Chem vocab quiz definitons
... Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more elements chemically bound together. Pure substances are bo ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more elements chemically bound together. Pure substances are bo ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ● Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers ○ All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons ○ The number of neutrons can vary ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37 ...
... ● Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers ○ All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons ○ The number of neutrons can vary ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37 ...
Chapter 21 Powerpoint: Nuclear Chemistry
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
Exam 1 Review Questions
... Covalent compounds contain both metal and nonmetal atoms. Ionic compounds are made of molecules. Dmitri Mendeleev published the first modern atomic theory in 1805. Fluorine is found as a metal in its pure form. Francium chloride FrCl is a covalent compound. Graphite is a compound containing carbon a ...
... Covalent compounds contain both metal and nonmetal atoms. Ionic compounds are made of molecules. Dmitri Mendeleev published the first modern atomic theory in 1805. Fluorine is found as a metal in its pure form. Francium chloride FrCl is a covalent compound. Graphite is a compound containing carbon a ...
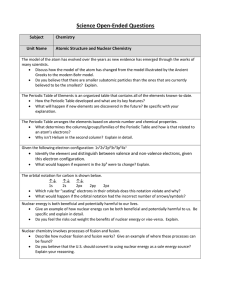
Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry OEQs
... How the Periodic Table developed and what are its key features? What will happen if new elements are discovered in the future? Be specific with your explanation. The Periodic Table arranges the elements based on atomic number and chemical properties. What determines the columns/groups/families ...
... How the Periodic Table developed and what are its key features? What will happen if new elements are discovered in the future? Be specific with your explanation. The Periodic Table arranges the elements based on atomic number and chemical properties. What determines the columns/groups/families ...
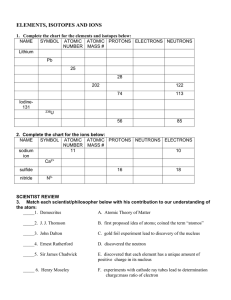
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __ ...
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __ ...
Properties of matter student notes[1]
... Element = Matter made of only _______________ kind of atom. Ex. Oxygen Can be naturally made or man-made. ...
... Element = Matter made of only _______________ kind of atom. Ex. Oxygen Can be naturally made or man-made. ...
Chemistry Exam Review
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properties of elements tends to repeat over specific atomic number intervals Law of definite prop ...
... The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properties of elements tends to repeat over specific atomic number intervals Law of definite prop ...
Chemistry Notes
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
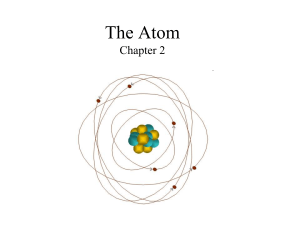
The Atom Chapter 2
... • Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule: a molecule made of two atoms that are different elements – NO ...
... • Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule: a molecule made of two atoms that are different elements – NO ...
– Units 5-7 Review Honors Chemistry Unit 5
... Define valence electron. How is the number of valence electrons of an element related to the group/family number? ...
... Define valence electron. How is the number of valence electrons of an element related to the group/family number? ...
Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide
... Ionization refers to the process of losing or gaining electrons. The valence electron of a lithium atom is easily removed to form a lithium ion with a charge of 1+. A lithium ion is much less reactive than a lithium atom because it has a full outermost energy level. Isotopes of an element have the s ...
... Ionization refers to the process of losing or gaining electrons. The valence electron of a lithium atom is easily removed to form a lithium ion with a charge of 1+. A lithium ion is much less reactive than a lithium atom because it has a full outermost energy level. Isotopes of an element have the s ...












![Properties of matter student notes[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009076956_1-3293fc3fecf578fd34e3f0f2700d471f-300x300.png)