Structure-Prop of Matter session
... Carbon-14 and Carbon-13 atoms’ are not as stable as carbon-12 and easily break down. If an isotope has too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons, it is unstable and will undergo radioactive decay. These radioactive isotopes become different elements in an effort to become more s ...
... Carbon-14 and Carbon-13 atoms’ are not as stable as carbon-12 and easily break down. If an isotope has too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons, it is unstable and will undergo radioactive decay. These radioactive isotopes become different elements in an effort to become more s ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
8.P.1.1 Warm-Up Questions for Website
... the mixture until the sand settles on the bottom. B.Pour the mixture through filter paper. C.Heat the mixture on a hot plate. D.Dissolve the salt by adding water to the mixture. ...
... the mixture until the sand settles on the bottom. B.Pour the mixture through filter paper. C.Heat the mixture on a hot plate. D.Dissolve the salt by adding water to the mixture. ...
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name:
... 16. What are the characteristics of each of the following reaction types? a) Synthesis b) Combustion c) Decomposition d) Double replacement e) Single replacement 17. Complete the word equation, write and balance the equation using symbols and indicate the type of the reaction on the left. a. Propane ...
... 16. What are the characteristics of each of the following reaction types? a) Synthesis b) Combustion c) Decomposition d) Double replacement e) Single replacement 17. Complete the word equation, write and balance the equation using symbols and indicate the type of the reaction on the left. a. Propane ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 3. An unknown sample is malleable and ductile. Where on the periodic table would the sample most likely be found? a. To the right of the zig-zag line. b. Bordering right on the zig-zag line. c. To the left of the zig-zag line. d. There are no elements that are both malleable and ductile found on the ...
... 3. An unknown sample is malleable and ductile. Where on the periodic table would the sample most likely be found? a. To the right of the zig-zag line. b. Bordering right on the zig-zag line. c. To the left of the zig-zag line. d. There are no elements that are both malleable and ductile found on the ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 1.How are elements named? 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elemen ...
... 1.How are elements named? 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elemen ...
Lecture
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
The Structure of the Atom
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...
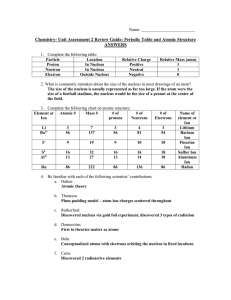
Unit 4 Test REVIEW
... 31. What is the mass number of an atom that has 20 protons, 22 neutrons and 20 electrons? 32. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning __________________. 33. In the synthesis of sulfur trifluoride, 33.0 g of sulfur combines with 24.0 g of fluorine. How many grams of sulfur trifluoride ...
... 31. What is the mass number of an atom that has 20 protons, 22 neutrons and 20 electrons? 32. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning __________________. 33. In the synthesis of sulfur trifluoride, 33.0 g of sulfur combines with 24.0 g of fluorine. How many grams of sulfur trifluoride ...
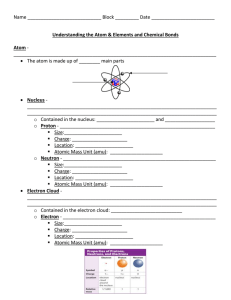
Understanding the Atom GN
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
Nuclear Physics Ch 30-31 Atom - word comes from the ancient
... is created when electrons jump down energy states - from high energy orbitals to low energy. Heisenberg and Schrodinger - particles can't be observed without altering their states. Wave properties - probability wave. ...
... is created when electrons jump down energy states - from high energy orbitals to low energy. Heisenberg and Schrodinger - particles can't be observed without altering their states. Wave properties - probability wave. ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means • 92 occur naturally on the Earth and in stars • Each is identified by a one- , two-, or three-letter abbreviation • Some elements known in ancient times like gold and mercury, have symbols that reflect th ...
... • A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means • 92 occur naturally on the Earth and in stars • Each is identified by a one- , two-, or three-letter abbreviation • Some elements known in ancient times like gold and mercury, have symbols that reflect th ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... Most of the mass of the atom and all of its positive charge is contained in a tiny core region called the nucleus The nucleus contains protons and neutrons (Chadwick, 1932) that have approximately the same mass The number of protons is the atomic number (Z) The total number of protons and ne ...
... Most of the mass of the atom and all of its positive charge is contained in a tiny core region called the nucleus The nucleus contains protons and neutrons (Chadwick, 1932) that have approximately the same mass The number of protons is the atomic number (Z) The total number of protons and ne ...
Neutron - Piscataway High School
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
Quiz review
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
(Questions 1-10) Write the letter of the answer that best complet
... How many oxygen atoms are there in Al2(SO4)3? A. 2 B. 3 C. 7 D. 12 E. 14 ...
... How many oxygen atoms are there in Al2(SO4)3? A. 2 B. 3 C. 7 D. 12 E. 14 ...
Chemistry Notes (pg. # 1)
... - Also, how did they determine that there is a ____________ and an electron “__________”? Evidence for the Negative Electron: ...
... - Also, how did they determine that there is a ____________ and an electron “__________”? Evidence for the Negative Electron: ...
Element Blocks Project
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
... AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS • The average atomic mass on the periodic table = the weighted ...
... AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS • The average atomic mass on the periodic table = the weighted ...
2.9 Use the helium-4 isotope to define atomic number and mass
... 2.24 Describe the changes in properties (from metals to nonmetals or from nonmetals to metals) as we move (a) down a periodic group and (b) across the periodic table from left to right. ...
... 2.24 Describe the changes in properties (from metals to nonmetals or from nonmetals to metals) as we move (a) down a periodic group and (b) across the periodic table from left to right. ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.