Grammar Quiz Study Guide
... Commas – are used to separate words in a list, interchangeable adjectives, two independent clauses, and dates, cities, or names. Example: I need to get milk, eggs, and bread at the store. Example: Some of my family lives in Indianapolis, Indiana. Adverb – a word or phrase that modifies an adjective, ...
... Commas – are used to separate words in a list, interchangeable adjectives, two independent clauses, and dates, cities, or names. Example: I need to get milk, eggs, and bread at the store. Example: Some of my family lives in Indianapolis, Indiana. Adverb – a word or phrase that modifies an adjective, ...
CFG Phrases for English
... • The direct object argument to “book” isn’t appearing in the right place. It is in fact a long way from where it’s supposed to appear. • And note that it’s separated from its verb by 2 other verbs. • In Penn Treebank, these types of movement are annotated by have an empty Trace constituent appea ...
... • The direct object argument to “book” isn’t appearing in the right place. It is in fact a long way from where it’s supposed to appear. • And note that it’s separated from its verb by 2 other verbs. • In Penn Treebank, these types of movement are annotated by have an empty Trace constituent appea ...
Document
... (b) case of the pronoun in subject: nominative (cf. accusative of objects) (c) verb agreement (d) subject-auxiliary inversion 2.2 Traditional errors in defining the subject: related to their inappropriateness at language-particular level (a) subject is not alway the actor (b) subject is not alway th ...
... (b) case of the pronoun in subject: nominative (cf. accusative of objects) (c) verb agreement (d) subject-auxiliary inversion 2.2 Traditional errors in defining the subject: related to their inappropriateness at language-particular level (a) subject is not alway the actor (b) subject is not alway th ...
Phrase Toolbox - Dive-Into-Language-Arts
... An absolute phrase (also called a nominative absolute) is a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun, an “ing” or “ed” verb form, and any related modifiers. Absolute phrases modify the whole sentence rather than a particular part of it. They are always set off from the rest of the sentence wit ...
... An absolute phrase (also called a nominative absolute) is a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun, an “ing” or “ed” verb form, and any related modifiers. Absolute phrases modify the whole sentence rather than a particular part of it. They are always set off from the rest of the sentence wit ...
Lecture 01 - ELTE / SEAS
... The syntactic contexts (e.g. a clause which begins with a wh-phrase) which prevent movement are often called Islands ...
... The syntactic contexts (e.g. a clause which begins with a wh-phrase) which prevent movement are often called Islands ...
Lecture 5 X-bar Theory and the Structure of the Sentence
... of the appropriate type and the complement in each case is a YP (NP, VP, AP, PP). In English and Romanian, the head precedes its complements. However, this is not always the case: in Japanese and Miskito the head follows the complement. Here, we have to do with the head parameter, variable in diffe ...
... of the appropriate type and the complement in each case is a YP (NP, VP, AP, PP). In English and Romanian, the head precedes its complements. However, this is not always the case: in Japanese and Miskito the head follows the complement. Here, we have to do with the head parameter, variable in diffe ...
Intro to Linguistics Syntax 2: A more perfect Tree
... j. DP → D (NP) d. PP → P DP e. AP → (AdvP) (Deg) A f. AdvP → (Deg) Adv In fact, there are even Ds which have specifiers (“subjects” of their own): 12) a. John’s book d. *John’s the book b. The man from Australia’s coat e. *A student’s it c. The very hungry linguistic student’s book ...
... j. DP → D (NP) d. PP → P DP e. AP → (AdvP) (Deg) A f. AdvP → (Deg) Adv In fact, there are even Ds which have specifiers (“subjects” of their own): 12) a. John’s book d. *John’s the book b. The man from Australia’s coat e. *A student’s it c. The very hungry linguistic student’s book ...
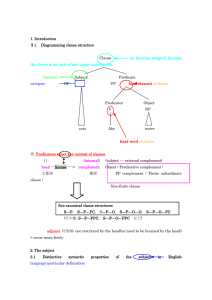
eng221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... choice of the complement is determined by properties of the head. On the other hand, object refers to a major constituent of a sentence or clause structure that is associated with the receiver and goal of an action. For example, in the expression: the boy kicked the ball, the ball is the object. Thu ...
... choice of the complement is determined by properties of the head. On the other hand, object refers to a major constituent of a sentence or clause structure that is associated with the receiver and goal of an action. For example, in the expression: the boy kicked the ball, the ball is the object. Thu ...
Ling 107 Syntax - The Study of Sentence Structure All human
... Head Complement Linguists commonly borrow terms from algebra to refer to the different parts of phrase structure: XP u ...
... Head Complement Linguists commonly borrow terms from algebra to refer to the different parts of phrase structure: XP u ...
Sign Language - Alumni Cse Ucsc
... in visual or spatial form. Independent of English Derived from French Sign Language ...
... in visual or spatial form. Independent of English Derived from French Sign Language ...
Instituto de Formación Docente Continua Lenguas Vivas Bariloche
... 1. Explain the difference between a phrase and a clause. Provide 3 examples of phrases and 3 of clauses (other than the ones that appear in the unit). First, a phrase is a sentence fragment that contains either a verb or a noun, but not both. Second, a clause is a segment fragment that contains both ...
... 1. Explain the difference between a phrase and a clause. Provide 3 examples of phrases and 3 of clauses (other than the ones that appear in the unit). First, a phrase is a sentence fragment that contains either a verb or a noun, but not both. Second, a clause is a segment fragment that contains both ...
LITERARY TERMS 1. onomatopoeia: The use of words whose
... 11. pun: a play on words (The coach keeps giving me the runaround when I ask him if I made the track team.) 12. idiom: when the phrase is not taken literally (We were just shooting the breeze – meaning not talking about anything important) 13. symbol: when something stands for something else. (The p ...
... 11. pun: a play on words (The coach keeps giving me the runaround when I ask him if I made the track team.) 12. idiom: when the phrase is not taken literally (We were just shooting the breeze – meaning not talking about anything important) 13. symbol: when something stands for something else. (The p ...
Document
... typically expresses location. It differs from ordinary locative adverbials in that it does not specify the circumstances of the action ‘placing’, ‘putting’, etc., but rather describes where the referent of the direct object ends up. ...
... typically expresses location. It differs from ordinary locative adverbials in that it does not specify the circumstances of the action ‘placing’, ‘putting’, etc., but rather describes where the referent of the direct object ends up. ...
Course 7: Syntax
... • One criticism of the phrase-based MT is that it does not model structural or syntactic aspects of the language. • Syntax based MT uses parse trees to capture linguistic differences such as word order and case marking. • Reordering for syntactic reasons – e.g., move German object to end of sentence ...
... • One criticism of the phrase-based MT is that it does not model structural or syntactic aspects of the language. • Syntax based MT uses parse trees to capture linguistic differences such as word order and case marking. • Reordering for syntactic reasons – e.g., move German object to end of sentence ...
Parallelism - St. Cloud State University
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
Similarities and Differences between Clauses and Nominals
... Because V2 moves the finite verb out of the clause (into the C°-position, to the left of the subject position), we have to look at sentences without V2 in order to be able to see which verb positions are possible in which languages. In English and French this is not difficult, as only main clause qu ...
... Because V2 moves the finite verb out of the clause (into the C°-position, to the left of the subject position), we have to look at sentences without V2 in order to be able to see which verb positions are possible in which languages. In English and French this is not difficult, as only main clause qu ...
Basic word/constituent order: Source: Source: Whaley, Comrie and
... For example, when we say ‘Bean, I don’t like’, we land up with an order of OSV in English, which of course is not the default order of the constituents in the language. So, it is very much clear that this order i.e. OSV is used for a very specific context and has to be explained by giving some extra ...
... For example, when we say ‘Bean, I don’t like’, we land up with an order of OSV in English, which of course is not the default order of the constituents in the language. So, it is very much clear that this order i.e. OSV is used for a very specific context and has to be explained by giving some extra ...
Ling 001: Syntax II
... moved from one position to another – How structures and meanings (including ambiguity) are mediated by syntax, particularly those “hidden” structures that we don’t see or hear but actually use – “John is easy to please” vs. “John is eager to please” – Some basic rules and two case studies of hidden ...
... moved from one position to another – How structures and meanings (including ambiguity) are mediated by syntax, particularly those “hidden” structures that we don’t see or hear but actually use – “John is easy to please” vs. “John is eager to please” – Some basic rules and two case studies of hidden ...
Seven basic sentence patterns
... SVO(主—动—宾) SV0O(主—动—宾-宾) SVOC(主—动—宾—补) SVA(主—动—状) SVOA(主—动—宾—状) ...
... SVO(主—动—宾) SV0O(主—动—宾-宾) SVOC(主—动—宾—补) SVA(主—动—状) SVOA(主—动—宾—状) ...
Grammar - Linguistic Society of America
... sentences that ask questions needing a yes or no answer, e.g. Can you hear me?, questions inviting some other kind of answer, e.g. What did you see?, sentences that express commands, e.g. Eat your potatoes!, and sentences that make assertions, e.g. Whales eat plankton. Word Order The syntactic princ ...
... sentences that ask questions needing a yes or no answer, e.g. Can you hear me?, questions inviting some other kind of answer, e.g. What did you see?, sentences that express commands, e.g. Eat your potatoes!, and sentences that make assertions, e.g. Whales eat plankton. Word Order The syntactic princ ...
SyntaxINTRO
... to the rules of classical languages Latin & Greek. Examples: 1. A sentence should never end in a preposition. When it doesn’t apply to English: This is the bank I invested my money in. 1. May I have a cookie? NOT Can I have a cookie? ...
... to the rules of classical languages Latin & Greek. Examples: 1. A sentence should never end in a preposition. When it doesn’t apply to English: This is the bank I invested my money in. 1. May I have a cookie? NOT Can I have a cookie? ...
Syntax
... Only constituents can be moved to another part of the sentence; only constituents can be substituted for in a sentence. ...
... Only constituents can be moved to another part of the sentence; only constituents can be substituted for in a sentence. ...
Antisymmetry

In linguistics, antisymmetry is a theory of syntactic linearization presented in Richard Kayne's 1994 monograph The Antisymmetry of Syntax. The crux of this theory is that hierarchical structure in natural language maps universally onto a particular surface linearization, namely specifier-head-complement branching order. The theory derives a version of X-bar theory. Kayne hypothesizes that all phrases whose surface order is not specifier-head-complement have undergone movements that disrupt this underlying order. Subsequently, there have also been attempts at deriving specifier-complement-head as the basic word order.Antisymmetry as a principle of word order is reliant on assumptions that many theories of syntax dispute, e.g. constituency structure (as opposed to dependency structure), X-bar notions such as specifier and complement, and the existence of ordering altering mechanisms such as movement and/or copying.