The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, t ...
... Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, t ...
Chapter 18
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
Chemical Bonds
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
A review of Atoms
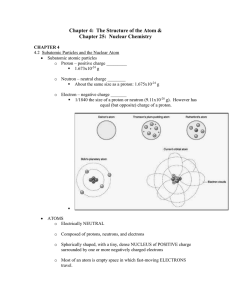
... nucleus.Here it is shown as a small dot circling the nucleus. There are the same number of electrons and protons in a neutral atom. ...
... nucleus.Here it is shown as a small dot circling the nucleus. There are the same number of electrons and protons in a neutral atom. ...
File
... This is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an element and is normally listed on the bottom of each elements’ box on the periodic table ...
... This is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an element and is normally listed on the bottom of each elements’ box on the periodic table ...
key - Greenslime.info
... From the one’s digit of the group number. For example, elements in group 1 have one valence electron, and elements in group 13 have three valance electrons. The only exception is helium, which only has two valence electrons, even though it is in group 18. ...
... From the one’s digit of the group number. For example, elements in group 1 have one valence electron, and elements in group 13 have three valance electrons. The only exception is helium, which only has two valence electrons, even though it is in group 18. ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
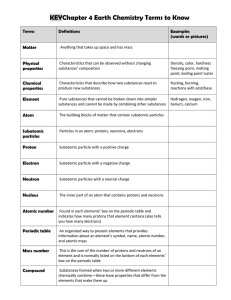
... Know definitions for the following vocabulary words: matter spectral line atom energy level nucleus electron cloud proton electromagnetic spectrum neutron charge electron Thomson’s atomic model proportion Rutherford’s atomic model Democritus Bohr’s atomic model Dalton element Lavoisier atomic number ...
... Know definitions for the following vocabulary words: matter spectral line atom energy level nucleus electron cloud proton electromagnetic spectrum neutron charge electron Thomson’s atomic model proportion Rutherford’s atomic model Democritus Bohr’s atomic model Dalton element Lavoisier atomic number ...
File
... What element is it and where is it on the PT? What is the atomic # of the element? This is equal to the # of protons. Is the atom neutral? Does it have a charge? If not, the # of electrons is equal to the # of protons. If I am given the mass number, I just have to subtract the # of protons from ...
... What element is it and where is it on the PT? What is the atomic # of the element? This is equal to the # of protons. Is the atom neutral? Does it have a charge? If not, the # of electrons is equal to the # of protons. If I am given the mass number, I just have to subtract the # of protons from ...
Atom through Periodic Table Study Guide
... 16. Periods go ____(which way) on the periodic table, while rows go ____(which way). 17. Which family has elements that are highly reactive non-metals and has 7 valence electrons? 18. The noble gases are found in which column of the periodic table? 19. The noble gases are non-reactive- they won’t b ...
... 16. Periods go ____(which way) on the periodic table, while rows go ____(which way). 17. Which family has elements that are highly reactive non-metals and has 7 valence electrons? 18. The noble gases are found in which column of the periodic table? 19. The noble gases are non-reactive- they won’t b ...
Periodic Table of Elements * Study Guide
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
GCSE Chemistry coursework: Research Study on `Francium and the
... model says that an atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that have circular orbits around the nucleus. This model was inspired by the workings of the solar system and says that electrons are kept attracted to the nucleus by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. [9] ...
... model says that an atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that have circular orbits around the nucleus. This model was inspired by the workings of the solar system and says that electrons are kept attracted to the nucleus by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. [9] ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
Fall Review
... names of families and groups...alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanide and actinide series, coinage metals, metalloids, essential elements trends in atomic / ionic radius down a column (family) atoms get larger due to increasing shielding effect acr ...
... names of families and groups...alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanide and actinide series, coinage metals, metalloids, essential elements trends in atomic / ionic radius down a column (family) atoms get larger due to increasing shielding effect acr ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a table of elements, arranged by atomic number, that shows the patterns in their properties. ...
... 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a table of elements, arranged by atomic number, that shows the patterns in their properties. ...
Introduction to Atomic Theory
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... have full outside energy levels do not react with other elements ...
... have full outside energy levels do not react with other elements ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...