Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
Zn 8 p + 8 p + 30 p + 8 n 8 n 35 n 8 e
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
File - Norris Science
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
Chapter 3
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
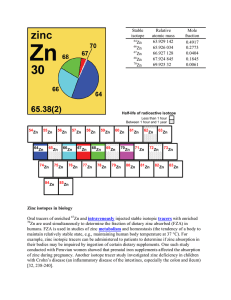
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
Lecture 2: Atoms - U of L Class Index
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
... Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
Unit 3 Note Outline
... History of the Atom Democritis - Ancient Greek Philosopher used the word Two discoveries led to the rebirth of the idea of the atom 1. Lavoisier 2. Proust (1799) This led to: ...
... History of the Atom Democritis - Ancient Greek Philosopher used the word Two discoveries led to the rebirth of the idea of the atom 1. Lavoisier 2. Proust (1799) This led to: ...
The Periodic Table
... Mass number is the count of nucleons in an isotope and atomic mass is the measure of the average mass of an atom including the relative abundance of its element’s isotopes. ...
... Mass number is the count of nucleons in an isotope and atomic mass is the measure of the average mass of an atom including the relative abundance of its element’s isotopes. ...
atomic number
... • Nuclear decay is a process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus changes into another more stable nucleus by emitting radiation. ...
... • Nuclear decay is a process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus changes into another more stable nucleus by emitting radiation. ...
04 Atoms_ molecules _ ions
... •Left three quarters of the chart •Lose electrons •Become positive ...
... •Left three quarters of the chart •Lose electrons •Become positive ...
Canyon High School Chemistry
... to its atomic number and atomic mass; 1e. Know the nucleus of the atom is smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass; 1f. Know transuranium elements are all synthesized in particle accelerators and know how to identify lanthanide, actinide and transactinide elements on the periodic table; 1 ...
... to its atomic number and atomic mass; 1e. Know the nucleus of the atom is smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass; 1f. Know transuranium elements are all synthesized in particle accelerators and know how to identify lanthanide, actinide and transactinide elements on the periodic table; 1 ...
Notes on Atomic Structure Structure of Atoms Atoms are composed
... Neutrons have No charge. They are Neutral. Electrons have a NEGATIVE (-) electrical charge. Element Key ...
... Neutrons have No charge. They are Neutral. Electrons have a NEGATIVE (-) electrical charge. Element Key ...
Keypoints of Basic Atomic Structure
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
ISOSTOPE NOTES - Mr. Collier`s 9th Grade Physical Science
... electrons • The number of neutrons can vary from one atom of an element to another. –These variations are called ISOTOPES. ...
... electrons • The number of neutrons can vary from one atom of an element to another. –These variations are called ISOTOPES. ...
Atom - Sites
... elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. ...
... elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. ...
Half-Life - Chemistry 1 at NSBHS
... pressure temperature concentration number of neutrons in nucleus ANS: D ...
... pressure temperature concentration number of neutrons in nucleus ANS: D ...
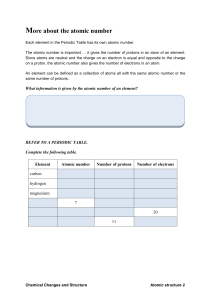
14 more about the atomic number
... More about the atomic number Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number ...
... More about the atomic number Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number ...
unit plan template
... PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist as stable or unstable isotopes. PS-2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic numbers. PS-2.4 Use the atomic number and the mass number to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and/ ...
... PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist as stable or unstable isotopes. PS-2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic numbers. PS-2.4 Use the atomic number and the mass number to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and/ ...
1. Of the three major categories of elements (metals, non
... protons in its nucleus). 17. What is an isotope? Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers (same number of protons but different number of neutrons). 18. Which element is in the same family as Carbon (C) and the same period as ...
... protons in its nucleus). 17. What is an isotope? Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers (same number of protons but different number of neutrons). 18. Which element is in the same family as Carbon (C) and the same period as ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
... number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
Unit 3 - Princeton High School
... Nuclear reactions can be induced when a nucleus is struck by a neutron or by another nucleus. Bombarding particles include the neutron whose symbol is __________ and alpha particles whose symbol is ___________. Charged particles can be accelerated to high speeds for bombardment in ______________ and ...
... Nuclear reactions can be induced when a nucleus is struck by a neutron or by another nucleus. Bombarding particles include the neutron whose symbol is __________ and alpha particles whose symbol is ___________. Charged particles can be accelerated to high speeds for bombardment in ______________ and ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.