Movement
... aspect of grammar in many languages and we will see many instances of it in today’s discussion. We will see the main theoretical considerations relating to movement processes and which play a role in the description of virtually all English sentences. We can see that it can be applied to a lot of li ...
... aspect of grammar in many languages and we will see many instances of it in today’s discussion. We will see the main theoretical considerations relating to movement processes and which play a role in the description of virtually all English sentences. We can see that it can be applied to a lot of li ...
What is a Phrase? What is a Clause?
... Independent Clause Dependent Clause Independent Clause Contains a subject and a verb Makes a complete statement or idea Can stand alone as a sentence Example: This school is a technical college. Dependent Clause Contains a subject and a verb Does not make a complete statement or idea ...
... Independent Clause Dependent Clause Independent Clause Contains a subject and a verb Makes a complete statement or idea Can stand alone as a sentence Example: This school is a technical college. Dependent Clause Contains a subject and a verb Does not make a complete statement or idea ...
Chapter 4
... structure ,the original XP rule can be expanded as follows so that it allows the various options. The Expanded XP Rule XP→ (Specifier)(Mod) X (Complement﹡)(Mod) ...
... structure ,the original XP rule can be expanded as follows so that it allows the various options. The Expanded XP Rule XP→ (Specifier)(Mod) X (Complement﹡)(Mod) ...
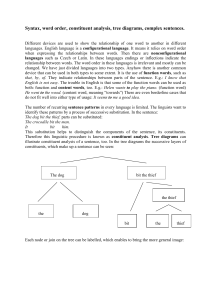
Syntax, word order, constituent analysis, tree diagrams
... Syntax, word order, constituent analysis, tree diagrams, complex sentences. Different devices are used to show the relationship of one word to another in different languages. English language is a configurational language. It means it relies on word order when expressing the relationships between wo ...
... Syntax, word order, constituent analysis, tree diagrams, complex sentences. Different devices are used to show the relationship of one word to another in different languages. English language is a configurational language. It means it relies on word order when expressing the relationships between wo ...
Answer - Philadelphia University Jordan
... 2. Dialect: is a language variety , mutually intelligible forms of a language that differ in systematic ways from each other used in a certain area as a means of communication e.g., American English. British English. OE. MidE, ModE. ...
... 2. Dialect: is a language variety , mutually intelligible forms of a language that differ in systematic ways from each other used in a certain area as a means of communication e.g., American English. British English. OE. MidE, ModE. ...
What sentence final particles tell us about the structure of
... Sentence final particles, such as Canadian eh, have long been explored in East Asian languages: there is a rich tradition of scholarship on their grammatical properties. This tradition spans from early descriptive grammatical work to current formal analyses in the generative tradition. In contrast, ...
... Sentence final particles, such as Canadian eh, have long been explored in East Asian languages: there is a rich tradition of scholarship on their grammatical properties. This tradition spans from early descriptive grammatical work to current formal analyses in the generative tradition. In contrast, ...
Lecture 2
... described and also how these objects relate to the speaker • Basis types of specifiers – Ordinals (e.g., first, second) – Cardinals (e.g., one, two) – Determiners (see next slide) ...
... described and also how these objects relate to the speaker • Basis types of specifiers – Ordinals (e.g., first, second) – Cardinals (e.g., one, two) – Determiners (see next slide) ...
Syntax - edms411-2
... What will Tiny Abner put on his head? Vs. what will Tiny Abner put a hat on his head? Katznelson is expected to run vs. Katznelson is expected will run ...
... What will Tiny Abner put on his head? Vs. what will Tiny Abner put a hat on his head? Katznelson is expected to run vs. Katznelson is expected will run ...
Declarative sentence
... Balanced/Parallel • 2 or more words or constructions must be in the same grammatical form (i.e., verbs, infinitives, participles, phrases, etc.) ...
... Balanced/Parallel • 2 or more words or constructions must be in the same grammatical form (i.e., verbs, infinitives, participles, phrases, etc.) ...
Chapter Two Syntactic Categories
... originally based at (V) position lower on the tree (at deep-structure) then it moves to (I) position to be inflected with tense, leaving a trace (t). Then the noun phrase in the specifier of VP position moves to IP specifier position then it terminates at the specifier of CP leaving traces on the IP ...
... originally based at (V) position lower on the tree (at deep-structure) then it moves to (I) position to be inflected with tense, leaving a trace (t). Then the noun phrase in the specifier of VP position moves to IP specifier position then it terminates at the specifier of CP leaving traces on the IP ...
Syntactic Analysis
... is simple. A constituent is any syntactic unit, regardless of length or syntactic category. A single word is the smallest possible constituent belonging to a particular syntactic category. So if a single word can substitute for a string of several words, then that's evidence that the single word and ...
... is simple. A constituent is any syntactic unit, regardless of length or syntactic category. A single word is the smallest possible constituent belonging to a particular syntactic category. So if a single word can substitute for a string of several words, then that's evidence that the single word and ...
Lecture 3. Phrases
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
Croft (2000: 65) - Noun, verb and adjective are not categories of
... it does not say anything about the boundary of a category […]. In fact, the universal typological theory of parts of speech defines only prototypes for the parts of speech; it does not define boundaries. Boundaries are features of language-particular categories. ...
... it does not say anything about the boundary of a category […]. In fact, the universal typological theory of parts of speech defines only prototypes for the parts of speech; it does not define boundaries. Boundaries are features of language-particular categories. ...
Introduction to Computational Natural Language
... phrase is. Roughly. the underlying principles that determine how the ingredients of a noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase (etc.) interact, are identical. Moreover, these principles apply cross linguistically. In English the head of a phrase (e.g. a verb or a preposition) comes before its ...
... phrase is. Roughly. the underlying principles that determine how the ingredients of a noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase (etc.) interact, are identical. Moreover, these principles apply cross linguistically. In English the head of a phrase (e.g. a verb or a preposition) comes before its ...
Morph & Synt supertut slides - Linguistics and English Language
... The verb in the main sentence, wants, takes a nonfinite clause as its complement here: a VP headed by the infinitive to go. ...
... The verb in the main sentence, wants, takes a nonfinite clause as its complement here: a VP headed by the infinitive to go. ...
PSY 369: Psycholinguistics - Illinois State University Department of
... Isolating languages: no endings, just word order (e.g., ...
... Isolating languages: no endings, just word order (e.g., ...
Statistical Natural Language Procesing: linguistic
... Tightly related verb arguments are called complements but less tightly related ones are called adjuncts. Prototypical examples of adjuncts tell us time, place, or manner of the action or state described by the verb. Verbs are classified according to the type of complements they permit. This called s ...
... Tightly related verb arguments are called complements but less tightly related ones are called adjuncts. Prototypical examples of adjuncts tell us time, place, or manner of the action or state described by the verb. Verbs are classified according to the type of complements they permit. This called s ...
that Mary helped George
... In earlier approaches to syntax, there was an attempt to produce an accurate description of the sequence of ordering of elements in a sentence. ...
... In earlier approaches to syntax, there was an attempt to produce an accurate description of the sequence of ordering of elements in a sentence. ...
Syntax
... Since matrix clauses can also be divided along the same lines, CP is also present and determines clause type in matrix contexts (even though there is no overt complementizer) ...
... Since matrix clauses can also be divided along the same lines, CP is also present and determines clause type in matrix contexts (even though there is no overt complementizer) ...
1 - Haiku
... A drop of ink, falling like dew upon a thought, can make millions think. 13. Introductory participles, singly or in a series: Perservering , determined to succeed, the pioneers forged a civilization out of the wilderness. 14. A single modifier out of place for emphasis: Below, the traffic looked lik ...
... A drop of ink, falling like dew upon a thought, can make millions think. 13. Introductory participles, singly or in a series: Perservering , determined to succeed, the pioneers forged a civilization out of the wilderness. 14. A single modifier out of place for emphasis: Below, the traffic looked lik ...
Syntax: samenvatting Category Main lexical categories Noun (N
... Wh-in situ languages (like Chinese): the Wh-phrase moves up (and back) to mark a clause as a question. The English what in “Who bought what” is comparable. OVERT: English, Dutch, French, … COVERT: Chinese, multiple questions in Dutch, English, ... Successive cyclic movement Partial Wh-movement indic ...
... Wh-in situ languages (like Chinese): the Wh-phrase moves up (and back) to mark a clause as a question. The English what in “Who bought what” is comparable. OVERT: English, Dutch, French, … COVERT: Chinese, multiple questions in Dutch, English, ... Successive cyclic movement Partial Wh-movement indic ...
Lecture 07
... permits a complement: -the topmost clause contains the verb think -its complement clause contains the verb say -its complement clause contains the verb report ...
... permits a complement: -the topmost clause contains the verb think -its complement clause contains the verb say -its complement clause contains the verb report ...
Basic ideas of syntax
... Syntax deals with sentences—specifically, the phrases that combine to make up a sentence. When a sentence is ungrammatical, we use a * to indicate its syntax is “off”. Syntax is not about meaning. (See Noam Chomsky’s famous example “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.”) Although we do use meaning ...
... Syntax deals with sentences—specifically, the phrases that combine to make up a sentence. When a sentence is ungrammatical, we use a * to indicate its syntax is “off”. Syntax is not about meaning. (See Noam Chomsky’s famous example “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.”) Although we do use meaning ...
Antisymmetry

In linguistics, antisymmetry is a theory of syntactic linearization presented in Richard Kayne's 1994 monograph The Antisymmetry of Syntax. The crux of this theory is that hierarchical structure in natural language maps universally onto a particular surface linearization, namely specifier-head-complement branching order. The theory derives a version of X-bar theory. Kayne hypothesizes that all phrases whose surface order is not specifier-head-complement have undergone movements that disrupt this underlying order. Subsequently, there have also been attempts at deriving specifier-complement-head as the basic word order.Antisymmetry as a principle of word order is reliant on assumptions that many theories of syntax dispute, e.g. constituency structure (as opposed to dependency structure), X-bar notions such as specifier and complement, and the existence of ordering altering mechanisms such as movement and/or copying.