
... 1. Most natural materials are mixtures of pure substances. 2. Pure substances are elements or compounds. 3. Law of constant composition-a compound always has the same composition. ...
... 1. Most natural materials are mixtures of pure substances. 2. Pure substances are elements or compounds. 3. Law of constant composition-a compound always has the same composition. ...
Atomic History
... multiple proportions. law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All el ...
... multiple proportions. law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All el ...
Atomic History notes
... multiple proportions. law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All el ...
... multiple proportions. law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All el ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... between a metal and nonmetal. • The metal gives away electrons, and the nonmetal picks them up (thus making them both ions ...
... between a metal and nonmetal. • The metal gives away electrons, and the nonmetal picks them up (thus making them both ions ...
Name: Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide Who was the Greek
... 28. The nuclei of isotopes contain different numbers of ____________________. ...
... 28. The nuclei of isotopes contain different numbers of ____________________. ...
Atomic Theory - rlhonorschem4
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
Unit 3 Notebook Notes
... 1808 John Dalton developed the “Atomic Theory” based on Experiments 1. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, ...
... 1808 John Dalton developed the “Atomic Theory” based on Experiments 1. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another ...
... and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... 32. What did the following say about orbital systems: a. Hund b. Aufbau c. Pauli 33. List parts of the visible electromagnetic spectrum & label in terms of frequency, wavelength, & energy. 34. What is the formula for the speed of light? 35. How is a photon created as an atom is heated? 36. Accordin ...
... 32. What did the following say about orbital systems: a. Hund b. Aufbau c. Pauli 33. List parts of the visible electromagnetic spectrum & label in terms of frequency, wavelength, & energy. 34. What is the formula for the speed of light? 35. How is a photon created as an atom is heated? 36. Accordin ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Chemical Symbols Chemical symbol – an abbreviated way to write the name of an element. -example: Carbon – C Proton – positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutron – neutrally charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleu ...
... Chemical Symbols Chemical symbol – an abbreviated way to write the name of an element. -example: Carbon – C Proton – positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutron – neutrally charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleu ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... (1) electrons, only (2) neutrons, only (3) protons and electrons (4) protons and neutrons 3. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom of sulfur in the ground state? ...
... (1) electrons, only (2) neutrons, only (3) protons and electrons (4) protons and neutrons 3. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom of sulfur in the ground state? ...
The History of the Atom Carousel Who-What-When
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
Chapter 4 - Bakersfield College
... 1. All matter is made up of very tiny, indivisible particles (atoms). 2. All atoms of a given element have the same chemical properties. 3. Compounds are made up of two or more different kinds of atoms. A compound has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
... 1. All matter is made up of very tiny, indivisible particles (atoms). 2. All atoms of a given element have the same chemical properties. 3. Compounds are made up of two or more different kinds of atoms. A compound has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
Regents Chemistry Review
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...