* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Declarative sentence
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sentence spacing wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive semantics wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Focus (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Musical syntax wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
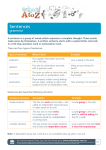
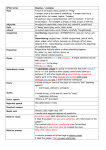
Declarative sentence • Basic statement that ends w/ a period Imperative sentence • Command (ends w/ period or exclamation point) Interrogatory sentence • Question Exclamatory sentence • Shows emphasis, excitement, etc. • Ends w/ an exclamation point Simple sentence • One subject and one verb only • Independent clause • May have phrases Compound sentence • More than 1 subject and/or more than 1 verb • Only independent clauses used • May have phrases Complex sentence • ONLY one independent clause (w/ one subject and one verb only) AND one or more dependent clauses • May have phrases Compound-Complex sentence • Independent clause has more than 1 subject and/or more than 1 verb AND there is at least 1 dependent clause • May have phrases Appositive phrase • Phrase that explains a noun, usually surrounded by commas • Ex: London, the English city on the Thames, offers many tourist attractions. Cumulative (Loose) Sentence • Starts with an independent clause and ends with a dependent clause Periodic Sentence • Starts with a dependent clause and ends with an independent clause Rhetorical question • creates active involvement with reader or audience by asking them to think Inversion • Verb comes before subject • Creates emphasis Polysyndeton • When a sentence uses several conjunctions (usually and) Asyndeton • When a sentence does not use any conjunctions Balanced/Parallel • 2 or more words or constructions must be in the same grammatical form (i.e., verbs, infinitives, participles, phrases, etc.) Anaphora • repetition of the same word or group of words at the beginnings of successive sentences • Ex: It is a luxury, it is a privilege, it is an indulgence Antithesis • Contrast of ideas, usually as parallel structure • Ex: Love is an ideal thing, marriage is a real thing. Chiasmus • The criss-cross or reversal of grammatical structures • “mirror image” • Ex: I am stuck on Band-Aid ‘cause Band- Aid’s stuck on me. Punctuation • Controls pace and flow of sentence • Any punctuation except periods or commas is unique and has a purpose (dashes, ellipses, parentheses, etc.) Purpose of Syntax/Structure #1 1. Build excitement or intensity Purpose of Syntax/Structure #2 2. Built to make a point of _____________ Purpose of Syntax/Structure #3 3. Explain a point of _____________ Purpose of Syntax/Structure #4 4. Pull the reader into the passage Purpose of Syntax/Structure #5 5. Add complexity Purpose of Syntax/Structure #6 6. Create rhythm Purpose of Syntax/Structure #7 7. Build an emotion